Title 40
SECTION 1066.610
1066.610 Dilution air background correction.
§ 1066.610 Dilution air background correction.(a) Correct the emissions in a gaseous sample for background using the following equation:
 Where:
x[emission]dexh = measured emission concentration in dilute
exhaust (after dry-to-wet correction, if applicable).
x[emission]bkgnd = measured emission concentration in the
dilution air (after dry-to-wet correction, if applicable).
DF = dilution factor, as determined in paragraph (b) of this
section.
Where:
x[emission]dexh = measured emission concentration in dilute
exhaust (after dry-to-wet correction, if applicable).
x[emission]bkgnd = measured emission concentration in the
dilution air (after dry-to-wet correction, if applicable).
DF = dilution factor, as determined in paragraph (b) of this
section. 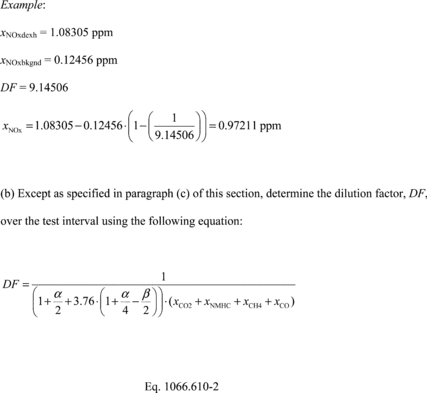 Where: xCO2 = amount of CO2 measured in the sample over the
test interval. xNMHC = amount of C1-equivalent NMHC measured
in the sample over the test interval. xCH4 = amount of CH4
measured in the sample over the test interval. xCO = amount
of CO measured in the sample over the test interval. a = atomic
hydrogen-to-carbon ratio of the test fuel. You may measure a or use
default values from Table 1 of 40 CFR 1065.655. b = atomic
oxygen-to-carbon ratio of the test fuel. You may measure b or use
default values from Table 1 of 40 CFR 1065.655.
Where: xCO2 = amount of CO2 measured in the sample over the
test interval. xNMHC = amount of C1-equivalent NMHC measured
in the sample over the test interval. xCH4 = amount of CH4
measured in the sample over the test interval. xCO = amount
of CO measured in the sample over the test interval. a = atomic
hydrogen-to-carbon ratio of the test fuel. You may measure a or use
default values from Table 1 of 40 CFR 1065.655. b = atomic
oxygen-to-carbon ratio of the test fuel. You may measure b or use
default values from Table 1 of 40 CFR 1065.655. 
(c) Determine the dilution factor, DF, over the test interval for partial-flow dilution sample systems using the following equation:
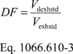 Where:
Where:
Vdexhstd = total dilute exhaust volume sampled over the test interval, corrected to standard reference conditions.
Vexhstd = total exhaust volume sampled from the vehicle, corrected to standard reference conditions.

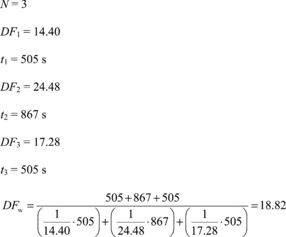
(d) Determine the time-weighted dilution factor, DFw, over the duty cycle using the following equation:
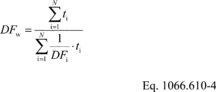 Where:
N = number of test intervals. i = test interval
number t = duration of the test interval. DF =
dilution factor over the test interval. Example:
Where:
N = number of test intervals. i = test interval
number t = duration of the test interval. DF =
dilution factor over the test interval. Example: