Appendix I to Subpart V of Part 85 - Recommended Test Procedures and Test Criteria and Recommended Durability Procedures To Demonstrate Compliance With Emission Critical Parameters
40:21.0.1.1.4.11.1.23.51 : Appendix I
Appendix I to Subpart V of Part 85 - Recommended Test Procedures
and Test Criteria and Recommended Durability Procedures To
Demonstrate Compliance With Emission Critical Parameters A.
Carburetor Vacuum Break (Choke Pull-Off)
1. Test Procedure and Criteria
a. Vacuum leakage: Apply 457 ±13 mm (18.0 ±0.5 inches) Hg.
vacuum to the vacuum unit to achieve full diaphragm displacement.
Seal vacuum source to unit. There shall be no visible loss of
diaphragm displacement or drop in vacuum gauge reading after a 15
second observation. Vacuum purge system and diaphragm displacement
adjusting screw holes should be temporarily sealed during this test
when applicable.
b. Diaphragm displacement: At stabilized temperature of −29 °C
and 121 °C (−20 °F and 250 °F) with 457 ±13 mm (18.0 ±0.5 inches)
Hg. vacuum applied to unit, the diaphragm displacement shall be
within ±1 mm (0.04 inches) of the nominal original equipment
displacement. The vacuum purge system must be open during this test
when applicable. Adjusting screws that limit displacement should be
temporarily removed and adjusting screw holes temporarily sealed
during this test.
c. Timed delay (when applicable): With 457 ±13 mm (18.0 ±0.5
inches) Hg. applied to the unit, the vacuum break diaphragm
displacement shall occur within ±20% of the original equipment time
over the specified range of displacement. The diaphragm
displacement shall be timed over the same distance for the original
equipment as the replacement part and shall not be less than 60% of
the total displacement range. The vacuum purge system must be open
and the adjusting screw holes should be temporarily sealed during
this test when applicable.
d. Modulated stem displacement (when applicable): With a force
sufficient to extend the modulated stem to its full displacement,
the displacement shall be within ±0.8 mm (±0.03 inches) of the
original equipment specification.
e. Modulated stem displacement force (when applicable): The
force required to start and finish the modulated stem displacement
shall be within ±35% of the original equipment specification for
forces up to 142 grams (5 ounces) and shall be within ±20% of the
original equipment specification for forces exceeding 142 grams (5
ounces).
2. Durability Procedures: After 250,000 full displacement
cycles (from atmospheric pressure to a minimum of 530mm (21 inches)
Hg. vacuum at a temperature of 79 °C (175 °F)) in air, the
following conditions shall be met:
a. Diaphragm displacement shall not degrade more than 10% from
the original test measurements of paragraph 1.b. above.
b. Timed delay shall not degrade more than 10% from the original
test measurement in paragraph 1.c. above.
c. Following these tests, the units must be free of visible
defects.
B. Carburetor Choke Thermostats
1. Test Procedures and Criteria
a. All chokes
i. Thermal deflection rate
When tested on a suitable fixture, the deflection rate shall be
within ±6% of the original equipment value. The initial temperature
and final temperature for purposes of this test may vary but shall
exhibit a test temperature range of at least 44 °C (80 °F).
Recommended test equipment, test procedures, and associated
calculations are outlined in ASTM B389 (latest revision) or
American National Standards Institute Z155-20.
ii. Mechanical torque rate
When tested on a suitable fixture, the torque rate shall be
within ±12% of the mean original equipment value. Recommended test
equipment, test procedures, and associated calculations are
outlined in ASTM B362 (latest revision) or American National
Standards Institute Z155-18 (latest revision).
iii. Index mark position
When stabilized for four hours at room temperature, the relative
position of the thermostatic coil outer tang or loop and the index
mark, when corrected to 24 °C (75 °F), shall be within ±5 angular
degrees of the mean original equipment positions.
b. Electrically-heated Chokes
i. Time to rotate coil tang
When tested on a suitable fixture, the time to rotate through a
prescribed angle at a prescribed temperature and prescribed
voltage, for the specfic choke device under test shall be within
±12 seconds or ±25% of the mean original equipment value whichever
is greater.
ii. Electrical circuit resistance
In an electrically-heated choke utilizing PTC type choke heater,
the circuit resistance shall be within ±1.5 ohms of the mean
original equipment value at 24 ±3 °C (75° ±5 °F) unenergized.
iii. Electrical switching temperature
In an electrically heated choke thermostat utilizing a
thermostatic disc switch in the electrical circuit, the temperature
to open the circuit shall be within ±5.5 °C (10 °F) and the
temperature to close the circuit shall be within ±11 °C (20 °F) of
the mean original equipment value. Circuit opening temperature
shall be measured on a decreasing temperature change, and the
circuit closing temperature shall be measured on an increasing
temperature change.
C. Carburetor Accelerator Pumps
1. Test Procedure and Criteria
a. Expose plunger or diaphragm assembly to temperatures of −30
°C (−20 °F) for 70 hours and at 70 °C (158 °F) for 24 hours, with a
commercial grade fuel or equivalent.
b. Within one hour after temperature exposure of 1.a. above,
each plunger or diaphragm assembly, when installed in an applicable
carburetor or test fixture, shall at room temperature deliver a
volume of test fluid (Stoddard solvent or equivalent) from a 10
stroke cycle,* within ±30% of the volume from a 10 stroke cycle of
an original equipment plunger or diaphragm assembly.
*10 stroke cycle: 10 strokes from closed throttle plate
position to wide open throttle plate position occurring within a
15-25 second time period.
2. Durability Procedure: After 250,000 operational
cycles, at approximately 30 cycles per minute at room temperature
in test fluid, the output of the plunger/diaphragm shall not drop
below 90% of the low limit as established in 1.b.
D. Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) Valve
1. Test Procedure and Criteria
a. Measure the flow of the PCV valve in standard cubic feet per
minute (SCFM) vs. pressure differential across the valve over a
range of operating pressures from 4-22 inches Hg., at standard
atmospheric conditions (21.1 °C (70 °F) at 755mm (29.92
inches).
b. A PCV valve shall flow within the vehicle manufacturer's
specifications or shall meet the following criteria: Whenever the
mean of the original equipment flow curve is below 1 SCFM, a
maximum deviation of the mean replacement PCV valve shall not
exceed ±0.1 SCFM. Whenever the mean original equipment curve is
equal to or greater than 1 SCFM, a maximum deviation of the mean of
the replacement PCV valve shall not exceed ±10%. The total flow
tolerance of the replacement valve shall not exceed the original
equipment variation from the mean, at any pressure
differential.
2. Durability Procedure: The flow of any specific PCV
valve must not deviate from the flow curve of the original
equipment PCV valve by more than the total original allowable
tolerance when each is similarly operated in the intended vehicle
application over the service interval stated by the certifier.
E. Breaker Points
1. Test Procedures and Criteria
a. Set up test system circuit and equipment per Figure 1 with an
OE breaker point assembly. Connect the primary to a 14 ±.5 V DC
regulated power supply.
b. Record dwell angle and open-circuit output voltage at 300 and
500 distributor rpm and at 500 rpm intervals up to the maximum
speed of the intended application.
c. Insert the replacement part in the test system and repeat the
observations per b above under identical test conditions.
d. The data observed with the replacement part in the system
must meet the following criteria:
(1) The dwell angle change: Not to exceed that of the original
equipment by more than ±2° at all measured rpm intervals.
