Title 40
PART 75 APPENDIX D
| Test number:____ Test completion date 1:__________ Test completion time 1:______ |
| Reinstallation date 2 (for testing under 2.1.5.1 only):__________ Reinstallation time 2:______ |
| Unit or pipe ID: Component/System ID: |
| Flowmeter serial number: Upper range value: |
| Units of measure for flowmeter and reference flow readings: |
| Measurement level (percent of URV) | Run No. | Time of run (HHMM) | Candidate flowmeter reading | Reference flow reading | Percent accuracy (percent of URV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (Minimum) level | 1 | ||||
| __ percent 3 of URV | 2 | ||||
| 3 | |||||
| Average | |||||
| Mid-level | 1 | ||||
| __ percent 3 of URV | 2 | ||||
| 3 | |||||
| Average | |||||
| High (Maximum) level | 1 | ||||
| __ percent 3 of URV | 2 | ||||
| 3 | |||||
| Average |
1 Report the date, hour, and minute that all test runs were completed.
2 For laboratory tests not performed inline, report the date and hour that the fuel flowmeter was reinstalled following the test.
3 It is required to test at least at three different levels: (1) normal full unit operating load, (2) normal minimum unit operating load, and (3) a load point approximately equally spaced between the full and minimum unit operating loads.
(a) Test the accuracy of each fuel flowmeter prior to use under this part and at least once every four fuel flowmeter QA operating quarters, as defined in § 72.2 of this chapter, thereafter. Notwithstanding these requirements, no more than 20 successive calendar quarters shall elapse after the quarter in which a fuel flowmeter was last tested for accuracy without a subsequent flowmeter accuracy test having been conducted. Test the flowmeter accuracy more frequently if required by manufacturer specifications.
(b) Except for orifice-, nozzle-, and venturi-type flowmeters, perform the required flowmeter accuracy testing using the procedures in either section 2.1.5.1 or section 2.1.5.2 of this appendix. Each fuel flowmeter must meet the accuracy specification in section 2.1.5 of this appendix.
(c) For orifice-, nozzle-, and venturi-type flowmeters, either perform the required flowmeter accuracy testing using the procedures in section 2.1.5.2 of this appendix or perform a transmitter accuracy test for the initial certification and once every four fuel flowmeter QA operating quarters thereafter. Perform a primary element visual inspection for the initial certification and once every 12 calendar quarters thereafter, according to the procedures in sections 2.1.6.1 through 2.1.6.4 of this appendix for periodic quality assurance.
(d) Notwithstanding the requirements of this section, if the procedures of section 2.1.7 (fuel flow-to-load test) of this appendix are performed during each fuel flowmeter QA operating quarter, subsequent to a required flowmeter accuracy test or (if applicable) transmitter accuracy test and primary element inspection, those procedures may be used to meet the requirement for periodic quality assurance testing for a period of up to 20 calendar quarters from the previous accuracy test or (if applicable) transmitter accuracy test and primary element inspection.
(e) When accuracy testing of the orifice, nozzle, or venturi meter is performed according to section 2.1.5.2 of this appendix, record the information displayed in Table D-1 in this section. At a minimum, record the overall accuracy results for the fuel flowmeter at the three flow rate levels specified in section 2.1.5.2 of this appendix.
(f) Report the results of all fuel flowmeter accuracy tests, transmitter or transducer accuracy tests, and primary element inspections, as applicable, in the emissions report for the quarter in which the quality assurance tests are performed, using the electronic format specified by the Administrator under § 75.64.
2.1.6.1 Transmitter or Transducer Accuracy Test for Orifice-, Nozzle-, and Venturi-Type Flowmeters(a) Calibrate the differential pressure transmitter or transducer, static pressure transmitter or transducer, and temperature transmitter or transducer, as applicable, using equipment that has a current certificate of traceability to NIST standards. Check the calibration of each transmitter or transducer by comparing its readings to that of the NIST traceable equipment at least once at each of the following levels: the zero-level and at least two other upscale levels (e.g., “mid” and “high”), such that the full range of transmitter or transducer readings corresponding to normal unit operation is represented. For temperature transmitters, the zero and upscale levels may correspond to fixed reference points, such as the freezing point or boiling point of water.
(b) Calculate the accuracy of each transmitter or transducer at each level tested, using the following equation:
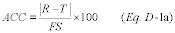 Where:
ACC = Accuracy of the transmitter or transducer as a percentage of
full-scale. R = Reading of the NIST traceable reference value (in
milliamperes, inches of water, psi, or degrees). T = Reading of the
transmitter or transducer being tested (in milliamperes, inches of
water, psi, or degrees, consistent with the units of measure of the
NIST traceable reference value). FS = Full-scale range of the
transmitter or transducer being tested (in milliamperes, inches of
water, psi, or degrees, consistent with the units of measure of the
NIST traceable reference value).
Where:
ACC = Accuracy of the transmitter or transducer as a percentage of
full-scale. R = Reading of the NIST traceable reference value (in
milliamperes, inches of water, psi, or degrees). T = Reading of the
transmitter or transducer being tested (in milliamperes, inches of
water, psi, or degrees, consistent with the units of measure of the
NIST traceable reference value). FS = Full-scale range of the
transmitter or transducer being tested (in milliamperes, inches of
water, psi, or degrees, consistent with the units of measure of the
NIST traceable reference value).
(c) If each transmitter or transducer meets an accuracy of 1.0 percent of its full-scale range at each level tested, the fuel flowmeter accuracy of 2.0 percent is considered to be met at all levels. If, however, one or more of the transmitters or transducers does not meet an accuracy of 1.0 percent of full-scale at a particular level, then the owner or operator may demonstrate that the fuel flowmeter meets the total accuracy specification of 2.0 percent at that level by using one of the following alternative methods. If, at a particular level, the sum of the individual accuracies of the three transducers is less than or equal to 4.0 percent, the fuel flowmeter accuracy specification of 2.0 percent is considered to be met for that level. Or, if at a particular level, the total fuel flowmeter accuracy is 2.0 percent or less, when calculated in accordance with Part 1 of American Gas Association Report No. 3, General Equations and Uncertainty Guidelines, the flowmeter accuracy requirement is considered to be met for that level.
2.1.6.2 Recordkeeping for Transmitter or Transducer Accuracy Results(a) Record the accuracy of the orifice, nozzle, or venturi meter or its individual transmitters or transducers and keep this information in a file at the site or other location suitable for inspection.
Table D-2 - Table of Flowmeter Transmitter or Transducer Accuracy Results
| Test number:____ Test completion date: __________ Unit or pipe ID: ______ |
| Flowmeter serial number: Component/System ID: |
| Full-scale value: Units of measure: 3 |
| Transducer/Transmitter Type (check one): |
| __ Differential Pressure |
| __ Static Pressure |
| __ Temperature |
| Measurement level (percent of full-scale) | Run number (if multiple runs) 2 | Run time (HHMM) | Transmitter/transducer input (pre-calibration) | Expected transmitter/transducer output (reference) | Actual transmitter/transducer output 3 | Percent accuracy (percent of full-scale) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (Minimum) level | ||||||
| __ percent 1 of full-scale | ||||||
| Mid-level | ||||||
| __ percent 1 of full-scale | ||||||
| (If tested at more than 3 levels) | ||||||
| 2nd Mid-level | ||||||
| __ percent 1 of full-scale | ||||||
| (If tested at more than 3 levels) | ||||||
| 3rd Mid-level | ||||||
| __ percent 1 of full-scale | ||||||
| High (Maximum) level | ||||||
| __ percent 1 of full-scale |
1 At a minimum, it is required to test at zero-level and at least two other levels across the range of the transmitter or transducer readings corresponding to normal unit operation.
2 It is required to test at least once at each level.
3 Use the same units of measure for all readings (e.g., use degrees (°), inches of water (in H2O), pounds per square inch (psi), or milliamperes (ma) for both transmitter or transducer readings and reference readings).
(b)-(c) [Reserved]
2.1.6.3 Failure of Transducer(s) or Transmitter(s)If, during a transmitter or transducer accuracy test conducted according to section 2.1.6.1 of this appendix, the flowmeter accuracy specification of 2.0 percent is not met at any of the levels tested, repair or replace transmitter(s) or transducer(s) as necessary until the flowmeter accuracy specification has been achieved at all levels. (Note that only transmitters or transducers which are repaired or replaced need to be re-tested; however, the re-testing is required at all three measurement levels, to ensure that the flowmeter accuracy specification is met at each level). The fuel flowmeter is “out-of-control” and data from the flowmeter are considered invalid, beginning with the date and hour of the failed accuracy test and continuing until the date and hour of completion of a successful transmitter or transducer accuracy test at all levels. In addition, if, during normal operation of the fuel flowmeter, one or more transmitters or transducers malfunction, data from the fuel flowmeter shall be considered invalid from the hour of the transmitter or transducer failure until the hour of completion of a successful 3-level transmitter or transducer accuracy test. During fuel flowmeter out-of-control periods, provide data from another fuel flowmeter that meets the requirements of § 75.20(d) and section 2.1.5 of this appendix, or substitute for fuel flow rate using the missing data procedures in section 2.4.2 of this appendix. Record and report test data and results, consistent with sections 2.1.6.1 and 2.1.6.2 of this appendix and § 75.59.
2.1.6.4 Primary Element Inspection(a) Conduct a visual inspection of the orifice, nozzle, or venturi meter at least once every twelve calendar quarters. Notwithstanding this requirement, the procedures of section 2.1.7 of this appendix may be used to reduce the inspection frequency of the orifice, nozzle, or venturi meter to at least once every twenty calendar quarters. The inspection may be performed using a baroscope. If the visual inspection is failed (if the orifice, nozzle, or venturi meter has become damaged or corroded), then:
(1) Replace the primary element with another primary element meeting the requirements of American Gas Association Report No. 3 or ASME MFC-3M-1989, as cited in section 2.1.5.1 of this appendix (both standards incorporated by reference under § 75.6). If the primary element size is changed, also calibrate the transmitters or transducers, consistent with the new primary element size;
(2) Replace the primary element with another primary element, and demonstrate that the overall flowmeter accuracy meets the accuracy specification in section 2.1.5 of this appendix, using the procedures of section 2.1.5.2 of this appendix; or
(3) Restore the damaged or corroded primary element to “as new” condition; determine the overall accuracy of the flowmeter, using either the specifications of American Gas Association Report No. 3 or ASME MFC-3M-1989, as cited in section 2.1.5.1 of this appendix (both standards incorporated by reference under § 75.6); and retest the transmitters or transducers prior to providing quality-assured data from the flowmeter.
(b) Data from the fuel flowmeter are considered invalid, beginning with the date and hour of a failed visual inspection and continuing until the date and hour when:
(1) The damaged or corroded primary element is replaced with another primary element meeting the requirements of American Gas Association Report No. 3 or ASME MFC-3M-1989, as cited in section 2.1.5.1 of this appendix (both standards incorporated by reference under § 75.6) and, if applicable, the transmitters have been successfully recalibrated;
(2) The damaged or corroded primary element is replaced, and the overall accuracy of the flowmeter is demonstrated to meet the accuracy specification in section 2.1.5 of this appendix, using the procedures of section 2.1.5.2 of this appendix; or
(3) The restored primary element is installed to meet the requirements of American Gas Association Report No. 3 or ASME MFC-3M-1989, as cited in section 2.1.5.1 of this appendix (both standards incorporated by reference under § 75.6) and its transmitters or transducers are retested to meet the accuracy specification in section 2.1.6.1 of this appendix.
(c) During each period of invalid fuel flowmeter data described in paragraph (b) of this section, provide data from another fuel flowmeter that meets the requirements of § 75.20(d) and section 2.1.5 of this appendix, or substitute for fuel flow rate using the missing data procedures in section 2.4.2 of this appendix.
2.1.7 Fuel Flow-to-Load Quality Assurance Testing for Certified Fuel FlowmetersThe procedures of this section may be used as an optional supplement to the quality assurance procedures in section 2.1.5.1, 2.1.5.2, 2.1.6.1, or 2.1.6.4 of this appendix when conducting periodic quality assurance testing of a certified fuel flowmeter. Note, however, that these procedures may not be used unless the 168-hour baseline data requirement of section 2.1.7.1 of this appendix has been met. If, following a flowmeter accuracy test or (if applicable) a flowmeter transmitter test and primary element inspection, the procedures of this section are performed during each subsequent fuel flowmeter QA operating quarter, as defined in § 72.2 of this chapter (excluding the quarter(s) in which the baseline data are collected), then these procedures may be used to meet the requirement for periodic quality assurance for a period of up to 20 calendar quarters from the previous periodic quality assurance procedure(s) performed according to sections 2.1.5.1, 2.1.5.2, or 2.1.6.1 through 2.1.6.4 of this appendix. The procedures of this section are not required for any quarter in which a flowmeter accuracy test or (if applicable) a transmitter accuracy test and a primary element inspection, are conducted. Notwithstanding the requirements of § 75.57(a), when using the procedures of this section, keep records of the test data and results from the previous flowmeter accuracy test under section 2.1.5.1 or 2.1.5.2 of this appendix, records of the test data and results from the previous transmitter or transducer accuracy test under section 2.1.6.1 of this appendix for orifice-, nozzle-, and venturi-type fuel flowmeters, and records of the previous visual inspection of the primary element required under section 2.1.6.4 of this appendix for orifice-, nozzle-, and venturi-type fuel flowmeters until the next flowmeter accuracy test, transmitter accuracy test, or visual inspection is performed, even if the previous flowmeter accuracy test, transmitter accuracy test, or visual inspection was performed more than three years previously.
2.1.7.1 Baseline Flow Rate-to-Load Ratio or Heat Input-to-Load Ratio(a) Determine Rbase, the baseline value of the ratio of fuel flow rate to unit load, following each successful periodic quality assurance procedure performed according to sections 2.1.5.1, 2.1.5.2, or 2.1.6.1 and 2.1.6.4 of this appendix. Establish a baseline period of data consisting, at a minimum, of 168 hours of quality-assured fuel flowmeter data. Baseline data collection shall begin with the first hour of fuel flowmeter operation following completion of the most recent quality assurance procedure(s), during which only the fuel measured by the fuel flowmeter is combusted (e.g., only gas, only residual oil, or only diesel fuel is combusted by the unit). During the baseline data collection period, the owner or operator may exclude as non-representative any hour in which the unit is “ramping” up or down, (i.e., the load during the hour differs by more than 15.0 percent from the load in the previous or subsequent hour) and may exclude any hour in which the unit load is in the lower 25.0 percent of the range of operation, as defined in section 6.5.2.1 of appendix A to this part (unless operation in this lower 25.0 percent of the range is considered normal for the unit). The baseline data must be obtained no later than the end of the fourth calendar quarter following the calendar quarter of the most recent quality assurance procedure for that fuel flowmeter. For orifice-, nozzle-, and venturi-type fuel flowmeters, if the fuel flow-to-load ratio is to be used as a supplement both to the transmitter accuracy test under section 2.1.6.1 of this appendix and to primary element inspections under section 2.1.6.4 of this appendix, then the baseline data must be obtained after both procedures are completed and no later than the end of the fourth calendar quarter following the calendar quarter in which both procedures were completed. From these 168 (or more) hours of baseline data, calculate the baseline fuel flow rate-to-load ratio as follows:
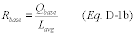 where:
Rbase = Value of the fuel flow rate-to-load ratio during the
baseline period; 100 scfh/MWe, 100 scfh/klb per hour steam load, or
100 scfh/mmBtu per hour thermal output for gas-firing; (lb/hr)/MWe,
(lb/hr)/klb per hour steam load, or (lb/hr)/mmBtu per hour thermal
output for oil-firing. Qbase = Arithmetic average fuel flow rate
measured by the fuel flowmeter during the baseline period, 100 scfh
for gas-firing and lb/hr for oil-firing. Lavg = Arithmetic average
unit load during the baseline period, megawatts, 1000 lb/hr of
steam, or mmBtu/hr thermal output.
where:
Rbase = Value of the fuel flow rate-to-load ratio during the
baseline period; 100 scfh/MWe, 100 scfh/klb per hour steam load, or
100 scfh/mmBtu per hour thermal output for gas-firing; (lb/hr)/MWe,
(lb/hr)/klb per hour steam load, or (lb/hr)/mmBtu per hour thermal
output for oil-firing. Qbase = Arithmetic average fuel flow rate
measured by the fuel flowmeter during the baseline period, 100 scfh
for gas-firing and lb/hr for oil-firing. Lavg = Arithmetic average
unit load during the baseline period, megawatts, 1000 lb/hr of
steam, or mmBtu/hr thermal output.
(b) In Equation D-1b, for a fuel flowmeter installed on a common pipe header, Lavg is the sum of the operating loads of all units that received fuel through the common pipe header during the baseline period, divided by the total number of hours of fuel flow rate data collected during the baseline period. For a unit that receives the same type of fuel through multiple pipes, Qbase is the sum of the fuel flow rates during the baseline period from all of the pipes, divided by the total number of hours of fuel flow rate data collected during the baseline period. Round off the value of Rbase to the nearest tenth.
(c) Alternatively, a baseline value of the gross heat rate (GHR) may be determined in lieu of Rbase. The baseline value of the GHR, GHRbase, shall be determined as follows:
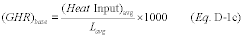 Where:
(GHR)base = Baseline value of the gross heat rate during the
baseline period, Btu/kwh, Btu/lb steam load, or 1000mmBtu heat
input/mmBtu thermal output. (Heat Input)avg = Average (mean) hourly
heat input rate recorded by the fuel flowmeter during the baseline
period, as determined using the average fuel flow rate and the fuel
GCV in the applicable equation in appendix F to this part,
mmBtu/hr. Lavg = Average (mean) unit load during the baseline
period, megawatts, 1000 lb/hr of steam, or mmBtu/hr thermal output.
Where:
(GHR)base = Baseline value of the gross heat rate during the
baseline period, Btu/kwh, Btu/lb steam load, or 1000mmBtu heat
input/mmBtu thermal output. (Heat Input)avg = Average (mean) hourly
heat input rate recorded by the fuel flowmeter during the baseline
period, as determined using the average fuel flow rate and the fuel
GCV in the applicable equation in appendix F to this part,
mmBtu/hr. Lavg = Average (mean) unit load during the baseline
period, megawatts, 1000 lb/hr of steam, or mmBtu/hr thermal output.
(d) Report the current value of Rbase (or GHRbase) and the completion date of the associated quality assurance procedure in each electronic quarterly report required under § 75.64.
(e) If a unit co-fires different fuels (e.g., oil and natural gas) as its normal mode of operation, the gross heat rate option in paragraph (c) of this section may be used to determine a value of (GHR)base, as follows. Derive the baseline data during co-fired hours. Then, use Equation D-1c to calculate (GHR)base, making sure that each hourly unit heat input rate used to calculate (Heat Input)avg includes the contribution of each type of fuel.
