Title 40
PART 80 APPENDIX
| Phosphorus, milligrams per liter | Equivalent, grams per gallon | Sample size, milliliter |
|---|---|---|
| 2.5 to 40 | 0.01 to 0.15 | 1.00 |
| 1.3 to 20 | 0.005 to 0.075 | 2.00 |
| 0.9 to 13 | 0.0037 to 0.05 | 3.00 |
| 1 or less | 0.0038 or less | 10.00 |
8.1 Transfer 2 ±0.2 g of zinc oxide into a conical pile in a clean, dry, unetched ignition dish.
Note 9:In order to obtain satisfactory accuracy with the small amounts of phosphorus involved, it is necessary to take extensive precautions in handling. The usual precautions of cleanliness, careful manipulation, and avoidance of contamination should be scrupulously observed; also, all glassware should be cleaned before use, with cleaning acid or by some procedure that does not involve use of commercial detergents. These compounds often contain alkali phosphates which are strongly adsorbed by glass surfaces and are not removed by ordinary rinsing. It is desirable to segregate a special stock of glassware for use only in the determination of phosphorus.
8.2 Make a deep depression in the center of the zinc oxide pile with a stirring rod.
8.3 Pipet the gasoline sample (Note 10) (see 7.2 for suggested sample volume) into the depression in the zinc oxide. Record the temperature of the fuel if the phosphorus content is required at 60 °F (15.6 °C) and make correction as directed in 9.2.
Note 10:For the 10-ml sample use multiple additions and a syringe. Hold the tip of the needle at approximately 2/3 of the depth of the zinc oxide layer and slowly deliver 2 ml of the sample: fast sample delivery may give low results. Give sufficient time for the gasoline to be absorbed by the zinc oxide. Follow step 8.6. Cool the dish to room temperature. Repeat steps 8.3 and 8.6 until all the sample has been burned. Safety - cool the ignition dish before adding the additional aliquots of gasoline to avoid a flash fire.
8.4 Cover the sample with a small amount of fresh zinc oxide from reagent bottle (use the tip of a small spatula to deliver approximately 0.2 g). Tap the sides of the ignition dish to pack the zinc oxide.
8.5 Prepare the blank, using the same amount of zinc oxide in an ignition dish.
8.6 Ignite the gasoline, using the flame from a bunsen burner. Allow the gasoline to burn to extinction (Note 10).
8.7 Place the ignition dishes containing the sample and blank in a hot muffle furnace set at a temperature of 1150 to 1300 °F (621 to 704 °C) for 10 min. Remove and cool the ignition dishes. When cool gently tap the sides of the dish to loosen the zinc oxide. Again place the dishes in the muffle furnace for 5 min. Remove and cool the ignition dishes to room temperature. The above treatment is usually sufficient to burn the carbon. If the carbon is not completely burned off place the dish into the oven for further 5-min. periods.
Note 11:Step 8.7 may also be accomplished by heating the ignition dish with a Meker burner gradually increasing the intensity of heat until the carbon from the sides of the dish has been burned, then cool to room temperature.
8.8 Pipet 25 ml of H2 SO4 (1 + 10) to each ignition dish. While pipeting, carefully wash all traces of zinc oxide from the sides of the ignition dish.
8.9 Cover the ignition dish with a borosilicate watch glass and warm the ignition dish on a hot plate until the zinc oxide is completely dissolved.
8.10 Transfer the solution through filter paper to a 100-ml volumetric flask. Rinse the watch glass and the dish several times with distilled water (do not exceed 25 ml) and transfer the washings through the filter paper to the volumetric flask.
8.11 Prepare the molybdate-hydrazine solution.
8.12 Add 50 ml of the molybdate-hydrazine solution by pipet to each 100-ml volumetric flask. Mix immediately by swirling.
8.13 Dilute to 100 ml with water and mix well. Remove stoppers from flasks after mixing.
8.14 Place the 100-ml flasks in the constant-temperature bath for 25 min. so that the contents of the flasks are below the liquid level of the bath. The temperature of the bath should be 180 to 190 °F (82.2 to 87.8 °C) (Note 1).
8.15 Transfer the 100-ml flasks to the cooling bath and cool the contents rapidly to room temperature (Note 6).
8.16 Allow the samples to stand at room temperature before measuring the absorbance.
Note 12:The color developed is stable for at least 4 h.