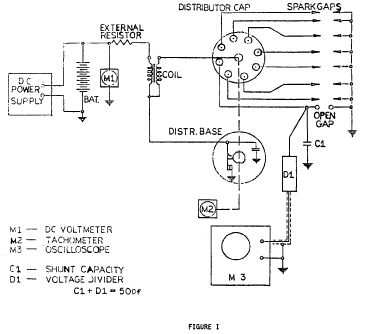
(2) The open circuit output voltage (M-3): Not less than 90% of
the OE breaker point assembly at any measured rpm.
e. Repeat step c above at −40 °C (−40 °F) and 100 °C (212
°F).
f. The breaker points shall operate without evidence of point
bounce at all test speeds and temperatures and shall operate easily
without binding when operated manually.
2. Durability Procedures
a. Set up a bench ignition system using an applicable
distributor or electro-mechanical equivalent.
b. Install the breaker point assembly under test in the
distributor, lubricate and adjust per applicable vehicle
manufacturer's specifications. Use applicable coil, primary
resistor, capacitor, cap and rotor.
c. Connect the primary of the test system with a power supply
regulated at 14 ±0.5 V DC for a 12V system.
d. The secondary portion of the test system is to be connected
to a 12 ±2KV spark gap.
e. An external heat source shall generate an ambient temperature
of 70° (158 °F) for the distributor.
f. Drive the distributor at 1750 ±50 rpm for 200 hours. After
each 50 hour interval, run the distributor for 5 minutes with one
open circuit spark gap instead of a 12KV gap.
g. The replacement breaker point assembly must have the
capability of performing throughout the duration of the test
without evidence of any failure resulting in loss of spark in the
12KV spark gap.
h. After the 200 hours repeat step 1.c. above. The open circuit
output voltage must be at least 90% of that measured in 1.c.
F. Capacitors/Condensers
1. Test Procedures and Criteria
a. The electrostatic capacitance of the replacement condenser
shall be within ±20% of the value of the original part at 20 ±3 °C
(68 ±5 °F). The capacitance is to be measured on a capacitance
bridge having an accuracy of ±1% at 1 KHz frequency.
b. Set up the test system in accordance with Figure 1. The
condenser series resistance shall be such that the output voltage
at 500 distributor rpm with the replacement condenser shall not be
less than 90% of the output voltage (M-3) with the original
equipment condenser.
c. The capacitor must be able to withstand a minimum test
voltage of 500V DC for a minimum of 0.1 seconds without
failure.
d. (1) Measure capacitance after 4 hours minimum soak at 70°
(158 °F).
(2) After one hour at room temperature, place capacitor at −18
°C (0 °F) for 4 hours minimum and measure capacitance.
(3) Place capacitor at room temperature for 4 hours minimum and
measure capacitance.
e. After thermal cycling, repeat 1.a. and b. The results must be
within ±10 percent of the intital measurements.
2. Durability Procedure
a. Set up a bench ignition system using an applicable
distributor or an electro-mechanical equivalent.
b. Install the capacitor under test in the distributor adjusted
to applicable vehicle manufacturer's specifications. Use applicable
coil, primary resistor, breaker points, cap and rotor.
c. Connect the primary of the test system with a power supply
regulated at 14 ±0.5V DC for 12V system.
d. The secondary portion of the test system is to be connected
to a 12 ±2KV spark gap.
e. An external heat source shall generate an ambient temperature
of 70 °C (158 °F) for the distributor.
f. Drive the distributor at 1750 ±50 rpm for 200 hours. After
each 50 hour interval, run the distributor for 5 minutes with one
open circuit spark gap instead of a 12KV gap.
g. The replacement part must have the capability of performing
throughout the duration of the test without evidence of any failure
resulting in loss of spark in the 12KV spark gap.
h. After the 200 hours, the condenser shall be within 10 percent
of the capacitance and voltage measured in 1.a. and b.
respectively.
G. Distributor Caps and/or Rotors
1. Test Procedures and Criteria
a. Set up test system in accordance with the circuit and
equipment per Figure 1 with OE distributor cap and/or rotor.