2.1.7.2 Data Preparation and Analysis(a) Evaluate the fuel flow rate-to-load ratio (or GHR) for each fuel flowmeter QA operating quarter, as defined in § 72.2 of this chapter. At the end of each fuel flowmeter QA operating quarter, use Equation D-1d in this appendix to calculate Rh, the hourly fuel flow-to-load ratio, for every quality-assured hourly average fuel flow rate obtained with a certified fuel flowmeter. Alternatively, the owner or operator may exclude non-representative hours from the data analysis, as described in section 2.1.7.3 of this appendix, prior to calculating the values of Rh.
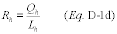 where: Rh
= Hourly value of the fuel flow rate-to-load ratio; 100 scfh/MWe,
(lb/hr)/MWe, 100 scfh/1000 lb/hr of steam load, (lb/hr)/1000 lb/hr
of steam load, 100 scfh/(mmBtu/hr of steam load), or
(lb/hr)/(mmBtu/hr thermal output). Qh = Hourly fuel flow rate, as
measured by the fuel flowmeter, 100 scfh for gas-firing or lb/hr
for oil-firing. Lh = Hourly unit load, megawatts, 1000 lb/hr of
steam, or mmBtu/hr thermal output.
where: Rh
= Hourly value of the fuel flow rate-to-load ratio; 100 scfh/MWe,
(lb/hr)/MWe, 100 scfh/1000 lb/hr of steam load, (lb/hr)/1000 lb/hr
of steam load, 100 scfh/(mmBtu/hr of steam load), or
(lb/hr)/(mmBtu/hr thermal output). Qh = Hourly fuel flow rate, as
measured by the fuel flowmeter, 100 scfh for gas-firing or lb/hr
for oil-firing. Lh = Hourly unit load, megawatts, 1000 lb/hr of
steam, or mmBtu/hr thermal output.
(b) For a fuel flowmeter installed on a common pipe header, Lh shall be the sum of the hourly operating loads of all units that receive fuel through the common pipe header. For a unit that receives the same type of fuel through multiple pipes, Qh will be the sum of the fuel flow rates from all of the pipes. Round off each value of Rh to the nearest tenth.
(c) Alternatively, calculate the hourly gross heat rates (GHR) in lieu of the hourly flow-to-load ratios. If this option is selected, calculate each hourly GHR value as follows:
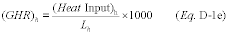 Where:
(GHR)h = Hourly value of the gross heat rate, Btu/kwh, Btu/lb steam
load, or mmBtu heat input/mmBtu thermal output. (Heat Input)h =
Hourly heat input rate, as determined using the hourly fuel flow
rate and the fuel GCV in the applicable equation in appendix F to
this part, mmBtu/hr. Lh = Hourly unit load, megawatts, 1000 lb/hr
of steam, or mmBtu/hr thermal output.
Where:
(GHR)h = Hourly value of the gross heat rate, Btu/kwh, Btu/lb steam
load, or mmBtu heat input/mmBtu thermal output. (Heat Input)h =
Hourly heat input rate, as determined using the hourly fuel flow
rate and the fuel GCV in the applicable equation in appendix F to
this part, mmBtu/hr. Lh = Hourly unit load, megawatts, 1000 lb/hr
of steam, or mmBtu/hr thermal output.
(d) Evaluate the calculated flow rate-to-load ratios (or gross heat rates) as follows.
(1) Perform a separate data analysis for each fuel flowmeter system following the procedures of this section. Base each analysis on a minimum of 168 hours of data. If, for a particular fuel flowmeter system, fewer than 168 hourly flow-to-load ratios (or GHR values) are available, or, if the baseline data collection period is still in progress at the end of the quarter and fewer than four calendar quarters have elapsed since the quarter in which the last successful fuel flowmeter system accuracy test was performed, a flow-to-load (or GHR) evaluation is not required for that flowmeter system for that calendar quarter. A one-quarter extension of the deadline for the next fuel flowmeter system accuracy test may be claimed for a quarter in which there is insufficient hourly data available to analyze or a quarter that ends with the baseline data collection period still in progress.
(2) For a unit that normally co-fires different types of fuel (e.g., oil and natural gas), include the contribution of each type of fuel in the value of (Heat Input)h, when using Equation D-1e.
(e) For each hourly flow-to-load ratio or GHR value, calculate the percentage difference (percent Dh) from the baseline fuel flow-to-load ratio using Equation D-1f.
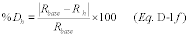 Where:
%Dh = Absolute value of the percentage difference between the
hourly fuel flow rate-to-load ratio and the baseline value of the
fuel flow rate-to-load ratio (or hourly and baseline GHR). Rh = The
hourly fuel flow rate-to-load ratio (or GHR). Rbase = The value of
the fuel flow rate-to-load ratio (or GHR) from the baseline period,
determined in accordance with section 2.1.7.1 of this appendix.
Where:
%Dh = Absolute value of the percentage difference between the
hourly fuel flow rate-to-load ratio and the baseline value of the
fuel flow rate-to-load ratio (or hourly and baseline GHR). Rh = The
hourly fuel flow rate-to-load ratio (or GHR). Rbase = The value of
the fuel flow rate-to-load ratio (or GHR) from the baseline period,
determined in accordance with section 2.1.7.1 of this appendix.
(f) Consistently use Rbase and Rh in Equation D-1f if the fuel flow-to-load ratio is being evaluated, and consistently use (GHR)base and (GHR)h in Equation D-1f if the gross heat rate is being evaluated.
(g) Next, determine the arithmetic average of all of the hourly percent difference (percent Dh) values using Equation D-1g, as follows:
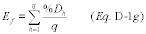 Where: Ef
= Quarterly average percentage difference between hourly flow
rate-to-load ratios and the baseline value of the fuel flow
rate-to-load ratio (or hourly and baseline GHR). %Dh = Percentage
difference between the hourly fuel flow rate-to-load ratio and the
baseline value of the fuel flow rate-to-load ratio (or hourly and
baseline GHR). q = Number of hours used in fuel flow-to-load (or
GHR) evaluation.
Where: Ef
= Quarterly average percentage difference between hourly flow
rate-to-load ratios and the baseline value of the fuel flow
rate-to-load ratio (or hourly and baseline GHR). %Dh = Percentage
difference between the hourly fuel flow rate-to-load ratio and the
baseline value of the fuel flow rate-to-load ratio (or hourly and
baseline GHR). q = Number of hours used in fuel flow-to-load (or
GHR) evaluation.
(h) When the quarterly average load value used in the data analysis is greater than 50 MWe (or 500 klb steam per hour), the results of a quarterly fuel flow rate-to-load (or GHR) evaluation are acceptable and no further action is required if the quarterly average percentage difference (Ef) is no greater than 10.0 percent. When the arithmetic average of the hourly load values used in the data analysis is ≤50 MWe (or 500 klb steam per hour), the results of the analysis are acceptable if the value of Ef is no greater than 15.0 percent. For units that normally co-fire different types of fuel, if the GHR option is used, apply the test results to each fuel flowmeter system used during the quarter.
2.1.7.3 Optional Data Exclusions(a) If Ef is outside the limits in section 2.1.7.2(h) of this appendix, the owner or operator may re-examine the hourly fuel flow rate-to-load ratios (or GHRs) that were used for the data analysis and may identify and exclude fuel flow-to-load ratios or GHR values for any non-representative hours, provided that such data exclusions were not previously made under section 2.1.7.2(a) of this appendix. Specifically, the Rh or (GHR)h values for the following hours may be considered non-representative:
(1) For units that do not normally co-fire fuels, any hour in which the unit combusted another fuel in addition to the fuel measured by the fuel flowmeter being tested; or
(2) Any hour for which the load differed by more than ±15.0 percent from the load during either the preceding hour or the subsequent hour; or
(3) For units that normally co-fire different fuels, any hour in which the unit burned only one type of fuel; or
(4) Any hour for which the unit load was in the lower 25.0 percent of the range of operation, as defined in section 6.5.2.1 of appendix A to this part (unless operation in the lower 25.0 percent of the range is considered normal for the unit).
(b) After identifying and excluding all non-representative hourly fuel flow-to-load ratios or GHR values, analyze the quarterly fuel flow rate-to-load data a second time. If fewer than 168 hourly fuel flow-to-load ratio or GHR values remain after the allowable data exclusions, a fuel flow-to-load ratio or GHR analysis is not required for that quarter, and a one-quarter extension of the fuel flowmeter accuracy test deadline may be claimed.
2.1.7.4 Consequences of Failed Fuel Flow-to-Load Ratio Test(a) If Ef is outside the applicable limit in section 2.1.7.2(h) of this appendix (after analysis using any optional data exclusions under section 2.1.7.3 of this appendix), perform transmitter accuracy tests according to section 2.1.6.1 of this appendix for orifice-, nozzle-, and venturi-type flowmeters, or perform a fuel flowmeter accuracy test, in accordance with section 2.1.5.1 or 2.1.5.2 of this appendix, for each fuel flowmeter for which Ef is outside of the applicable limit. In addition, for an orifice-, nozzle-, or venturi-type fuel flowmeter, repeat the fuel flow-to-load ratio comparison of section 2.1.7.2 of this appendix using six to twelve hours of data following a passed transmitter accuracy test in order to verify that no significant corrosion has affected the primary element. If, for the abbreviated 6-to-12 hour test, the orifice-, nozzle-, or venturi-type fuel flowmeter is not able to meet the limit in section 2.1.7.2 of this appendix, then perform a visual inspection of the primary element according to section 2.1.6.4 of this appendix, and repair or replace the primary element, as necessary.
(b) Substitute for fuel flow rate, for any hour when that fuel is combusted, using the missing data procedures in section 2.4.2 of this appendix, beginning with the first hour of the calendar quarter following the quarter for which Ef was found to be outside the applicable limit and continuing until quality-assured fuel flow data become available. Following a failed flow rate-to-load or GHR evaluation, data from the flowmeter shall not be considered quality-assured until the hour in which all required flowmeter accuracy tests, transmitter accuracy tests, visual inspections and diagnostic tests have been passed. Additionally, a new value of Rbase or (GHR)base shall be established no later than two fuel flowmeter QA operating quarters (as defined in § 72.2 of this chapter) after the quarter in which the required quality assurance tests are completed (note that for orifice-, nozzle-, or venturi-type fuel flowmeters, establish a new value of Rbase or (GHR)base only if both a transmitter accuracy test and a primary element inspection have been performed).
2.1.7.5 Test ResultsReport the results of each quarterly flow rate-to-load (or GHR) evaluation, as determined from Equation D-1g, in the electronic quarterly report required under § 75.64. Table D-3 is provided as a reference on the type of information to be recorded under § 75.59 and reported under § 75.64.
Table D-3 - Baseline Information and Test Results For Fuel Flow-to-Load Test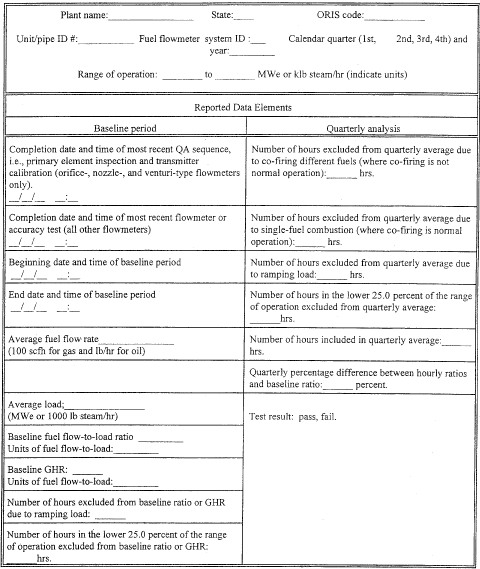 2.2 Oil Sampling
and Analysis
2.2 Oil Sampling
and Analysis
Perform sampling and analysis of oil to determine the following fuel properties for each type of oil combusted by a unit: percentage of sulfur by weight in the oil; gross calorific value (GCV) of the oil; and, if necessary, the density of the oil. Use the sulfur content, density, and gross calorific value, determined under the provisions of this section, to calculate SO2 mass emission rate and heat input rate for each fuel using the applicable procedures of section 3 of this appendix. The designated representative may petition for reduced GCV and or density sampling under § 75.66 if the fuel combusted has a consistent and relatively non-variable GCV or density.
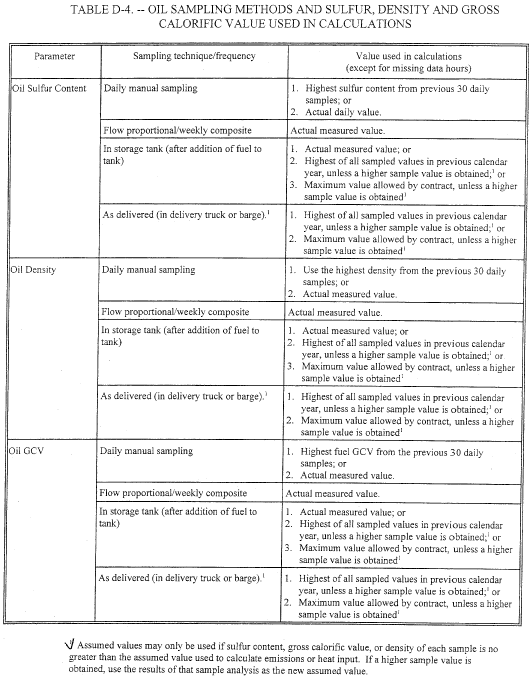
2.2.1 When combusting oil, use one of the following methods to sample the oil (see Table D-4): sample from the storage tank for the unit after each addition of oil to the storage tank, in accordance with section 2.2.4.2 of this appendix; or sample from the fuel lot in the shipment tank or container upon receipt of each oil delivery or from the fuel lot in the oil supplier's storage container, in accordance with section 2.2.4.3 of this appendix; or use the flow proportional sampling methodology in section 2.2.3 of this appendix; or use the daily manual sampling methodology in section 2.2.4.1 of this appendix. For purposes of this appendix, a fuel lot of oil is the mass or volume of product oil from one source (supplier or pretreatment facility), intended as one shipment or delivery (e.g., ship load, barge load, group of trucks, discrete purchase of diesel fuel through pipeline, etc.). A storage tank is a container at a plant holding oil that is actually combusted by the unit, such that no blending of any other fuel with the fuel in the storage tank occurs from the time that the fuel lot is transferred to the storage tank to the time when the fuel is combusted in the unit.
2.2.2 [Reserved] 2.2.3 Flow Proportional SamplingConduct flow proportional oil sampling or continuous drip oil sampling in accordance with ASTM D4177-95 (Reapproved 2000), “Standard Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products” (incorporated by reference under § 75.6), every day the unit is combusting oil. Extract oil at least once every hour and blend into a composite sample. The sample compositing period may not exceed 7 calendar days (168 hrs). Use the actual sulfur content (and where density data are required, the actual density) from the composite sample to calculate the hourly SO2 mass emission rates for each operating day represented by the composite sample. Calculate the hourly heat input rates for each operating day represented by the composite sample, using the actual gross calorific value from the composite sample.
2.2.4 Manual Sampling 2.2.4.1 Daily SamplesRepresentative oil samples may be taken from the storage tank or fuel flow line manually every day that the unit combusts oil according to ASTM ASTM D4057-95 (Reapproved 2000), Standard Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products (incorporated by reference under § 75.6 of this part). Use either the actual daily sulfur content or the highest fuel sulfur content recorded at that unit from the most recent 30 daily samples for the purpose of calculating SO2 emissions under section 3 of this appendix. Use either the gross calorific value measured from that day's sample or the highest GCV from the previous 30 days' samples to calculate heat input. If oil supplies with different sulfur contents are combusted on the same day, sample the highest sulfur fuel combusted that day.
2.2.4.2 Sampling From a Unit's Storage TankTake a manual sample after each addition of oil to the storage tank. Do not blend additional fuel with the sampled fuel prior to combustion. Sample according to the single tank composite sampling procedure or all-levels sampling procedure in ASTM ASTM D4057-95 (Reapproved 2000), Standard Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products (incorporated by reference under § 75.6 of this part). Use the sulfur content and GCV value (and where required, the density) of either the most recent sample or one of the conservative assumed values described in section 2.2.4.3(c) of this appendix to calculate SO2 mass emission rate. Calculate heat input rate using the gross calorific value from either:
(a) The most recent oil sample taken or
(b) One of the conservative assumed values described in section 2.2.4.3(c) of this appendix. Follow the applicable provisions in section 2.2.4.3(d) of this appendix, regarding the use of assumed values.
2.2.4.3 Sampling From Each Delivery(a) Alternatively, an oil sample may be taken from -
(1) The shipment tank or container upon receipt of each lot of fuel oil or
(2) The supplier's storage container which holds the lot of fuel oil. (Note: a supplier need only sample the storage container once for sulfur content, GCV and, where required, the density so long as the fuel sulfur content and GCV do not change and no fuel is added to the supplier's storage container.)
(b) For the purpose of this section, a lot is defined as a shipment or delivery (e.g., ship load, barge load, group of trucks, discrete purchase of diesel fuel through a pipeline, etc.) of a single fuel.
(c) Oil sampling may be performed either by the owner or operator of an affected unit, an outside laboratory, or a fuel supplier, provided that samples are representative and that sampling is performed according to either the single tank composite sampling procedure or the all-levels sampling procedure in ASTM ASTM D4057-95 (Reapproved 2000), Standard Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products (incorporated by reference under § 75.6 of this part). Except as otherwise provided in this section, calculate SO2 mass emission rate using the sulfur content (and where required, the density) from one of the two following conservative assumed values, and calculate heat input using the gross calorific value from one of the assumed values:
(1) The highest value sampled during the previous calendar year (this option is allowed for any consistent fuel which comes from a single source whether or not the fuel is supplied under a contractual agreement) or
(2) The maximum value indicated in the contract with the fuel supplier. Continue to use this assumed contract value unless and until the actual sampled sulfur content, density, or gross calorific value of a delivery exceeds the assumed value.
(d) Continue using the assumed value(s), so long as the sample results do not exceed the assumed value(s). However, if the actual sampled sulfur content, gross calorific value, or density of an oil sample is greater than the assumed value for that parameter, then, consistent with section 2.3.7 of this appendix, begin to use the actual sampled value for sulfur content, gross calorific value, or density of fuel to calculate SO2 mass emission rate or heat input rate. Consider the sampled value to be the new assumed sulfur content, gross calorific value, or density. Continue using this new assumed value to calculate SO2 mass emission rate or heat input rate unless and until: it is superseded by a higher value from an oil sample; or (if applicable) it is superseded by a new contract in which case the new contract value becomes the assumed value at the time the fuel specified under the new contract begins to be combusted in the unit; or (if applicable) both the calendar year in which the sampled value exceeded the assumed value and the subsequent calendar year have elapsed.