8.17 Set the spectrophotometer to the wavelength of maximum absorbance as determined in 6.9. Adjust the spectrophotometer to zero absorbance, using distilled water in both cells.
8.18 Measure the absorbance of the samples at the wavelength of maximum absorbance with distilled water in the reference cell.
8.19 Subtract the absorbance of the blank from the absorbance of each sample (Note 7).
8.20 Determine the micrograms of phosphorous in the sample, using the calibration curve from 6.12 and the corrected absorbance.
9. Calculations.9.1 Calculate the milligrams of phosphorus per litre of sample as follows:
P, mg/litre = P/V where: P = micrograms of phosphorus read from calibration curve, and V = millilitres of gasoline sample. To convert to grams of phosphorus per U.S. gallon of sample, multiply mg P/litre by 0.0038.9.2 If the gasoline sample was taken at a temperature other than 60 °F (15.6 °C) make the following temperature correction:
mg P/litre at 15.6 °C = [mg P/litre at t] [1 + 0.001 (t−15.6)] where: t = observed temperature of the gasoline, °C.9.3 Concentrations below 2.5 mg/litre or 0.01 g/gal should be reported to the nearest 0.01 mg/litre or 0.0001 g/U.S. gal.
9.3.1 For higher concentrations, report results to the nearest 1 mg P/litre or 0.005 g P/U.S. gal.
10. Precision.10.1 The following criteria should be used for judging the acceptability of results (95 percent confidence):
10.2 Repeatability - Duplicate results by the same operator should be considered suspect if they differ by more than the following amounts:
| g P/U.S. gal (mg·P/litre) | Repeatability |
|---|---|
| 0.0008 to 0.005 (0.2 to 1.3) | 0.0002 g P/U.S. gal (0.05 mg P/litre). |
| 0.005 to 0.15 (1.3 to 40) | 7% of the mean. |
10.3 Reproducibility - The results submitted by each of two laboratories should not be considered suspect unless they differ by more than the following amounts:
| g P/U.S. gal (mg·P/litre) | Reproducibility |
|---|---|
| 0.0008 to 0.005 (0.2 to 1.3) | 0.0005 g P/U.S. gal (0.13 mg P/litre). |
| 0.005 to 0.15 (1.3 to 40) | 13% of the mean. |
Appendix B to Part 80 - Test Methods for Lead in Gasoline
40:19.0.1.1.1.17.93.1.2 : Appendix B
Appendix B to Part 80 - Test Methods for Lead in Gasoline Link to an amendment published at 85 FR 78467, Dec. 4, 2020. Method 1 - Standard Method Test for Lead in Gasoline by Atomic Absorption Spectrometry 1. Scope.1.1. This method covers the determination of the total lead content of gasoline. The procedure's calibration range is 0.010 to 0.10 gram of lead/U.S. gal. Samples above this level should be diluted to fall within this range or a higher level calibration standard curve must be prepared. The higher level curve must be shown to be linear and measurement of lead at these levels must be shown to be accurate by the analysis of control samples at a higher level of alkyl lead content. The method compensates for variations in gasoline composition and is independent of lead alkyl type.
2. Summary of method.2.1 The gasoline sample is diluted with methyl isobutyl ketone and the alkyl lead compounds are stabilized by reaction with iodine and a quarternary ammonium salt. The lead content of the sample is determined by atomic absorption flame spectrometry at 2833 A, using standards prepared from reagent grade lead chloride. By the use of this treatment, all alkyl lead compounds give identical response.
3. Apparatus.3.1 Atomic Absorption Spectometer, capable of scale expansion and nebulizer adjustment, and equipped with a slot burner and premix chamber for use with an air-acetylene flame.
3.2 Volumetric Flasks, 50-ml, 100-ml, 250-ml, and one litre sizes.
3.3 Pipets, 2-ml, 5-ml, 10-ml, 20-ml, and 50-ml sizes.
3.4 Micropipet, 100-µl, Eppendorf type or equivalent.
4. Reagents.4.1 Purity of Reagents - Reagent grade chemicals shall be used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Committee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society, where such specifications are available. Other grades may be used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of sufficiently high purity to permit its use without lessening the accuracy of the determination.
4.2 Purity of Water - Unless otherwise indicated, references to water shall be understood to mean distilled water or water of equal purity.
4.3 Aliquat 336 (tricapryl methyl ammonium chloride).
4.4 Aliquat 336/MIBK Solution (10 percent v/v) - Dissolve and dilute 100 ml (88.0 g) of Aliquat 336 with MIBK to one liter.
4.5 Aliquat 336/MIBK Solution (1 percent v/v) - Dissolve and dilute 10 ml (8.8 g) of Aliquat 336 with MIBK to one liter.
4.6 Iodine Solution - Dissolve and dilute 3.0 g iodine crystals with Toluene to 100 ml.
4.7 Lead Chloride.
4.8 Lead-Sterile Gasoline - Gasoline containing less than 0.005 g Pb/gal.
4.9 Lead, Standard Solution (5.0 g Pb/gal) - Dissolve 0.4433 g of lead chloride (PbCl2) previously dried at 105 °C for 3 h in about 200 ml of 10 percent Aliquat 336/MIBK solution in a 250-ml volumetric flask. Dilute to the mark with the 10 percent Aliquat solution, mix, and store in a brown bottle having a polyethylene-lined cap. This solution contains 1,321 µg Pb/ml, which is equivalent to 5.0 g Pb/gal.
4.10 Lead, Standard Solution (1.0 g Pb/gal) - By means of a pipet, accurately transfer 50.0 ml of the 5.0 g Pb/gal solution to a 250-ml volumetric flask, dilute to volume with 1 percent Aliquat/MIBK solution. Store in a brown bottle having a polyethylene-lined cap.
4.11 Lead, Standard Solutions (0.02, 0.05, and 0.10 g Pb/gal) - Transfer accurately by means of pipets 2.0, 5.0, and 10.0 ml of the 1.0-g Pb/gal solution to 100-ml volumetric flasks; add 5.0 ml of 1 percent Aliquat 336 solution to each flask; dilute to the mark with MIBK. Mix well and store in bottles having polyethylene-lined caps.
4.12 Methyl Isobutyl Ketone (MIBK). (4-methyl-2-pentanone).
5. Calibration.5.1 Preparation of Working Standards - Prepare three working standards and a blank using the 0.02, 0.05, and 0.10-g Pb/gal standard lead solutions described in 4.11.
5.1.1 To each of four 50-ml volumetric flasks containing 30 ml of MIBK, add 5.0 ml of low lead standard solution and 5.0 ml of lead-free gasoline. In the case of the blank, add only 5.0 ml of lead-free gasoline.
5.1.2 Add immediately 0.1 ml of iodine/toluene solution by means of the 100-µl Eppendorf pipet. Mix well. 1
1 EPA practice will be to mix well by shaking vigorously for approximately one minute.
5.1.3 Add 5 ml of 1 percent Aliquat 336 solution and mix.
5.1.4 Dilute to volume with MIBK and mix well.
5.2 Preparation of Instrument - Optimize the atomic absorption equipment for lead at 2833 A. Using the reagent blank, adjust the gas mixture and the sample aspiration rate to obtain an oxidizing flame.
5.2.1 Aspirate the 0.1-g Pb/gal working standard and adjust the burner position to give maximum response. Some instruments require the use of scale expansion to produce a reading of 0.150 to 0.170 for this standard.
5.2.2 Aspirate the reagent blank to zero the instrument and check the absorbances of the three working standards for linearity.
6. Procedure.6.1 To a 50 ml volumetric flask containing 30 ml MIBK, add 5.0 ml of gasoline sample and mix. 2
2 The gasoline should be allowed to come to room temperature (25 °C).
6.1.1 Add 0.10 ml (100 µl) of iodine/toluene solution and allow the mixture to react about 1 minute. 3
3 See footnote 1 of section 5.1.2.
6.1.2 Add 5.0 ml of 1 percent Aliquot 336/MIBK solution and mix.
6.1.3 Dilute to volume with MIBK and mix.
6.2 Aspirate the samples and working standards and record the absorbance values with frequent checks of the zero.
6.3 Any sample resulting in a peak greater than 0.05 g Pb/gal will be run in duplicate. Samples registering greater than 0.10 g Pb/gal should be diluted with iso-octane or unleaded fuel to fall within the calibration range or a higher level calibration standard curve must be prepared. The higher level curve must be shown to be linear and measurement of lead at these levels must be shown to be accurate by the analysis of control samples at a higher level of alkyl lead content.