Connect the primary to a 14 ±.5V DC regulated power supply.
b. Record open circuit output voltage (M-3) at 300 and 500
distributor rpm and at intervals of 500 distributor rpm up to the
maximum speed of the intended application.
c. Insert the intended replacement part(s) in the system and
repeat step b. above under identical test conditions.
d. Subject the intended replacement part to the following
thermal sequence through five complete cycles:
1. 12 hours at −40 °C (−40 °F)
2. 2 hours at room temperature
3. 4 hours at 100 °C (212 °F)
4. 2 hours at room temperature.
e. Repeat step b. above with the replacement part(s).
f. The output voltages measured with the replacement part(s) in
the system must be at least 90% of the output voltage with the OE
cap and/or rotor.
2. Durability Procedures
a. Set up test system in accordance with circuit and equipment
per Figure 1.
b. Install the cap and/or rotor under test in distributor,
lubricate and adjust per applicable vehicle manufacturer's
specifications. Use equivalent coil, primary resistor, breaker
points and capacitor.
c. Connect the primary of the test system with a power supply
regulated at 14 ±0.5 V D.C.
1. In breaker point operated systems, connect secondary to a 12
KV±2 KV gap.
2. In electronic ignition systems, connect secondary to a gap
equivalent to at least 50% of peak open-circuit voltage.
d. An external heat source shall generate an ambient temperature
of 70° (158 °F) for the distributor.
e. Distributor shall be driven at 1750 ±50 rpm for 200 hours.
After each 50 hours interval, run the distributor for 5 minutes
with one open-circuit spark gap instead of a 12KV gap.
f. The replacement part(s) must have the capability of
performing throughout the duration of the test without evidence of
any failure resulting in loss of spark at the spark gap.
g. Repeat step 1.c. above. The open circuit output voltage must
be at least 90% of that measured in step 1.c.
h. The replacement cap and/or rotor must be free of any visual
cracks, arcing or melting.
H. Spark Plugs
1. Test Procedures and Criteria
a. Heat rating: When comparatively rated in the SAE 17.6 Spark
Plug Rating engine according to the SAE J549A Recommended Practice,
the comparative average rating of at least five (5) replacement
spark plugs shall be within 15 percent of the average IMEP of at
least five (5) OE spark plugs.
b. Gap spacing: The electrode spark gap shall be equivalent or
adjustable to the recommended gap for the original equipment spark
plug.
c. Gap location: The electrode gap position in the chamber shall
be the same as specified by the vehicle manufacturer.
d. Flashover: The spark plug terminal end, with the properly
fitted connecting boot, shall not flash-over at peak anticipated
voltage for the intended application when electrode gap is 15%
larger than vehicle manufacturer's gap specifications.
I. Inductive System Coils
1. Test Procedures and Criteria
a. Set up the circuit in accordance with Figure 1. Operate the
circuit by an applicable distributor or equivalent triggering
device and applicable primarly resistor with a 50 pf load at 14.0
±0.50 volts DC input as applicable and stabilized at an ambient
temperature of 20 °C ±3 °C (68 °F ±5 °F).
b. With the original equipment coil installed, record the
predominant minimum peak voltage and rise time at 300 and 500
distributor rpm, and at 500 rpm intervals up to the maximum
intended operating speed. The measurement is to be taken after 4
minutes operation at each speed.
c. Install the replacement coil to be tested and repeat step b.
above.
d. The replacement coil shall have an open-circuit output
voltage (M-3) at least 90% of the OE coil output voltage and a rise
time not to exceed 110% of original equipment coil at each
distributor test speed.
2. Durability Procedure
a. Install the replacement ignition coil in the ignition system
using the applicable rotor, cap, capacitor, breaker points, and
primary resistor.
b. Operate the circuit with a regulated power supply of 14.0 ±.5
volts DC connected to the primary at an ambient temperature of 70
°C (158 °F) at 1750 ±50 distributor rpm for a duration of 200
hours. After each 50 hour interval, run the distributor for 5
minutes with one open-circuit spark gap instead of a 12KV gap.
c. The ignition coil shall perform throughout the test without
any evidence of coil failure which would result in the loss of the
spark in the 12 KV spark gap.
d. Repeat Step 1.c. above. The open-circuit output voltage must
be at least 90% of that measured in 1.c.