2.2.5 For each oil sample that is taken on-site at the affected facility, split and label the sample and maintain a portion (at least 200 cc) of it throughout the calendar year and in all cases for not less than 90 calendar days after the end of the calendar year allowance accounting period. This requirement does not apply to oil samples taken from the fuel supplier's storage container, as described in section 2.2.4.3 of this appendix. Analyze oil samples for percent sulfur content by weight in accordance with ASTM D129-00, Standard Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Products (General Bomb Method), ASTM D1552-01, Standard Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Products (High-Temperature Method), ASTM D2622-98, Standard Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Products by Wavelength Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry, ASTM D4294-98, Standard Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum and Petroleum Products by Energy-Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry, or ASTM D5453-06, Standard Test Method for Determination of Total Sulfur in Light Hydrocarbons, Spark Ignition Engine Fuel, Diesel Engine Fuel, and Engine Oil by Ultraviolet Fluorescence (all incorporated by reference under § 75.6 of this part). Alternatively, the oil samples may be analyzed for percent sulfur by any consensus standard method prescribed for the affected unit under part 60 of this chapter.
2.2.6 Where the flowmeter records volumetric flow rate rather than mass flow rate, analyze oil samples to determine the density or specific gravity of the oil. Determine the density or specific gravity of the oil sample in accordance with ASTM D287-92 (Reapproved 2000), Standard Test Method for API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Petroleum Products (Hydrometer Method), ASTM D1217-93 (Reapproved 1998), Standard Test Method for Density and Relative Density (Specific Gravity) of Liquids by Bingham Pycnometer, ASTM D1481-93 (Reapproved 1997), Standard Test Method for Density and Relative Density (Specific Gravity) of Viscous Materials by Lipkin Bicapillary Pycnometer, ASTM D1480-93 (Reapproved 1997), Standard Test Method for Density and Relative Density (Specific Gravity) of Viscous Materials by Bingham Pycnometer, ASTM D1298-99, Standard Test Method for Density, Relative Density (Specific Gravity), or API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Products by Hydrometer Method, or ASTM D4052-96 (Reapproved 2002), Standard Test Method for Density and Relative Density of Liquids by Digital Density Meter (all incorporated by reference under § 75.6 of this part). Alternatively, the oil samples may be analyzed for density or specific gravity by any consensus standard method prescribed for the affected unit under part 60 of this chapter.
2.2.7 Analyze oil samples to determine the heat content of the fuel. Determine oil heat content in accordance with ASTM D240-00, ASTM D4809-00, ASTM D5865-01a, or D5865-10 (all incorporated by reference under § 75.6) or any other procedures listed in section 5.5 of appendix F of this part. Alternatively, the oil samples may be analyzed for heat content by any consensus standard method prescribed for the affected unit under part 60 of this chapter.
2.2.8 Results from the oil sample analysis must be available no later than thirty calendar days after the sample is composited or taken. However, during an audit, the Administrator may require that the results of the analysis be available as soon as practicable, and no later than 5 business days after receipt of a request from the Administrator.
2.3 SO2 Emissions From Combustion of Gaseous Fuels(a) Account for the hourly SO2 mass emissions due to combustion of gaseous fuels for each hour when gaseous fuels are combusted by the unit using the procedures in this section.
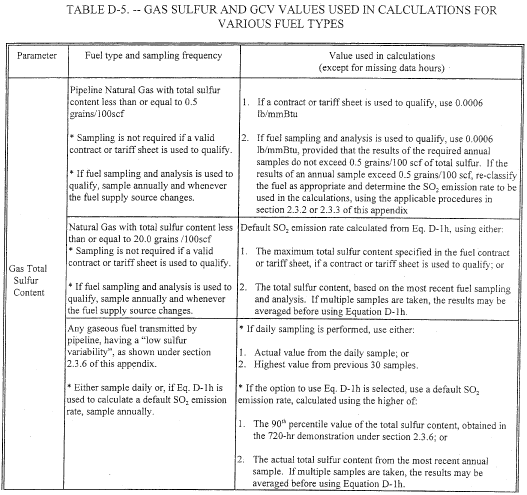
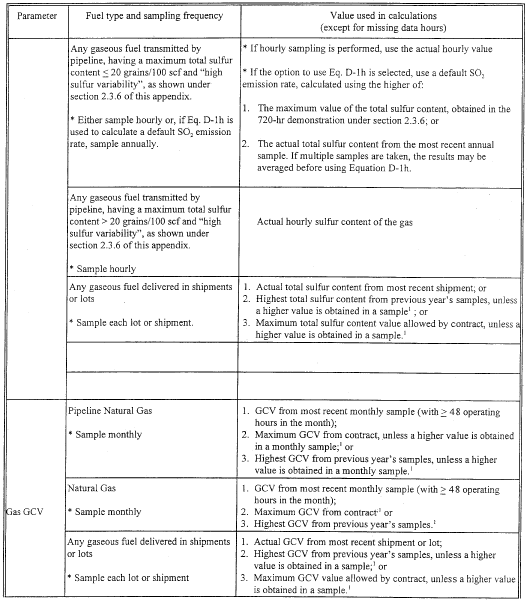
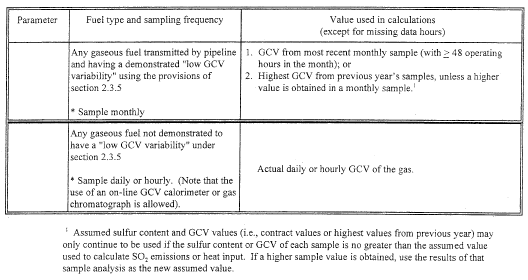
(b) The procedures in sections 2.3.1 and 2.3.2 of this appendix, respectively, may be used to determine SO2 mass emissions from combustion of pipeline natural gas and natural gas, as defined in § 72.2 of this chapter. The procedures in section 2.3.3 of this appendix may be used to account for SO2 mass emissions from any gaseous fuel combusted by a unit. For each type of gaseous fuel, the appropriate sampling frequency and the sulfur content and GCV values used for calculations of SO2 mass emission rates are summarized in the following Table D-5.
 2.3.1 Pipeline
Natural Gas Combustion
2.3.1 Pipeline
Natural Gas Combustion
The owner or operator may determine the SO2 mass emissions from the combustion of a fuel that meets the definition of pipeline natural gas, in § 72.2 of this chapter, using the procedures of this section.
2.3.1.1 SO2 Emission RateFor a fuel that meets the definition of pipeline natural gas under § 72.2 of this chapter, the owner or operator may determine the SO2 mass emissions using either a default SO2 emission rate of 0.0006 lb/mmBtu and the procedures of this section, the procedures in section 2.3.2 for natural gas, or the procedures of section 2.3.3 for any gaseous fuel. For each affected unit using the default rate of 0.0006 lb/mmBtu, the owner or operator must document that the fuel combusted is actually pipeline natural gas, using the procedures in section 2.3.1.4 of this appendix.
2.3.1.2 Hourly Heat Input RateCalculate hourly heat input rate, in mmBtu/hr, for a unit combusting pipeline natural gas, using the procedures of section 3.4.1 of this appendix. Use the measured fuel flow rate from section 2.1 of this appendix and the gross calorific value from section 2.3.4.1 of this appendix in the calculations.
2.3.1.3 SO2 Hourly Mass Emission Rate and Hourly Mass EmissionsFor pipeline natural gas combustion, calculate the SO2 mass emission rate, in lb/hr, using Equation D-5 in section 3.3.2 of this appendix (when the default SO2 emission rate is used) or Equation D-4 (if daily or hourly fuel sampling is used). Then, use the calculated SO2 mass emission rate and the unit operating time to determine the hourly SO2 mass emissions from pipeline natural gas combustion, in lb, using Equation D-12 in section 3.5.1 of this appendix.
2.3.1.4 Documentation that a Fuel is Pipeline Natural Gas(a) A fuel may initially qualify as pipeline natural gas, if information is provided in the monitoring plan required under § 75.53, demonstrating that the definition of pipeline natural gas in § 72.2 of this chapter has been met. The information must demonstrate that the fuel meets either the percent methane or GCV requirement and has a total sulfur content of 0.5 grains/100scf or less. The demonstration must be made using one of the following sources of information:
(1) The gas quality characteristics specified by a purchase contract, tariff sheet, or by a pipeline transportation contract; or
(2) Historical fuel sampling data for the previous 12 months, documenting the total sulfur content of the fuel and the GCV and/or percentage by volume of methane. The results of all sample analyses obtained by or provided to the owner or operator in the previous 12 months shall be used in the demonstration, and each sample result must meet the definition of pipeline natural gas in § 72.2 of this chapter, except where the results of at least 100 daily (or more frequent) total sulfur samples are provided by the fuel supplier. In that case you may opt to convert these data to monthly averages and then if, for each month, the average total sulfur content is 0.5 grains/100 scf or less, and if the GCV or percent methane requirement is also met, the fuel qualifies as pipeline natural gas. Alternatively, the fuel qualifies as pipeline natural gas if ≥98 percent of the 100 (or more) samples have a total sulfur content of 0.5 grains/100 scf or less and if the GCV or percent methane requirement is also met; or
(3) If the requirements of paragraphs (a)(1) and (a)(2) of this section cannot be met, a fuel may initially qualify as pipeline natural gas if at least one representative sample of the fuel is obtained and analyzed for total sulfur content and for either the gross calorific value (GCV) or percent methane, and the results of the sample analysis show that the fuel meets the definition of pipeline natural gas in § 72.2 of this chapter. Use the sampling methods specified in sections 2.3.3.1.2 and 2.3.4 of this appendix. The required fuel sample may be obtained and analyzed by the owner or operator, by an independent laboratory, or by the fuel supplier. If multiple samples are taken, each sample must meet the definition of pipeline natural gas in § 72.2 of this chapter.
(b) If the results of the fuel sampling under paragraph (a)(2) or (a)(3) of this section show that the fuel does not meet the definition of pipeline natural gas in § 72.2 of this chapter, but those results are believed to be anomalous, the owner or operator may document the reasons for believing this in the monitoring plan for the unit, and may immediately perform additional sampling. In such cases, a minimum of three additional samples must be obtained and analyzed, and the results of each sample analysis must meet the definition of pipeline natural gas.