7. Calculations.7.1 Plot the absorbance values versus concentration represented by the working standards and read the concentrations of the samples from the graph.
8. Precision.8.1 The following criteria should be used for judging the acceptability of results (95 percent confidence):
8.1.1 Repeatability - Duplicate results by the same operator should be considered suspect if they differ by more than 0.005 g/gal.
8.1.2 Reproductibility - The results submitted by each of two laboratories should not be considered suspect unless the two results differ by more than 0.01 g/gal.
Method 2 - Automated Method Test for Lead in Gasoline by Atomic Absorption Spectrometry 1. Scope and application.1.1 This method covers the determination of the total lead content of gasoline. The procedure's calibration range is 0.010 to 0.10 gram of lead/U.S. gal. Samples above this level should be diluted to fall within this range or a higher level calibration standard curve must be prepared. The higher level curve must be shown to be linear and measurement of lead at these levels must be shown to be accurate by the analysis of control samples at a higher level of alkyl lead content. The method compensates for variations in gasoline composition and is independent of lead alkyl type.
1.2 This method may be used as an alternative to the Standard Method set forth above.
1.3 Where trade names or specific products are noted in the method, equivalent apparatus and chemical reagents may be used. Mention of trade names or specific products is for the assistance of the user and does not constitute endorsement by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
2. Summary of method.2.1 The gasoline sample is diluted with methly isobutyl ketone (MIBK) and the alkyl lead compounds are stabilized by reacting with iodine and a quarternary ammonium salt. An automated system is used to perform the diluting and the chemical reactions and feed the products to the atomic absorption spectrometer with an air-acetylene flame.
2.2 The dilution of the gasoline with MIBK compensates for severe non-atomic absorption, scatter from unburned carbon containing species and matrix effects caused in part by the burning characteristics of gasoline.
2.3 The in-situ reaction of alkyl lead in gasoline with iodine eliminates the problem of variations in response due to different alkyl types by leveling the response of all alkyl lead compounds.
2.4 The addition of the quarternary ammonium salt improves response and increases the stability of the alkyl iodide complex.
3. Sample handling and preservation.3.1 Samples should be collected and stored in containers which will protect them from changes in the lead content of the gasoline such as from loss of volatile fractions of the gasoline by evaporation or leaching of the lead into the container or cap.
3.2 If samples have been refrigerated they should be brought to room temperature prior to analysis.
4. Apparatus.4.1 AutoAnalyzer system consisting of:
4.1.1 Sampler 20/hr cam, 30/hr cam.
4.1.2 Proportioning pump.
4.1.3 Lead in gas manifold.
4.1.4 Disposable test tubes.
4.1.5 Two 2-liter and one 0.5 liter Erlenmeyer solvent displacement flasks. Alternatively, high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) or syringe pumps may be used.
4.2 Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) Detector System consisting of:
4.2.1 Atomic absorption spectrometer.
4.2.2 10″ strip chart recorder.
4.2.3 Lead hollow cathode lamp or electrodeless discharge lamp (EDL).
5. Reagents.5.1 Aliquat 336/MIBK solution (10% v/v): Dissolve and dilute 100 ml (88.0 g) of Aliquat 336 (Aldrich Chemical Co., Milwaukee, Wisconsin) with MIBK (Burdick & Jackson Lab., Inc., Muskegon, Michigan) to one liter.
5.2 Aliquat 336/iso-octane solution (1% v/v): Dissolve and dilute 10 ml (8.8 g) of Alquat 336 (reagent 5.1) with iso-octane to one liter.
5.3 Iodine solution (3% w/v): Dissolve and dilute 3.0 g iodine crystals (American Chemical Society) with toluene (Burdick & Jackson Lab., Inc., Muskegon, Michigan) to 100 ml.
5.4 Iodine working solution (0.24% w/v): Dilute 8 ml of reagent 5.3 to 100 ml with toluene.
5.5 Methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK) (4-methlyl-2-pentanone).
5.6 Certified unleaded gasoline (Phillips Chemical Co., Borger, Texas) or iso-octane (Burdick & Jackson Lab, Inc., Muskegon, Michigan).
