Title 40
SECTION 63.10009
63.10009 May I use emissions averaging to comply with this subpart
§ 63.10009 May I use emissions averaging to comply with this subpart?(a) General eligibility. (1) You may use emissions averaging as described in paragraph (a)(2) of this section as an alternative to meeting the requirements of § 63.9991 for filterable PM, SO2, HF, HCl, non-Hg HAP metals, or Hg on an EGU-specific basis if:
(i) You have more than one existing EGU in the same subcategory located at one or more contiguous properties, belonging to a single major industrial grouping, which are under common control of the same person (or persons under common control); and
(ii) You use CEMS (or sorbent trap monitoring systems for determining Hg emissions) or quarterly emissions testing for demonstrating compliance.
(2) You may demonstrate compliance by emissions averaging among the existing EGUs in the same subcategory, if your averaged Hg emissions for EGUs in the “unit designed for coal ≥8,300 Btu/lb” subcategory are equal to or less than 1.2 lb/TBtu or 1.3E-2 lb/GWh on a 30-boiler operating day basis or if your averaged emissions of individual, other pollutants from other subcategories of such EGUs are equal to or less than the applicable emissions limit in Table 2 to this subpart, according to the procedures in this section. Note that except for the alternate Hg emissions limit from EGUs in the “unit designed for coal ≥ 8,300 Btu/lb” subcategory, the averaging time for emissions averaging for pollutants is 30-group boiler operating days (rolling daily) using data from CEMS and sorbent trap monitoring (for Hg), or a combination of data from CEMS and emissions testing (for other pollutants). The averaging time for emissions averaging for the alternate Hg limit (equal to or less than 1.0 lb/TBtu or 1.1E-2 lb/GWh) from EGUs in the “unit designed for coal ≥ 8,300 Btu/lb” subcategory is 90-group boiler operating days (rolling daily) using data from CEMS, sorbent trap monitoring, or a combination of data from CEMS and sorbent trap monitoring. For the purposes of this paragraph, 30- (or 90-) group boiler operating days is defined as a period during which at least one unit in the emissions averaging group operates on each of the 30 or 90 days. You must calculate the weighted average emissions rate for the group in accordance with the procedures in this paragraph using the data from all units in the group including any that operate fewer than 30 (or 90) of the preceding 30- (or 90-) group boiler operating days.
(i) You may choose to have your EGU emissions averaging group meet either the heat input basis (MMBtu or TBtu, as appropriate for the pollutant) or gross output basis (MWh or GWh, as appropriate for the pollutant).
(ii) You may not mix bases within your EGU emissions averaging group.
(iii) You may use emissions averaging for affected units in different subcategories if the units vent to the atmosphere through a common stack (see paragraph (m) of this section).
(b) Equations. Use the following equations when performing calculations for your EGU emissions averaging group:
(1) Group eligibility equations.
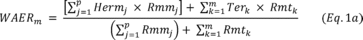 Where:
WAERm = Maximum Weighted Average Emission Rate in terms of lb/heat
input or lb/gross output, Hermi,j = hourly emission rate
(e.g., lb/MMBtu, lb/MWh) from CEMS or sorbent trap
monitoring as determined during the initial compliance
determination from EGU j, Rmmj = Maximum rated heat input, MMBtu/h,
or maximum rated gross output, MWh/h, for EGU j, p = number of EGUs
in emissions averaging group that rely on CEMS, Terk = Emissions
rate (lb/MMBTU or lb/MWh) as determined during the initial
compliance determination of EGU k, Rmtk = Maximum rated heat input,
MMBtu/h, or maximum rated gross output, MWh/h, for EGU k, and m =
number of EGUs in emissions averaging group that rely on emissions
testing.
Where:
WAERm = Maximum Weighted Average Emission Rate in terms of lb/heat
input or lb/gross output, Hermi,j = hourly emission rate
(e.g., lb/MMBtu, lb/MWh) from CEMS or sorbent trap
monitoring as determined during the initial compliance
determination from EGU j, Rmmj = Maximum rated heat input, MMBtu/h,
or maximum rated gross output, MWh/h, for EGU j, p = number of EGUs
in emissions averaging group that rely on CEMS, Terk = Emissions
rate (lb/MMBTU or lb/MWh) as determined during the initial
compliance determination of EGU k, Rmtk = Maximum rated heat input,
MMBtu/h, or maximum rated gross output, MWh/h, for EGU k, and m =
number of EGUs in emissions averaging group that rely on emissions
testing. 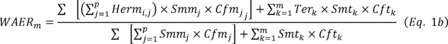 Where:
Where:
Variables with the similar names share the descriptions for Equation 1a of this section,
Smmj = maximum steam generation, lbsteam/h or lb/gross output, for EGU j, Cfmj = conversion factor, calculated from the most recent compliance test results, in terms units of heat output or gross output per pound of steam generated (MMBtu/lbsteam or MWh/lbsteam) from EGU j, Smtk = maximum steam generation, lbsteam/h or lb/gross output, for EGU k, and Cfmk = conversion factor, calculated from the most recent compliance test results, in terms units of heat output or gross output per pound of steam generated (MMBtu/lbsteam or MWh/lbsteam) from EGU k.(2) Weighted 30-boiler operating day rolling average emissions rate equations. Use Equation 2a or 2b of this section to calculate the 30 day rolling average emissions daily.
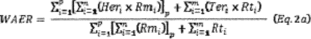 Where:
Heri = hourly emission rate (e.g., lb/MMBtu, lb/MWh) from
unit i's CEMS or sorbent trap monitoring system for the preceding
30-group boiler operating days, Rmi = hourly heat input or gross
output from unit i for the preceding 30-group boiler operating
days, p = number of EGUs in emissions averaging group that rely on
CEMS or sorbent trap monitoring, n = number of hours that hourly
rates are collected over 30-group boiler operating days, Teri =
Emissions rate from most recent emissions test of unit i in terms
of lb/heat input or lb/gross output, Rti = Total heat input or
gross output of unit i for the preceding 30-boiler operating days,
and m = number of EGUs in emissions averaging group that rely on
emissions testing.
Where:
Heri = hourly emission rate (e.g., lb/MMBtu, lb/MWh) from
unit i's CEMS or sorbent trap monitoring system for the preceding
30-group boiler operating days, Rmi = hourly heat input or gross
output from unit i for the preceding 30-group boiler operating
days, p = number of EGUs in emissions averaging group that rely on
CEMS or sorbent trap monitoring, n = number of hours that hourly
rates are collected over 30-group boiler operating days, Teri =
Emissions rate from most recent emissions test of unit i in terms
of lb/heat input or lb/gross output, Rti = Total heat input or
gross output of unit i for the preceding 30-boiler operating days,
and m = number of EGUs in emissions averaging group that rely on
emissions testing. 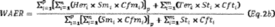 Where: variables
with similar names share the descriptions for Equation 2a of this
section, Smi = steam generation in units of pounds from unit i that
uses CEMS for the preceding 30-group boiler operating days, Cfmi =
conversion factor, calculated from the most recent compliance test
results, in units of heat input per pound of steam generated or
gross output per pound of steam generated, from unit i that uses
CEMS from the preceding 30 group boiler operating days, Sti = steam
generation in units of pounds from unit i that uses emissions
testing, and Cfti = conversion factor, calculated from the most
recent compliance test results, in units of heat input per pound of
steam generated or gross output per pound of steam generated, from
unit i that uses emissions testing.
Where: variables
with similar names share the descriptions for Equation 2a of this
section, Smi = steam generation in units of pounds from unit i that
uses CEMS for the preceding 30-group boiler operating days, Cfmi =
conversion factor, calculated from the most recent compliance test
results, in units of heat input per pound of steam generated or
gross output per pound of steam generated, from unit i that uses
CEMS from the preceding 30 group boiler operating days, Sti = steam
generation in units of pounds from unit i that uses emissions
testing, and Cfti = conversion factor, calculated from the most
recent compliance test results, in units of heat input per pound of
steam generated or gross output per pound of steam generated, from
unit i that uses emissions testing.
(3) Weighted 90-boiler operating day rolling average emissions rate equations for Hg emissions from EGUs in the “coal-fired unit not low rank virgin coal” subcategory. Use Equation 3a or 3b of this section to calculate the 90-day rolling average emissions daily.
 Where:
Heri = Hourly emission rate from unit i's Hg CEMS or Hg sorbent
trap monitoring system for the preceding 90-group boiler operating
days, Rmi = Hourly heat input or gross output from unit i for the
preceding 90-group boiler operating days, p = Number of EGUs in the
emissions averaging group, n = Number of hours that hourly rates
are collected over the 90-group boiler operating days.