(c) If several affected units are supplied by a common source of gaseous fuel, a single sampling result may be applied to all of the units and it is not necessary to obtain a separate sample for each unit, provided that the composition of the fuel is not altered by blending or mixing it with other gaseous fuel(s) when it is transported from the sampling location to the affected units. For the purposes of this paragraph, the term “other gaseous fuel(s)” excludes compounds such as mercaptans when they are added in trace quantities for safety reasons.
(d) If the results of fuel sampling and analysis under paragraph (a)(2), (a)(3), or (b) of this section show that the fuel does not qualify as pipeline natural gas, proceed as follows:
(1) If the fuel still qualifies as natural gas under section 2.3.2.4 of this appendix, re-classify the fuel as natural gas and determine the appropriate default SO2 emission rate for the fuel, according to section 2.3.2.1.1 of this appendix; or
(2) If the fuel does not qualify either as pipeline natural gas or natural gas, re-classify the fuel as “other gaseous fuel” and implement the procedures of section 2.3.3 of this appendix, within 180 days of the end of the quarter in which the disqualifying sample was taken. In addition, the owner or operator shall use Equation D-1h in this appendix to calculate a default SO2 emission rate for the fuel, based on the results of the sample analysis that exceeded 20 grains/100 scf of total sulfur, and shall use that default emission rate to report SO2 mass emissions under this part until section 2.3.3 of this appendix has been fully implemented.
(e) If a fuel qualifies as pipeline natural gas based on the specifications in a fuel contract or tariff sheet, no additional, on-going sampling of the fuel's total sulfur content is required, provided that the contract or tariff sheet is current, valid and representative of the fuel combusted in the unit. If the fuel qualifies as pipeline natural gas based on fuel sampling and analysis, on-going sampling of the fuel's sulfur content is required annually and whenever the fuel supply source changes. For the purposes of this paragraph (e), sampling “annually” means that at least one sample is taken in each calendar year. If the results of at least 100 daily (or more frequent) total sulfur samples have been provided by the fuel supplier since the last annual assessment of the fuel's sulfur content, the data may be used as follows to satisfy the annual sampling requirement for the current year. If this option is chosen, all of the data provided by the fuel supplier shall be used. First, convert the data to monthly averages. Then, if, for each month, the average total sulfur content is 0.5 grains/100 scf or less, and if the GCV or percent methane requirement is also met, the fuel qualifies as pipeline natural gas. Alternatively, the fuel qualifies as pipeline natural gas if the analysis of the 100 (or more) total sulfur samples since the last annual assessment shows that ≥98 percent of the samples have a total sulfur content of 0.5 grains/100 scf or less and if the GCV or percent methane requirement is also met. The effective date of the annual total sulfur sampling requirement is January 1, 2003.
(f) On-going sampling of the GCV of the pipeline natural gas is required under section 2.3.4.1 of this appendix.
(g) For units that are required to monitor and report NOX mass emissions and heat input under subpart H of this part, but which are not affected units under the Acid Rain Program, the owner or operator is exempted from the requirements in paragraphs (a) and (e) of this section to document the total sulfur content of the pipeline natural gas.
2.3.2 Natural Gas CombustionThe owner or operator may determine the SO2 mass emissions from the combustion of a fuel that meets the definition of natural gas, in § 72.2 of this chapter, using the procedures of this section.
2.3.2.1 SO2 Emission RateThe owner or operator may account for SO2 emissions either by using a default SO2 emission rate, as determined under section 2.3.2.1.1 of this appendix, or by daily sampling of the gas sulfur content using the procedures of section 2.3.3 of this appendix. For each affected unit using a default SO2 emission rate, the owner or operator must provide documentation that the fuel combusted is actually natural gas according to the procedures in section 2.3.2.4 of this appendix.
2.3.2.1.1 In lieu of daily sampling of the sulfur content of the natural gas, the owner or operator may either use the total sulfur content specified in a contract or tariff sheet as the SO2 default emission rate or may calculate the default SO2 emission rate based on fuel sampling results, using Equation D-1h. In Equation D-1h, the total sulfur content and GCV values shall be determined in accordance with Table D-5 of this appendix. Round off the calculated SO2 default emission rate to the nearest 0.0001 lb/mmBtu.
Where: ER = Default SO2 emission rate for natural gas combustion, lb/mmBtu. Stotal = Total sulfur content of the natural gas, gr/100scf. GCV = Gross calorific value of the natural gas, Btu/100scf. 7000 = Conversion of grains/100scf to lb/100scf. 2.0 = Ratio of lb SO2/lb S. 10 6 = Conversion factor (Btu/mmBtu). 2.3.2.1.2 [Reserved] 2.3.2.2 Hourly Heat Input RateCalculate hourly heat input rate for natural gas combustion, in mmBtu/hr, using the procedures in section 3.4.1 of this appendix. Use the measured fuel flow rate from section 2.1 of this appendix and the gross calorific value from section 2.3.4.2 of this appendix in the calculations.
2.3.2.3 SO2 Mass Emission Rate and Hourly Mass EmissionsFor natural gas combustion, calculate the SO2 mass emission rate, in lb/hr, using Equation D-5 in section 3.3.2 of this appendix, when the default SO2 emission rate is used. Then, use the calculated SO2 mass emission rate and the unit operating time to determine the hourly SO2 mass emissions from natural gas combustion, in lb, using Equation D-12 in section 3.5.1 of this appendix.
2.3.2.4 Documentation that a Fuel Is Natural Gas(a) A fuel may initially qualify as natural gas, if information is provided in the monitoring plan required under § 75.53, demonstrating that the definition of natural gas in § 72.2 of this chapter has been met. The information must demonstrate that the fuel meets either the percent methane or GCV requirement and has a total sulfur content of 20.0 grains/100 scf or less. This demonstration must be made using one of the following sources of information:
(1) The gas quality characteristics specified by a purchase contract, tariff sheet, or by a transportation contract; or
(2) Historical fuel sampling data for the previous 12 months, documenting the total sulfur content of the fuel and the GCV and/or percentage by volume of methane. The results of all sample analyses obtained by or provided to the owner or operator in the previous 12 months shall be used in the demonstration, and each sample result must meet the definition of natural gas in § 72.2 of this chapter; or
(3) If the requirements of paragraphs (a)(1) and (a)(2) of this section cannot be met, a fuel may initially qualify as natural gas if at least one representative sample of the fuel is obtained and analyzed for total sulfur content and for either the gross calorific value (GCV) or percent methane, and the results of the sample analysis show that the fuel meets the definition of natural gas in § 72.2 of this chapter. Use the sampling methods specified in sections 2.3.3.1.2 and 2.3.4 of this appendix. The required fuel sample may be obtained and analyzed by the owner or operator, by an independent laboratory, or by the fuel supplier. If multiple samples are taken, each sample must meet the definition of natural gas in § 72.2 of this chapter.
(b) If the results of the fuel sampling under paragraph (a)(2) or (a)(3) of this section show that the fuel does not meet the definition of natural gas in § 72.2 of this chapter, but those results are believed to be anomalous, the owner or operator may document the reasons for believing this in the monitoring plan for the unit, and may immediately perform additional sampling. In such cases, a minimum of three additional samples must be obtained and analyzed, and the results of each sample analysis must meet the definition of natural gas.
(c) If several affected units are supplied by a common source of gaseous fuel, a single sampling result may be applied to all of the units and it is not necessary to obtain a separate sample for each unit, provided that the composition of the fuel is not altered by blending or mixing it with other gaseous fuel(s) when it is transported from the sampling location to the affected units. For the purposes of this paragraph, the term “other gaseous fuel(s)” excludes compounds such as mercaptans when they are added in trace quantities for safety reasons.
(d) If the results of fuel sampling and analysis under paragraph (a)(2), (a)(3), or (b) of this section show that the fuel does not qualify as natural gas, the owner or operator shall re-classify the fuel as “other gaseous fuel” and shall implement the procedures of section 2.3.3 of this appendix, within 180 days of the end of the quarter in which the disqualifying sample was taken. In addition, the owner or operator shall use Equation D-1h in this appendix to calculate a default SO2 emission rate for the fuel, based on the results of the sample analysis that exceeded 20 grains/100 scf of total sulfur, and shall use that default emission rate to report SO2 mass emissions under this part until section 2.3.3 of this appendix has been fully implemented.
(e) If a fuel qualifies as natural gas based on the specifications in a fuel contract or tariff sheet, no additional, on-going sampling of the fuel's total sulfur content is required, provided that the contract or tariff sheet is current, valid and representative of the fuel combusted in the unit. If the fuel qualifies as natural gas based on fuel sampling and analysis, the owner or operator shall sample the fuel for total sulfur content at least annually and when the fuel supply source changes. For the purposes of this paragraph, (e), sampling “annually” means that at least one sample is taken in each calendar year. The effective date of the annual total sulfur sampling requirement is January 1, 2003.
(f) On-going sampling of the GCV of the natural gas is required under section 2.3.4.2 of this appendix.
(g) For units that are required to monitor and report NOX mass emissions and heat input under subpart H of this part, but which are not affected units under the Acid Rain Program, the owner or operator is exempted from the requirements in paragraphs (a) and (e) of this section to document the total sulfur content of the natural gas.
2.3.3 SO2 Mass Emissions From Any Gaseous FuelThe owner or operator of a unit may determine SO2 mass emissions using this section for any gaseous fuel (including fuels such as refinery gas, landfill gas, digester gas, coke oven gas, blast furnace gas, coal-derived gas, producer gas or any other gas which may have a variable sulfur content).