6. Calibration standards.6.1 Stock 5.0 g Pb/gal Standard:
Dissolve 0.4433 gram of lead chloride (PbCl2) previously dried at 105 °C for 3 hours in 200 ml of 10% v/v Aliquat 336/MIBK solution (reagent 5.1) in a 250 ml volumetric flask. Dilute to volume with reagent 5.1 and store in an amber bottle.
6.2 Intermediate 1.0 g Pb/gal Standard:
Pipet 50 ml of the 5.0 g Pb/gal standard into a 250 ml volumetric flask and dilute to volume with a 1% v/v Aliquat 336/iso-octane solution (reagent 5.2). Store in an amber bottle.
6.3 Working 0.02, 0.05, 0.10 g Pb/gal Standards:
Pipet 2.0, 5.0, and 10.0 ml of the 1.0 g Pb/gal solution to 100 ml volumetric flasks. Add 5 ml of a 1% Aliquat 336/iso-octane solution to each flask. Dilute to volume with iso-octane. These solutions contain 0.02, 0.05, and 0.10 g Pb/gal in a 0.05% Aliquat 336/iso-octane solution.
7. AAS Instrumental conditions.7.1 Lead hollow cathode lamp.
7.2 Wavelength: 283.3 nm.
7.3 Slit: 4 (0.7mm).
7.4 Range: UV.
7.5 Fuel: Acetylene (approx. 20 ml/min at 8 psi).
7.6 Oxidant: Air (approx. 65 ml/min at 31 psi).
7.7 Nebulizer: 5.2 ml/min.
7.8 Chart speed: 10 in/hr.
8. Procedures.8.1 AAS start-up.
8.1.1 Assure that instrumental conditions have been optimized and aligned according to Section 7 and the instrument has had substantial time for warm-up.
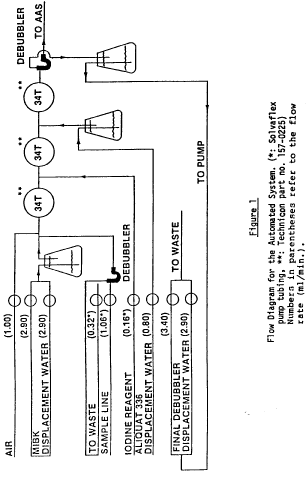
8.2 Auto Analyzer start-up [see figure 1].
8.2.1 Check all pump tubing and replace as necessary. Iodine tubing should be changed daily. All pump tubing should be replaced after one week of use. Place the platen on the pump.
8.2.2 Withdraw any water from the sample wash cup and fill with certified unleaded gasoline (reagent 5.6).
8.2.3 Fill the 2-liter MIBK dilution displacement Erlenmeyer flask (reagent 5.5) and the 0.5 liter Aliquat 336/MIBK 1% v/v (reagent 5.2) displacement flask and place the rubber stopper glass tubing assemblies in their respective flasks.
8.2.4 Fill a 2-liter Erlenmeyer flask with distilled water. The water will be used to displace the solvents. Therefore, place the appropriate lines in this flask. This procedure is not relevant if syringe pumps are used.
8.2.5 Fill the final debubbler reverse displacement 2-liter Erlenmeyer flask with distilled water and place the rubber stopper glass tubing assembly in the flask.
8.2.6 Place the appropriate lines for the iodine reagent (reagent 5.4) and the wash solution (reagent 5.6) in their respective bottles.
8.2.7 Start the pump and connect the aspiration line from the manifold to the AAS.
8.2.8 Some initial checks to assure that the reagents are being added are:
a. A good uniform bubble pattern.
b. Yellow color evident due to iodine in the system.
c. No surging in any tubing.
8.3 Calibration.
8.3.1 Turn the chart drive on and obtain a steady baseline.
8.3.2 Load standards and samples into sample tray.
8.3.3 Start the sampler and run the standards (Note: first check the sample probe positioning with an empty test tube).
8.3.4 Check the linearity of calibration standards response and slope by running a least squares fit. Check these results against previously obtained results. They should agree within 10%.