Where:
Heri = Hourly emission rate from unit i's Hg CEMS or Hg sorbent
trap monitoring system for the preceding 90-group boiler operating
days, Rmi = Hourly heat input or gross output from unit i for the
preceding 90-group boiler operating days, p = Number of EGUs in the
emissions averaging group, n = Number of hours that hourly rates
are collected over the 90-group boiler operating days.  Where: Heri =
Hourly emission rate from unit i's Hg CEMS or Hg sorbent trap
monitoring system for the preceding 90-group boiler operating days,
Smi = Steam generation in units of pounds from unit i that uses Hg
CEMS or Hg sorbent trap monitoring for the preceding 90-group
boiler operating days, Cfmi = Conversion factor, calculated from
the most recent compliance test results, in units of heat input per
pound of steam generated or gross output per pound of steam
generated, from unit i that uses Hg CEMS or sorbent trap monitoring
from the preceding 90-group boiler operating days, p = Number of
EGUs in the emissions averaging group, n = Number of hours that
hourly rates are collected over the 90-group boiler operating days.
Where: Heri =
Hourly emission rate from unit i's Hg CEMS or Hg sorbent trap
monitoring system for the preceding 90-group boiler operating days,
Smi = Steam generation in units of pounds from unit i that uses Hg
CEMS or Hg sorbent trap monitoring for the preceding 90-group
boiler operating days, Cfmi = Conversion factor, calculated from
the most recent compliance test results, in units of heat input per
pound of steam generated or gross output per pound of steam
generated, from unit i that uses Hg CEMS or sorbent trap monitoring
from the preceding 90-group boiler operating days, p = Number of
EGUs in the emissions averaging group, n = Number of hours that
hourly rates are collected over the 90-group boiler operating days.
(c) Separate stack requirements. For a group of two or more existing EGUs in the same subcategory that each vent to a separate stack, you may average filterable PM, SO2, HF, HCl, non-Hg HAP metals, or Hg emissions to demonstrate compliance with the limits in Table 2 to this subpart if you satisfy the requirements in paragraphs (d) through (j) of this section.
(d) For each existing EGU in the averaging group:
(1) The emissions rate achieved during the initial performance test for the HAP being averaged must not exceed the emissions level that was being achieved 180 days after April 16, 2015, or the date on which emissions testing done to support your emissions averaging plan is complete (if the Administrator does not require submission and approval of your emissions averaging plan), or the date that you begin emissions averaging, whichever is earlier; or
(2) The control technology employed during the initial performance test must not be less than the design efficiency of the emissions control technology employed 180 days after April 16, 2015 or the date that you begin emissions averaging, whichever is earlier.
(e) The weighted-average emissions rate from the existing EGUs participating in the emissions averaging option must be in compliance with the limits in Table 2 to this subpart at all times following the date that you begin emissions averaging.
(f) Emissions averaging group eligibility demonstration. You must demonstrate the ability for the EGUs included in the emissions averaging group to demonstrate initial compliance according to paragraph (f)(1) or (2) of this section using the maximum rated heat input or gross output over a 30- (or 90-) boiler operating day period of each EGU and the results of the initial performance tests. For this demonstration and prior to preparing your emissions averaging plan, you must conduct required emissions monitoring for 30- (or 90-) days of boiler operation and any required manual performance testing to calculate maximum weighted average emissions rate in accordance with this section. If, before the start of your initial compliance demonstration, the Administrator becomes aware that you intend to use emissions averaging for that demonstration, or if your initial Notification of Compliance Status (NOCS) indicates that you intend to implement emissions averaging at a future date, the Administrator may require you to submit your proposed emissions averaging plan and supporting data for approval. If the Administrator requires approval of your plan, you may not begin using emissions averaging until the Administrator approves your plan.
(1) You must use Equation 1a in paragraph (b) of this section to demonstrate that the maximum weighted average emissions rates of filterable PM, HF, SO2, HCl, non-Hg HAP metals, or Hg emissions from the existing units participating in the emissions averaging option do not exceed the emissions limits in Table 2 to this subpart.
(2) If you are not capable of monitoring heat input or gross output, and the EGU generates steam for purposes other than generating electricity, you may use Equation 1b of paragraph (b) of this section as an alternative to using Equation 1a of paragraph (b) of this section to demonstrate that the maximum weighted average emissions rates of filterable PM, HF, SO2, HCl, non-Hg HAP metals, or Hg emissions from the existing units participating in the emissions averaging group do not exceed the emission limits in Table 2 to this subpart.
(g) You must determine the weighted average emissions rate in units of the applicable emissions limit on a 30 group boiler operating day rolling average basis (or, if applicable, on a 90 group boiler operating day rolling average basis for Hg) according to paragraphs (g)(1) and (2) of this section. The first averaging period ends on the 30th (or, if applicable, 90th for the alternate Hg emission limit) group boiler operating day after the date that you begin emissions averaging.
(1) You must use Equation 2a or 3a of paragraph (b) of this section to calculate the weighted average emissions rate using the actual heat input or gross output for each existing unit participating in the emissions averaging option.