2.3.3.1 Sulfur Content Determination2.3.3.1.1 Analyze the total sulfur content of the gaseous fuel in grains/100 scf, at the frequency specified in Table D-5 of this appendix. That is: for fuel delivered in discrete shipments or lots, sample each shipment or lot. For fuel transmitted by pipeline, sample hourly unless a demonstration is provided under section 2.3.6 of this appendix showing that the gaseous fuel qualifies for less frequent (i.e., daily or annual) sampling. If daily sampling is required, determine the sulfur content using either manual sampling or a gas chromatograph. If hourly sampling is required, determine the sulfur content using a gas chromatograph. For units that are required to monitor and report NOX mass emissions and heat input under subpart H of this part, but which are not affected units under the Acid Rain Program, the owner or operator is exempted from the requirements of this section to document the total sulfur content of the gaseous fuel.
2.3.3.1.2 Use one of the following methods when using manual sampling (as applicable to the type of gas combusted) to determine the sulfur content of the fuel: ASTM D1072-06, Standard Test Method for Total Sulfur in Fuel Gases by Combustion and Barium Chloride Titration, ASTM D4468-85 (Reapproved 2006), Standard Test Method for Total Sulfur in Gaseous Fuels by Hydrogenolysis and Rateometric Colorimetry, ASTM D5504-01, Standard Test Method for Determination of Sulfur Compounds in Natural Gas and Gaseous Fuels by Gas Chromatography and Chemiluminescence, ASTM D6667-04, Standard Test Method for Determination of Total Volatile Sulfur in Gaseous Hydrocarbons and Liquefied Petroleum Gases by Ultraviolet Fluorescence, or ASTM D3246-96, Standard Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Gas by Oxidative Microcoulometry, (all incorporated by reference under § 75.6 of this part). Alternatively, the gas samples may be analyzed for percent sulfur by any consensus standard method prescribed for the affected unit under part 60 of this chapter.
2.3.3.1.3 The sampling and analysis of daily manual samples may be performed by the owner or operator, an outside laboratory, or the gas supplier. If hourly sampling with a gas chromatograph is required, or a source chooses to use an online gas chromatograph to determine daily fuel sulfur content, the owner or operator shall develop and implement a program to quality assure the data from the gas chromatograph, in accordance with the manufacturer's recommended procedures. The quality assurance procedures shall be kept on-site, in a form suitable for inspection.
2.3.3.1.4 Results of all sample analyses must be available no later than thirty calendar days after the sample is taken.
2.3.3.2 SO2 Mass Emission RateCalculate the SO2 mass emission rate for the gaseous fuel, in lb/hr, using Equation D-4 or D-5 (as applicable) in section 3.3.1 of this appendix. Equation D-5 may only be used if a demonstration is performed under section 2.3.6 of this appendix, showing that the fuel qualifies to use a default SO2 emission rate to account for SO2 mass emissions under this part. Use the appropriate sulfur content or default SO2 emission rate in Equation D-4 or D-5, as specified in Table D-5 of this appendix. If the fuel qualifies to use Equation D-5, the default SO2 emission rate shall be calculated using Equation D-1h in section 2.3.2.1.1 of this appendix, replacing the words “natural gas” in the equation nomenclature with the words, “gaseous fuel”. In all cases, for reporting purposes, apply the results of the required periodic total sulfur samples in accordance with the provisions of section 2.3.7 of this appendix.
2.3.3.3 Hourly Heat Input RateCalculate the hourly heat input rate for combustion of the gaseous fuel, using the provisions in section 3.4.1 of this appendix. Use the measured fuel flow rate from section 2.1 of this appendix and the gross calorific value from section 2.3.4.3 of this appendix in the calculations.
2.3.4 Gross Calorific Values for Gaseous FuelsDetermine the GCV of each gaseous fuel at the frequency specified in this section, using one of the following methods: ASTM D1826-94 (Reapproved 1998), ASTM D3588-98, ASTM D4891-89 (Reapproved 2006), GPA Standard 2172-96, Calculation of Gross Heating Value, Relative Density and Compressibility Factor for Natural Gas Mixtures from Compositional Analysis, or GPA Standard 2261-00, Analysis for Natural Gas and Similar Gaseous Mixtures by Gas Chromatography (all incorporated by reference under § 75.6 of this part). Use the appropriate GCV value, as specified in section 2.3.4.1, 2.3.4.2, or 2.3.4.3 of this appendix, in the calculation of unit hourly heat input rates. Alternatively, the gas samples may be analyzed for heat content by any consensus standard method prescribed for the affected unit under part 60 of this chapter.
2.3.4.1 GCV of Pipeline Natural GasDetermine the GCV of fuel that is pipeline natural gas, as defined in § 72.2 of this chapter, at least once per calendar month. For GCV used in calculations use the specifications in Table D-5: either the value from the most recent monthly sample, the highest value specified in a contract or tariff sheet, or the highest value from the previous year. The fuel GCV value from the most recent monthly sample shall be used for any month in which that value is higher than a contract limit. If a unit combusts pipeline natural gas for less than 48 hours during a calendar month, the sampling and analysis requirement for GCV is waived for that calendar month. The preceding waiver is limited by the condition that at least one analysis for GCV must be performed for each quarter the unit operates for any amount of time. If multiple GCV samples are taken and analyzed in a particular month, the GCV values from all samples shall be averaged arithmetically to obtain the monthly GCV. Then, apply the monthly average GCV value as described in paragraph (c) in section 2.3.7 of this appendix.
2.3.4.2 GCV of Natural GasDetermine the GCV of fuel that is natural gas, as defined in § 72.2 of this chapter, on a monthly basis, in the same manner as described for pipeline natural gas in section 2.3.4.1 of this appendix.
2.3.4.3 GCV of Other Gaseous FuelsFor gaseous fuels other than natural gas or pipeline natural gas, determine the GCV as specified in section 2.3.4.3.1, 2.3.4.3.2 or 2.3.4.3.3, as applicable. For reporting purposes, apply the results of the required periodic GCV samples in accordance with the provisions of section 2.3.7 of this appendix.
2.3.4.3.1 For a gaseous fuel that is delivered in discrete shipments or lots, determine the GCV for each shipment or lot. The determination may be made by sampling each delivery or by sampling the supply tank after each delivery. For sampling of each delivery, use the highest GCV in the previous year's samples. For sampling from the tank after each delivery, use either the most recent GCV sample, the maximum GCV specified in the fuel contract or tariff sheet, or the highest GCV from the previous year's samples.
2.3.4.3.2 For any gaseous fuel that does not qualify as pipeline natural gas or natural gas, which is not delivered in shipments or lots, and for which the owner or operator performs the 720 hour test under section 2.3.5 of this appendix, if the results of the test demonstrate that the gaseous fuel has a low GCV variability, determine the GCV at least monthly (as described in section 2.3.4.1 of this appendix). In calculations of hourly heat input for a unit, use either the most recent monthly sample, the maximum GCV specified in the fuel contract or tariff sheet, or the highest fuel GCV from the previous year's samples.
2.3.4.3.3 For any other gaseous fuel, determine the GCV at least daily and use the actual fuel GCV in calculations of unit hourly heat input. If an online gas chromatograph or on-line calorimeter is used to determine fuel GCV each day, the owner or operator shall develop and implement a program to quality assure the data from the gas chromatograph or on-line calorimeter, in accordance with the manufacturer's recommended procedures. The quality assurance procedures shall be kept on-site, in a form suitable for inspection.
2.3.5 Demonstration of Fuel GCV Variability(a) This optional demonstration may be made for any fuel which does not qualify as pipeline natural gas or natural gas, and is not delivered only in shipments or lots. The demonstration data may be used to show that monthly sampling of the GCV of the gaseous fuel or blend is sufficient, in lieu of daily GCV sampling.
(b) To make this demonstration, proceed as follows. Provide a minimum of 720 hours of data, indicating the GCV of the gaseous fuel or blend (in Btu/100 scf). The demonstration data shall be obtained using either: hourly sampling and analysis using the methods in section 2.3.4 to determine GCV of the fuel; an on-line gas chromatograph capable of determining fuel GCV on an hourly basis; or an on-line calorimeter. For gaseous fuel produced by a variable process, the data shall be representative of and include all process operating conditions including seasonal and yearly variations in process which may affect fuel GCV.
(c) The data shall be reduced to hourly averages. The mean GCV value and the standard deviation from the mean shall be calculated from the hourly averages. Specifically, the gaseous fuel is considered to have a low GCV variability, and monthly gas sampling for GCV may be used, if the mean value of the GCV multiplied by 1.075 is greater than the sum of the mean value and one standard deviation. If the gaseous fuel or blend does not meet this requirement, then daily fuel sampling and analysis for GCV, using manual sampling, a gas chromatograph or an on-line calorimeter is required.
2.3.6 Demonstration of Fuel Sulfur Variability(a) This demonstration may be made for any fuel which does not qualify as pipeline natural gas or natural gas, and is not delivered only in shipments or lots. The results of the demonstration may be used to show that daily sampling for sulfur in the fuel is sufficient, rather than hourly sampling. The procedures in this section may also be used to demonstrate that a particular gaseous fuel qualifies to use a default SO2 emission rate (calculated using Equation D-1h in section 2.3.2.1.1 of this appendix) for the purpose of reporting hourly SO2 mass emissions under this part. To make this demonstration, proceed as follows. Provide a minimum of 720 hours of data, indicating the total sulfur content of the gaseous fuel (in gr/100 scf). The demonstration data shall be obtained using either manual hourly sampling or an on-line gas chromatograph (GC) capable of determining fuel total sulfur content on an hourly basis. For gaseous fuel produced by a variable process, the data shall be representative of all process operating conditions including seasonal or annual variations which may affect fuel sulfur content.