8.3.5 If the above is in control then start the sample analysis.
8.4 Sample Analysis.
8.4.1 To minimize gasoline vapor in the laboratory, load the sample tray about 5-10 test tubes ahead of the sampler.
8.4.2 Record the sample number on the strip chart corresponding to the appropriate peak.
8.4.3 Every ten samples run the high calibration standard and a previously analyzed sample (duplicate). Also let the sampler skip to check the baseline.
8.4.4 After an acceptable peak (within the calibration range) is obtained, pour the excess sample from the test tube into the waste gasoline can.
8.4.5 Any sample resulting in a peak greater than 0.05 g Pb/gal will be run in duplicate. Samples registering greater than 0.10 g Pb/gal should be diluted with iso-octane or unleaded fuel to fall within the calibration range or a higher level calibration standard curve must be prepared. The higher level curve must be shown to be linear and measurement of lead at these levels must be shown to be accurate by the analysis of control samples at a higher level of alkyl lead content.
8.5 Shut Down.
8.5.1 Replace the solvent displacement flask with flasks filled with distilled water. Also place all other lines in a beaker of distilled water. Rinse the system with distilled water for 15 minutes.
8.5.2 Withdraw the gasoline from the wash cup and fill with water.
8.5.3 Dispose of all solvent waste in waste glass bottles.
8.5.4 Turn the AAS off after extinguishing the flame. Also turn the recorder and pump off. Remove the platen and release the pump tubing.
8.5.5 Shut the acetylene off at the tank and bleed the line.
9. Quality control.9.1 Precision.
9.1.1 All duplicate results should be considered suspect if they differ by more than 0.005 g Pb/gal.
9.2 Accuracy.
9.2.1 All quality control standard checks should agree within 10% of the nominal value of the standard.
9.2.2 All spikes should agree within 10% of the known addition.
10. Past quality control data.10.1 Precision.
10.1.1 Duplicate analysis for 156 samples in a single laboratory has resulted in an average difference of 0.00011 g Pb/gal with a standard deviation of 0.0023.
10.1.2 Replicate analysis in a single laboratory (greater than 5 determinations) of samples at concentrations of 0.010, 0.048, and 0.085 g Pb/gal resulted in relative standard deviations of 4.2%, 3.5%, and 3.3% respectively.
10.2 Accuracy.
10.2.1 The analysis of National Bureau of Standards (NBS) lead in reference fuel of known concentrations in a single laboratory has resulted in found values deviating from the true value for 11 determinations of 0.0322 g Pb/gal by an average of 0.56% with a standard deviation of 6.8%, for 15 determinations of 0.0519 g Pb/gal by an average of −1.1% with a standard deviation of 5.8%, and for 7 determinations of 0.0725 g Pb/gal by an average of 3.5% with a standard deviation of 4.8%.
10.2.2 Twenty-three analyses of blind reference samples in a single laboratory (U.S. EPA, RTP, N.C.) have resulted in found values differing from the true value by an average of −0.0009 g Pb/gal with a standard deviation of 0.004.
10.2.3 In a single laboratory, the average percent recovery of 108 spikes made to samples was 101% with a standard deviation of 5.6%.
 Method 3
- Test for Lead in Gasoline by X-Ray Spectrometry 1. Scope and
application.
Method 3
- Test for Lead in Gasoline by X-Ray Spectrometry 1. Scope and
application.
1.1 This method covers the determination of the total lead content of gasoline. The procedure's calibration range is 0.010 to 5.0 grams of lead/U.S. gallon. Samples above this level should be diluted to fall within the range of 0.05 to 5.0 grams of lead/U.S. gallon. The method compensates for variations in gasoline composition and is independent of lead alkyl type.
1.2 This method may be used as an alternative to Method 1 - Standard Method Test for Lead in Gasoline by Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, or to Method 2 - Automated Method Test for Lead in Gasoline by Atomic Absorption Spectrometry.
1.3 Where trade names or specific products are noted in the method, equivalent apparatus and chemical reagents may be used. Mention of trade names or specific products is for the assistance of the user and does not constitute endorsement by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
2. Summary of method.2.1 A portion of the gasoline sample is placed in an appropriate holder and loaded into an X-ray spectrometer. The ratio of the net X-ray intensity of the lead L alpha radiation to the net intensity of the incoherently scattered tungsten L alpha radiation is measured. The lead content is determined by reference to a linear calibration equation which relates the lead content to the measured ratio.
