Title 40
SECTION 1066.635
1066.635 NMOG determination.
§ 1066.635 NMOG determination.For vehicles subject to an NMOG standard, determine NMOG as described in paragraph (a) of this section. Except as specified in the standard-setting part, you may alternatively calculate NMOG results based on measured NMHC emissions as described in paragraphs (c) through (f) of this section.
(a) Determine NMOG by independently measuring alcohols and carbonyls as described in 40 CFR 1065.805 and 1065.845. Use good engineering judgment to determine which alcohols and carbonyls you need to measure. This would typically require you to measure all alcohols and carbonyls that you expect to contribute 1% or more of total NMOG. Calculate the mass of NMOG in the exhaust, mNMOG, with the following equation, using density values specified in § 1066.1005(f):
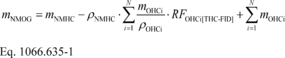 Where:
mNMHC = the mass of NMHC and all oxygenated hydrocarbon
(OHC) in the exhaust, as determined using Eq. 1066.605-2. Calculate
NMHC mass based on ρNMHC. rNMHC = the effective
C1-equivalent density of NMHC as specified in § 1066.1005(f).
mOHCi = the mass of oxygenated species i in the
exhaust calculated using Eq. 1066.605-2. rOCHi = the C1-equivalent
density of oxygenated species i. RFOHCi[THC-FID] =
the response factor of a THC-FID to oxygenated species i
relative to propane on a C1-equivalent basis as determined in 40
CFR 1065.845.
Where:
mNMHC = the mass of NMHC and all oxygenated hydrocarbon
(OHC) in the exhaust, as determined using Eq. 1066.605-2. Calculate
NMHC mass based on ρNMHC. rNMHC = the effective
C1-equivalent density of NMHC as specified in § 1066.1005(f).
mOHCi = the mass of oxygenated species i in the
exhaust calculated using Eq. 1066.605-2. rOCHi = the C1-equivalent
density of oxygenated species i. RFOHCi[THC-FID] =
the response factor of a THC-FID to oxygenated species i
relative to propane on a C1-equivalent basis as determined in 40
CFR 1065.845.
(b) The following example shows how to determine NMOG as described in paragraph (a) of this section for (OHC) compounds including ethanol (C2H5OH), methanol (CH3OH), acetaldehyde (C2H4O), and formaldehyde (CH2O) as C1-equivalent concentrations:
mNMHC = 0.0125 g mCH3OH = 0.0002 g mC2H5OH = 0.0009 g mCH2O = 0.0001 g mC2H4O = 0.00005 g RFCH3OH[THC-FID] = 0.63 RFC2H5OH[THC-FID] = 0.75 RFCH2O[THC-FID] = 0.00 RFC2H4O[THC-FID] = 0.50 rNMHC-liq = 576.816 g/m 3 rCH3OH = 1332.02 g/m 3 rC2H5OH = 957.559 g/m 3 rCH2O = 1248.21 g/m 3 rC2H4O = 915.658 g/m 3
(c) For gasoline containing less than 25% ethanol by volume, you may calculate NMOG from measured NMHC emissions as follows:
(1) For hot-start and hot-running test cycles or intervals other than the FTP, you may determine NMOG based on the NMHC emission rate using the following equation:
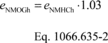 Where:
eNMOGh = mass emission rate of NMOG from the hot-running
test cycle. eNMHCh = mass emission rate of NMHC from the
hot-running test cycle, calculated using rNMHC-liq. Example:
eNMHCh = 0.025 g/mi eNMOGh = 0.025 · 1.03 = 0.026
g/mi
Where:
eNMOGh = mass emission rate of NMOG from the hot-running
test cycle. eNMHCh = mass emission rate of NMHC from the
hot-running test cycle, calculated using rNMHC-liq. Example:
eNMHCh = 0.025 g/mi eNMOGh = 0.025 · 1.03 = 0.026
g/mi
(2) You may determine weighted composite NMOG for FTP testing based on the weighted composite NMHC emission rate and the volume percent of ethanol in the fuel using the following equation:
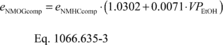 Where:
eNMOGcomp = weighted FTP composite mass emission rate of
NMOG. eNMHCcomp = weighted FTP composite mass emission rate
of NMHC, calculated using rNMHC-liq. VPEtOH = volume
percentage of ethanol in the test fuel. Use good engineering
judgment to determine this value either as specified in 40 CFR
1065.710 or based on blending volumes, taking into account any
denaturant. Example: eNMHCcomp = 0.025 g/mi VPEtOH =
10.1% eNMOGcomp = 0.025 · (1.0302 + 0.0071 · 10.1) = 0.0275
g/mi
Where:
eNMOGcomp = weighted FTP composite mass emission rate of
NMOG. eNMHCcomp = weighted FTP composite mass emission rate
of NMHC, calculated using rNMHC-liq. VPEtOH = volume
percentage of ethanol in the test fuel. Use good engineering
judgment to determine this value either as specified in 40 CFR
1065.710 or based on blending volumes, taking into account any
denaturant. Example: eNMHCcomp = 0.025 g/mi VPEtOH =
10.1% eNMOGcomp = 0.025 · (1.0302 + 0.0071 · 10.1) = 0.0275
g/mi
(3) You may determine NMOG for the transient portion of the FTP cold-start test for use in fuel economy and CREE calculations based on the NMHC emission rate for the test interval and the volume percent of ethanol in the fuel using the following equation:
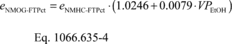 Where:
eNMOG-FTPct = mass emission rate of NMOG from the transient
portion of the FTP cold-start test (generally known as bag 1).