J. Primary Resistors
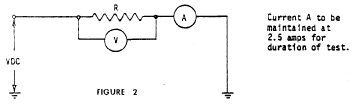
1. Test Procedures and Criteria.
a. Configure the circuit shown in Figure 2, using the original
equipment resistor.
b. At 20 ±3 °C (68 ±5 °F), apply voltage for 15 minutes;
maintain current at 2.5 amps. At conclusion of 15 minutes, read
voltage and current. Calculate resistance using the
relationship
R = E/I, where: R = Resistance in ohms, E = Voltage (V) in volts, I
= Current (A) in amps.
c. Replace OE test sample with part to be certified and repeat
step b. above.
d. Resistance of the part shall be within ±20% of original
equipment resistance.
2. Durability Procedure.
a. Using the circuit shown in Figure 1, apply current at 70 °C
(150 °F), for 200 hours.
b. After 200 hours retest as in step 1.c. above, and verify that
resistance is within ±20% of the value as measured in step 1.b.
above.
K. Distributors - Breaker Point
1. Test Procedures and Criteria.
a. Using an appropriate test installation, operate the
distributor through its intended speed range.
b. The advance mechanism shall function within the tolerance of
the vehicle manufacturer's original specification over the speed
range of the intended application as to vacuum and centrifugal
advance.
c. The advance mechanism shall repeatedly return to the zero
setting
±0.5 distributor degrees after advancing and retarding through the
operating range.
d. The distributor firing angle accuracy shall remain within the
originally specified tolerances throughout the speed range of the
intended application.
e. The distributor shall be capable of maintaining the dwell
angle of the original equipment specification with ±2 degrees
throughout the speed range of the intended application.
f. The distributor shall be capable of open-circuit output
voltage (M-3) equal to at leat 90 percent of the voltage produced
by the original equipment system over the speed range of the
intended application.
2. Durability Procedure.
a. At an ambient temperature of 70 °C (150 °F), operate the
distributor at 1750 ±50 rpm for 200 hours.
b. The distributor must meet the requirements of paragraph 1.b.
through f. after the 200 hours.
L. Reserved for Engine Valves M. Reserved for Camshafts N. Reserved
for Pistons O. Oxidizing Catalytic Converters
1. Test Procedures and Criteria.
(a) The fresh and aged conversion efficiencies of the
replacement oxidizing catalytic converter shall be equal to or
exceed those of the original equipment converter for CO and HC
emissions. The fresh and aged Light-off Time (LOT) of the
replacement converter shall be equal to or less than those of the
original equipment converter for CO and HC emissions. These
parameters shall be determined for both fresh and aged converters
under the same conditions using the following steady state feed gas
concentrations and conditions for LOT and Conversion Efficiency
respectively:
|
LOT |
Conversion efficiency |
| Exhaust mass flow
rate |
See note (2) |
See note (1). |
| Total
hydrocarbons |
See note (3) |
See note (3). |
| Carbon
monoxide |
1.0 to 2.5% |
1.0 to 2.5%. |
| Hydrogen |
0.33 × % CO maximum |
0.33 × % CO maximum. |
| Oxygen |
1.5 × % CO minimum |
1.5 × % CO minimum. |
| Converter inlet
gas temperature |
650 °F to 850 °F |
650 °F to 850 °F. |
Note 1:
Not less than peak air flow of the vehicle or engine
configuration being certified for. If more than one vehicle or
engine application is to be covered by a generic converter, the
greatest peak vehicle or engine air flow shall be used.
Note 2:
Between 0.10 and 0.40 times the value determined in Note 1.