2.2 The incoherently scattered tungsten radiation is used to compensate for variations in gasoline samples.
3. Sample handling and preservation.3.1 Samples should be collected and stored in containers which will protect them from changes in the lead content of the gasoline, such as loss of volatile fractions of the gasoline by evaporation or leaching of the lead into the container or cap.
3.2 If samples have been refrigerated they should be brought to room temperature prior to analysis.
3.3 Gasoline is extremely flammable and should be handled cautiously and with adequate ventilation. The vapors are harmful if inhaled and prolonged breathing of vapors should be avoided. Skin contact should be minimized. See precautionary statements in Annex Al.3.
4. Apparatus.4.1 X-ray Spectrometer, capable of exciting and measuring the fluorescence lines mentioned in 2.1 and of being operated under the following instrumental conditions or others giving equivalent results: a tungsten target tube operated at 50 kV, a lithium fluoride analyzing crystal, an air or helium optical path and a proportional or scintillation detector.
4.2 Some manufacturers of X-ray Spectrometer units no longer allow use of air as the beam path medium because the X-ray beam produces ozone, which may degrade seals and electronics. In addition, use of the equipment with liquid gasoline in close proximity to the hot X-ray tube could pose flammability problems with any machine in case of a rupture of the sample container. Therefore, use of the helium alternative is recommended.
5. Reagents.5.1 Isooctane. Isooctane is flammable and the vapors may be harmful. See precautions in Annex Al.1.
5.2 Lead standard solution, in isooctane, toluene or a mixture of these two solvents, containing approximately 5 gm Pb/U.S. gallon may be prepared from a lead-in-oil concentrate such as those prepared by Conostan (Conoco, Inc., Ponca City, Oklahoma). Isooctane and toluene are flammable and the vapors may be harmful. See precautionary statements in Annex Al.1 and Al.2.
6. Calibration.6.1 Make exact dilutions with isooctane of the lead standard solution to give solutions with concentrations of 0.01, 0.05, 0.10, 0.50, 1.0, 3.0 and 5.0 g Pb/U.S. gallon. If a more limited range is desired as required for linearity, such range shall be covered by at least five standard solutions approximately equally spaced and this range shall not be exceeded by any of the samples. Place each of the standard solutions in a sample cell using techniques consistent with good operating practice for the spectrometer employed. Insert the sample in the spectrometer and allow the spectrometer atmosphere to reach equilibrium (if appropriate). Measure the intensity of the lead L alpha peak at 1.175 angstroms, the Compton scatter peak of the tungsten L alpha line at 1.500 angstroms and the background at 1.211 angstroms. Each measured intensity should exceed 200,000 counts or the time of measurement should be at least 30 seconds. The relative standard deviation of each measurement, based on counting statistics, should be one percent or less. The Compton scatter peak given above is for 90° instrument geometry and should be changed for other geometries. The Compton scatter peak (in angstroms) is found at the wavelength of the tungsten L alpha line plus 0.024 (1-cos phi), where phi is the angle between the incident radiation and the take-off collimator.
6.2 For Each of the standards, as well as for an isooctane blank, determine the net lead intensity by subtracting the corrected background from the gross intensity. Determine the corrected background by multiplying the intensity of the background at 1.211 angstroms by the following ratio obtained on an isooctane blank:
6.3 Determine the corrected lead intensity ratio, which is the net lead intensity corrected for matrix effects by division by the net incoherently scattered tungsten radiation. The net scattered intensity is calculated by subtracting the background intensity at 1.211 angstroms from the gross intensity of the incoherently scattered tungsten L alpha peak. The equation for the corrected lead intensity ratio follows:
6.4 Obtain a linear calibration curve by performing a least squares fit of the corrected lead intensity ratios to the standard concentrations.
7. Procedure.7.1 Prepare a calibration curve as described in 6. Since the scattered tungsten radiation serves as an internal standard, the calibration curve should serve for at least several days. Each day the suitability of the calibration curve should be checked by analyzing several National Bureau of Standards (NBS) lead-in-reference-fuel standards or other suitable standards.
7.2 Determine the corrected lead intensity ratio for a sample in the same manner as was done for the standards. The samples should be brought to room temperature before analysis.