(2) If you are not capable of monitoring heat input or gross output, you may use Equation 2b or 3b of paragraph (b) of this section as an alternative to using Equation 2a of paragraph (b) of this section to calculate the average weighted emission rate using the actual steam generation from the units participating in the emissions averaging option.
(h) CEMS (or sorbent trap monitoring) use. If an EGU in your emissions averaging group uses CEMS (or a sorbent trap monitor for Hg emissions) to demonstrate compliance, you must use those data to determine the 30 (or 90) group boiler operating day rolling average emissions rate.
(i) Emissions testing. If you use manual emissions testing to demonstrate compliance for one or more EGUs in your emissions averaging group, you must use the results from the most recent performance test to determine the 30 (or 90) day rolling average. You may use CEMS or sorbent trap data in combination with data from the most recent manual performance test in calculating the 30 (or 90) group boiler operating day rolling average emissions rate.
(j) Emissions averaging plan. You must develop an implementation plan for emissions averaging according to the following procedures and requirements in paragraphs (j)(1) and (2) of this section.
(1) You must include the information contained in paragraphs (j)(1)(i) through (v) of this section in your implementation plan for all the emissions units included in an emissions averaging:
(i) The identification of all existing EGUs in the emissions averaging group, including for each either the applicable HAP emission level or the control technology installed as of 180 days after February 16, 2015, or the date on which you complete the emissions measurements used to support your emissions averaging plan (if the Administrator does not require submission and approval of your emissions averaging plan), or the date that you begin emissions averaging, whichever is earlier; and the date on which you are requesting emissions averaging to commence;
(ii) The process weighting parameter (heat input, gross output, or steam generated) that will be monitored for each averaging group;
(iii) The specific control technology or pollution prevention measure to be used for each emission EGU in the averaging group and the date of its installation or application. If the pollution prevention measure reduces or eliminates emissions from multiple EGUs, you must identify each EGU;
(iv) The means of measurement (e.g., CEMS, sorbent trap monitoring, manual performance test) of filterable PM, SO2, HF, HCl, individual or total non-Hg HAP metals, or Hg emissions in accordance with the requirements in § 63.10007 and to be used in the emissions averaging calculations; and
(v) A demonstration that emissions averaging can produce compliance with each of the applicable emission limit(s) in accordance with paragraph (b)(1) of this section.
(2) If, as described in paragraph (f) of this section, the Administrator requests you to submit the averaging plan for review and approval, you must receive approval before initiating emissions averaging.
(i) The Administrator shall use following criteria in reviewing and approving or disapproving the plan:
(A) Whether the content of the plan includes all of the information specified in paragraph (j)(1) of this section; and
(B) Whether the plan presents information sufficient to determine that compliance will be achieved and maintained.
(ii) The Administrator shall not approve an emissions averaging implementation plan containing any of the following provisions:
(A) Any averaging between emissions of different pollutants or between units located at different facilities; or
(B) The inclusion of any emissions unit other than an existing unit in the same subcategory.
(k) Common stack requirements. For a group of two or more existing affected units, each of which vents through a single common stack, you may average emissions to demonstrate compliance with the limits in Table 2 to this subpart if you satisfy the requirements in paragraph (l) or (m) of this section.
(l) For a group of two or more existing units in the same subcategory and which vent through a common emissions control system to a common stack that does not receive emissions from units in other subcategories or categories, you may treat such averaging group as a single existing unit for purposes of this subpart and comply with the requirements of this subpart as if the group were a single unit.
(m) For all other groups of units subject to paragraph (k) of this section, you may elect to conduct manual performance tests according to procedures specified in § 63.10007 in the common stack. If emissions from affected units included in the emissions averaging and from other units not included in the emissions averaging (e.g., in a different subcategory) or other nonaffected units all vent to the common stack, you must shut down the units not included in the emissions averaging and the nonaffected units or vent their emissions to a different stack during the performance test. Alternatively, you may conduct a performance test of the combined emissions in the common stack with all units operating and show that the combined emissions meet the most stringent emissions limit. You may also use a CEMS or sorbent trap monitoring to apply this latter alternative to demonstrate that the combined emissions comply with the most stringent emissions limit on a continuous basis.
(n) Combination requirements. The common stack of a group of two or more existing EGUs in the same subcategory subject to paragraph (k) of this section may be treated as a single stack for purposes of paragraph (c) of this section and included in an emissions averaging group subject to paragraph (c) of this section.
[77 FR 9464, Feb. 16, 2012, as amended at 77 FR 23403, Apr. 19, 2012; 78 FR 24085, Apr. 24, 2013; 81 FR 20183, Apr. 6, 2016; 85 FR 55757, Sept. 9, 2020]