Note 3:
500-2000 parts per million by volume minimum based on Methane
calibration. If a non-engine simulator gas source is used, a
mixture ratio of 10% propane to 90% propylene by volume will
constitute an acceptable synthetic for total exhaust
hydrocarbons.
(i) LOT tests shall be conducted by exposing the converter to a
step change in temperature, from ambient to that specified above:
650°-850 °F. Converter inlet and outlet exhaust emissions as
measured. Light-off Time is then determined by recording the time
required for the converter to reduce the outlet emissions (HC and
CO) to 50% of the inlet emissions, on a volumetric concentration
basis, measured from the step temperature change.
(ii) Conversion efficiency measurements shall be obtained by
passing stabilized-feed gas through the converter (at conditions
specified above) and making simultaneous measurements of inlet and
outlet emission volume concentrations. The conversion efficiency
for CO and HC is then calculated.
(iii) The particular conditions for which LOT and conversion
efficiency are measured (i.e., exhaust mass flow rate, total
hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, hydrogen, oxygen, and converter
inlet temperature) for the replacement converter and original
equipment converter tests must not vary from one another by more
than 10%.
(b) Fresh and aged catalytic converters may be obtained by
operating the converter on individual vehicle or engine application
for which it is intended on the Federal Test Procedure road
durability driving cycle. A fresh converter results when the
converter has operated between 2000 and 5000 miles or equivalent
hours. An aged converter results when the converter has been
operated for the warranted life of the original equipment
converter.
(c) Where one generic converter is intended to cover multiple
vehicle or engine configurations, converter aging may be obtained
per Paragraph (b) above, on a vehicle or engine which represents
the greatest peak air flow of the group of vehicle configurations
to be covered, and whose calibration and feed gas concentrations
are representative of the vehicle or engine configurations being
certified for.
2. Other Considerations.
(a) Replacement converter must fit within the width and length
space envelope of the original equipment converter. Converter
spacing from the underbody and for ground clearance must be the
same or greater than the original equipment converter
application.
(b) Pressure drop measured between inlet and outlet pipe
interconnecting points on the replacement converter shall be within
±25% of similar measurements for the original equipment converter
being replaced, when measured at each of three flow conditions 50
SCFM, 100 SCFM, and 150 SCFM with a suitable fluid medium such as
air. Maximum allowable exhaust gas leakage from the replacement
coverter shall be 0.4 cubic feet per minute measured at 4.0 pounds
per square inch differential. All measurements must be normalized
to equal density conditions.
(c) Converter skin temperature shall be measured during the
converter efficiency test. The skin temperature for the replacement
converter must equal or be less than that for the original
equipment converter.
P. Air Cleaner Filter Element
1. Test Procedures and Criteria.
(a) Using test equipment and procedures specified in SAE-J726c,
perform:
(i) Air Flow and Pressure Drop Test (2.3) at 200 SCFM, record
test conditions and pressure drop.
(ii) Efficiency Test (2.4) to measure full life efficiency at
200 SCFM to a total pressure drop of 9 inches of water, record test
conditions and test duration from first to last addition of
standard dust, weigh test element and absolute filter at end of
test using three randomly selected original equipment air filter
elements.
(b) Perform tests as in (a) above, under conditions controlled
to within ±10% of the corresponding original equipment test
conditions, for three randomly selected replacement air filter
elements.
(c) The replacement air filter element average recorded test
results. The pressure drop in (i) and absolute filter weight in
(ii) must be equal to or less than those average results for the
original equipment test results. The replacement air filter
averaged test results for element weight in (ii) must be equal to
or larger than averaged result for the original equipment averaged
test results.
2. Durability Procedure.
(a) After use in the intended vehicle or engine application for
the recommended service interval, the replacement element shall
evidence an increase in pressure drop (as measured in 1 (a)(i)
above) equal to or less than that of the original equipment air
filter element tested in the identical manner.
[45 FR 78464, Nov. 25, 1980, as amended at 54 FR 32593, Aug. 8,
1989]