7.3 Determine the lead concentration of the sample from the calibration curve. If the sample concentration is greater than 5.0 g Pb/U.S. gallon or the range calibrated for in 6.1, the sample should be diluted so that the result is within the calibration span of the instrument.
7.4 Quality control standards, such as NBS standard reference materials, should be analyzed at least once every testing session.
7.5 For each group of ten samples, a spiked sample should be prepared by adding a known amount of lead to a sample. This known addition should be at least 0.05 g Pb/U.S. gallon, at least 50% of the measured lead content of the unspiked sample, and not more than 200% of the measured lead content of the unspiked sample (unless the minimum addition of 0.05 g Pb/U.S. gallon exceeds 200%). Both the spiked and unspiked samples should be analyzed.
8. Quality control.8.1 The difference between duplicates should not exceed 0.005 g Pb/U.S. gallon or a relative difference of 6%.
8.2 All quality control standard check samples should agree within 10% of the nominal value of the standard.
8.3 All spiked samples should have a percent recovery of 100% ±10%. The percent recovery, P, is calculated as follows:
P = 100 × (A − B) / K where A = the analytical result from the spiked sample, B = the analytical result from the unspiked sample, and K = the known addition.8.4 The difference between independent analyses of the same sample in different laboratories should not exceed 0.01 g Pb/U.S. gallon or a relative difference of 12%.
9. Past quality control data.9.1 Duplicate analysis for 26 samples in the range of 0.01 to 0.10 g Pb/U.S. gallon resulted in an average relative difference of 5.2% with a standard deviation of 5.4%. Duplicate analysis of 14 samples in the range 0.1 to 0.5 g Pb/U.S. gallon resulted in an average relative difference of 2.3% with a standard deviation of 2.0. Duplicate analysis of 47 samples in the range of 0.5 to 5 g Pb/U.S. gallon resulted in an average relative difference of 2.1% with a standard deviation of 1.8%.
9.2 The average percent recovery for 23 spikes made to samples in the 0.0 to 0.1 g Pb/U.S. gallon range was 103% with a standard deviation of 3.2%. For 42 spikes made to samples in the 0.1 to 5.0 g Pb/U.S. gallon range, the average percent recovery was 102% with a standard deviation of 4.2%.
9.3 The analysis of National Bureau of Standards lead-in-reference-fuel standards of known concentrations in a single laboratory has resulted in found values deviating from the true value for 14 determinations of 0.0490 g Pb/U.S. gallon by an average of 2.8% with a standard deviation of 6.4%, for 11 determinations of 0.065 g Pb/U.S. gallon by an average of 4.4% with a standard deviation of 2.9%, and for 15 determinations of 1.994 g Pb/U.S. gallon by an average of 0.3% with a standard deviation of 1.3%.
9.4 Eighteen analyses of reference samples (U.S. EPA, Research Triangle Park, NC) have resulted in found values differing from the true value by an average of 0.0004 g Pb/U.S. gallon with a standard deviation of 0.004 g Pb/U.S. gallon.
Annex A1. Precautionary Statements A1.1 Isooctane Danger - Extremely flammable. Vapors harmful if inhaled. Vapor may cause flash fire. Keep away from heat, sparks, and open flame. Vapors are heavier than air and may gather in low places, resulting in explosion hazard. Keep container closed. Use adequate ventilation. Avoid buildup of vapors. Avoid prolonged breathing of vapor or spray mist. Avoid prolonged or repeated skin contact. A1.2 Toluene Warning - Flammable. Vapor harmful. Keep away from heat, sparks, and open flame. Keep container closed. Use with adequate ventilation. Avoid breathing of vapor or spray mist. Avoid prolonged or repeated contact with skin. A1.3 Gasoline Danger - Extremely flammable. Vapors harmful if inhaled. Vapor may cause flash fire. Keep away from heat, sparks, and open flame. Vapors are heavier than air and may gather in low places, resulting in explosion hazard. Keep container closed. Use adequate ventilation. Avoid buildup of vapors. Avoid prolonged breathing of vapor or spray mist. Avoid prolonged or repeated skin contact. [39 FR 24891, July 8, 1974; 39 FR 25653, July 12, 1974; 39 FR 26287, July 18, 1974, as amended at 47 FR 765, Jan. 7, 1982; 52 FR 259, Jan. 5, 1987; 56 FR 13768, Apr. 4, 1991]