eNMHC-FTPct = mass emission rate of NMHC from the transient
portion of the FTP cold-start test (bag 1), calculated using
rNMHC-liq. Example: eNMHC-FTPct = 0.052 g/mi VPEtOH =
10.1% eNMOG-FTPct = 0.052 · (1.0246 + 0.0079 · 10.1) =
0.0574 g/mi
Where:
eNMOG-FTPct = mass emission rate of NMOG from the transient
portion of the FTP cold-start test (generally known as bag 1).
eNMHC-FTPct = mass emission rate of NMHC from the transient
portion of the FTP cold-start test (bag 1), calculated using
rNMHC-liq. Example: eNMHC-FTPct = 0.052 g/mi VPEtOH =
10.1% eNMOG-FTPct = 0.052 · (1.0246 + 0.0079 · 10.1) =
0.0574 g/mi
(4) You may determine NMOG for the stabilized portion of the FTP test for either the cold-start test or the hot-start test (bag 2 or bag 4) for use in fuel economy and CREE calculations based on the corresponding NMHC emission rate and the volume percent of ethanol in the fuel using the following equation:
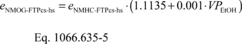 Where:
eNMOG-FTPcs-hs = mass emission rate of NMOG from the
stabilized portion of the FTP test (bag 2 or bag 4).
eNMHC-FTPcs-hs = mass emission rate of NMHC from the
stabilized portion of the FTP test (bag 2 or bag 4), calculated
using rNMHC-liq.
Where:
eNMOG-FTPcs-hs = mass emission rate of NMOG from the
stabilized portion of the FTP test (bag 2 or bag 4).
eNMHC-FTPcs-hs = mass emission rate of NMHC from the
stabilized portion of the FTP test (bag 2 or bag 4), calculated
using rNMHC-liq.
(5) You may determine NMOG for the transient portion of the FTP hot-start test for use in fuel economy and CREE calculations based on the NMHC emission rate for the test interval and the volume percent of ethanol in the fuel using the following equation:
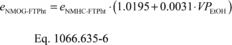 Where:
eNMOG-FTPht = mass emission rate of NMOG from the transient
portion of the FTP hot-start test (bag 3). eNMHC-FTPht =
mass emission rate of NMHC from the transient portion of the FTP
hot-start test (bag 3), calculated using rNMHC-liq.
Where:
eNMOG-FTPht = mass emission rate of NMOG from the transient
portion of the FTP hot-start test (bag 3). eNMHC-FTPht =
mass emission rate of NMHC from the transient portion of the FTP
hot-start test (bag 3), calculated using rNMHC-liq.
(6) For PHEVs, you may determine NMOG based on testing over one full UDDS using Eq. 1066.635-3.
(d) You may take the following alternative steps when determining fuel economy and CREE under 40 CFR part 600 for testing with ethanol-gasoline blends that have up to 25% ethanol by volume:
(1) Calculate NMOG by test interval using Eq. 1066.635-3 for individual bag measurements from the FTP.
(2) For HEVs, calculate NMOG for two-bag FTPs using Eq. 1066.635-3 as described in 40 CFR 600.114.
(e) We consider NMOG values for diesel-fueled vehicles, CNG-fueled vehicles, LNG-fueled vehicles, and LPG-fueled vehicles to be equivalent to NMHC emission values for all test cycles.
(f) For all fuels not covered by paragraphs (c) and (e) of this section, manufacturers may propose a methodology to calculate NMOG results from measured NMHC emissions. We will approve adjustments based on comparative testing that demonstrates how to properly represent NMOG based on measured NMHC emissions.
[79 FR 23823, Apr. 28, 2014, as amended at 80 FR 9122, Feb. 19, 2015; 81 FR 74212, Oct. 25, 2016]