(b) If the data are collected with an on-line GC, reduce the data to hourly average values of the total sulfur content of the fuel. If manual hourly sampling is used, the results of each hourly sample analysis shall be the total sulfur value for that hour. Express all hourly average values of total sulfur content in units of grains/100 scf. Use all of the hourly average values of total sulfur content in grains/100 scf to calculate the mean value and the standard deviation. Also determine the 90th percentile and maximum hourly values of the total sulfur content for the data set. If the standard deviation of the hourly values from the mean does not exceed 5.0 grains/100 scf, the fuel has a low sulfur variability. If the standard deviation exceeds 5.0 grains/100 scf, the fuel has a high sulfur variability. Based on the results of this determination, establish the required sampling frequency and SO2 mass emissions methodology for the gaseous fuel, as follows:
(1) If the gaseous fuel has a low sulfur variability (irrespective of the total sulfur content), the owner or operator may either perform daily sampling of the fuel's total sulfur content using manual sampling or a GC, or may report hourly SO2 mass emissions data using a default SO2 emission rate calculated by substituting the 90th percentile value of the total sulfur content in Equation D-1h.
(2) If the gaseous fuel has a high sulfur variability, but the maximum hourly value of the total sulfur content does not exceed 20 grains/100 scf, the owner or operator may either perform hourly sampling of the fuel's total sulfur content using an on-line GC, or may report hourly SO2 mass emissions data using a default SO2 emission rate calculated by substituting the maximum value of the total sulfur content in Equation D-1h.
(3) If the gaseous fuel has a high sulfur variability and the maximum hourly value of the total sulfur content exceeds 20 grains/100 scf, the owner or operator shall perform hourly sampling of the fuel's total sulfur content, using an on-line GC.
(4) Any gaseous fuel under paragraph (b)(1) or (b)(2) of this section, for which the owner or operator elects to use a default SO2 emission rate for reporting purposes is subject to the annual total sulfur sampling requirement under section 2.3.2.4(e) of this appendix.
2.3.7 Application of Fuel Sampling ResultsFor reporting purposes, apply the results of the required periodic fuel samples described in Tables D-4 and D-5 of this appendix as follows. Use Equation D-1h to recalculate the SO2 emission rate, as necessary.
(a) For daily samples of total sulfur content or GCV:
(1) If the actual value is to be used in the calculations, apply the results of each daily sample to all hours in the day on which the sample is taken; or
(2) If the highest value in the previous 30 daily samples is to be used in the calculations, apply that value to all hours in the current day. If, for a particular unit, fewer than 30 daily samples have been collected, use the highest value from all available samples until 30 days of historical sampling results have been obtained.
(b) For annual samples of total sulfur content:
(1) For pipeline natural gas, use the results of annual sample analyses in the calculations only if the results exceed 0.5 grains/100 scf. In that case, if the fuel still qualifies as natural gas, follow the procedures in paragraph (b)(2) of this section. If the fuel does not qualify as natural gas, the owner or operator shall implement the procedures in section 2.3.3 of this appendix, in the time frame specified in sections 2.3.1.4(d) and 2.3.2.4(d) of this appendix;
(2) For natural gas, if only one sample is taken, apply the results beginning at the date on which the sample was taken. If multiple samples are taken and averaged, apply the results beginning at the date on which the last sample used in the annual assessment was taken;
(3) For other gaseous fuels with an annual sampling requirement under section 2.3.6(b)(4) of this appendix, use the sample results in the calculations only if the results exceed the 90th percentile value or maximum value (as applicable) from the 720-hour demonstration of fuel sulfur content and variability under section 2.3.6 of this appendix.
(c) For monthly samples of the fuel GCV:
(1) If the actual monthly value is to be used in the calculations and only one sample is taken, apply the results starting from the date on which the sample was taken. If multiple samples are taken and averaged, apply the monthly average GCV value to the entire month; or
(2) If an assumed value (contract maximum or highest value from previous year's samples) is to be used in the calculations, apply the assumed value to all hours in each month of the quarter unless a higher value is obtained in a monthly GCV sample (or, if multiple samples are taken and averaged, if the monthly average exceeds the assumed value). In that case, if only one monthly sample is taken, use the sampled value, starting from the date on which the sample was taken. If multiple samples are taken and averaged, use the average value for the entire month in which the assumed value was exceeded. Consider the sample (or, if applicable, monthly average) results to be the new assumed value. Continue using the new assumed value unless and until one of the following occurs (as applicable to the reporting option selected): The assumed value is superseded by a higher value from a subsequent monthly sample (or by a higher monthly average); or the assumed value is superseded by a new contract in which case the new contract value becomes the assumed value at the time the fuel specified under the new contract begins to be combusted in the unit; or both the calendar year in which the new sampled value (or monthly average) exceeded the assumed value and the subsequent calendar year have elapsed.
(d) For samples of gaseous fuel delivered in shipments or lots:
(1) If the actual value for the most recent shipment is to be used in the calculations, apply the results of the most recent sample, from the date on which the sample was taken until the date on which the next sample is taken; or
(2) If an assumed value (contract maximum or highest value from previous year's samples) is to be used in the calculations, apply the assumed value unless a higher value is obtained in a sample of a shipment. In that case, use the sampled value, starting from the date on which the sample was taken. Consider the sample results to be the new assumed value. Continue using the new assumed value unless and until: it is superseded by a higher value from a sample of a subsequent shipment; or (if applicable) it is superseded by a new contract in which case the new contract value becomes the assumed value at the time the fuel specified under the new contract begins to be combusted in the unit; or (if applicable) both the calendar year in which the sampled value exceeded the assumed value and the subsequent calendar year have elapsed.
(e) When the owner or operator elects to use assumed values in the calculations, the results of periodic samples of sulfur content and GCV which show that the assumed value has not been exceeded need not be reported. Keep these sample results on file, in a format suitable for inspection.
(f) Notwithstanding the requirements of paragraphs (b) through (d) of this section, in cases where the sample results are provided to the owner or operator by the supplier of the fuel, the owner or operator shall begin using the sampling results on the date of receipt of those results, rather than on the date that the sample was taken.
2.4 Missing Data Procedures.When data from the procedures of this part are not available, provide substitute data using the following procedures.
2.4.1 Missing Data for Oil and Gas SamplesWhen fuel sulfur content, gross calorific value or, when necessary, density data are missing or invalid for an oil or gas sample taken according to the procedures in section 2.2.3, 2.2.4.1, 2.2.4.2, 2.2.4.3, 2.2.5, 2.2.6, 2.2.7, 2.3.3.1.2, or 2.3.4 of this appendix, then substitute the maximum potential sulfur content, density, or gross calorific value of that fuel from Table D-6 of this appendix. Except for the annual samples of fuel sulfur content required under sections 2.3.1.4(e), 2.3.2.4(e) and 2.3.6(b)(5) of this appendix, the missing data values in Table D-6 shall be reported whenever the results of a required sample of sulfur content, GCV or density is missing or invalid in the current calendar year, irrespective of which reporting option is selected (i.e., actual value, contract value or highest value from the previous year). For the annual samples of fuel sulfur content required under sections 2.3.1.4(e), 2.3.2.4(e) and 2.3.6(b)(5) of this appendix, if a valid annual sample has not been obtained by the end of a particular calendar year, the appropriate missing data value in Table D-6 shall be reported, beginning with the first unit operating hour in the next calendar year. The substitute data value(s) shall be used until the next valid sample for the missing parameter(s) is obtained. Note that only actual sample results shall be used to determine the “highest value from the previous year” when that reporting option is used; missing data values shall not be used in the determination.
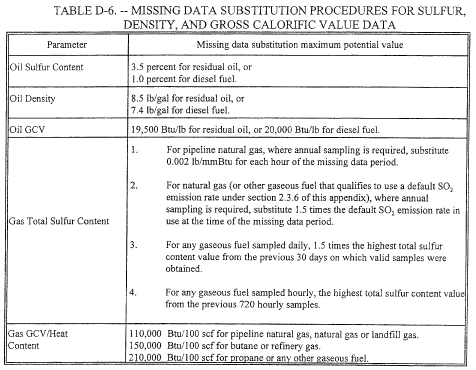
2.4.2 Missing Data Procedures for Fuel Flow Rate
Whenever data are missing from any primary fuel flowmeter system (as defined in § 72.2 of this chapter) and there is no backup system available to record the fuel flow rate, use the procedures in sections 2.4.2.2 and 2.4.2.3 of this appendix to account for the flow rate of fuel combusted at the unit for each hour during the missing data period. Alternatively, for a fuel flowmeter system used to measure the fuel combusted by a peaking unit, the simplified fuel flow missing data procedure in section 2.4.2.1 of this appendix may be used. Before using the procedures in sections 2.4.2.2 and 2.4.2.3 of this appendix, establish load ranges for the unit using the procedures of section 2 in appendix C to this part, except for units that do not produce electrical output (i.e., megawatts) or thermal output (e.g., klb of steam per hour). The owner or operator of a unit that does not produce electrical or thermal output shall either perform missing data substitution without segregating the fuel flow rate data into bins, or may petition the Administrator under § 75.66 for permission to segregate the data into operational bins. When load ranges are used for fuel flow rate missing data purposes, separate, fuel-specific databases shall be created and maintained. A database shall be kept for each type of fuel combusted in the unit, for the hours in which the fuel is combusted alone in the unit. An additional database shall be kept for each type of fuel, for the hours in which it is co-fired with any other type(s) of fuel(s).
2.4.2.1 Simplified Fuel Flow Rate Missing Data Procedure for Peaking UnitsIf no fuel flow rate data are available for a fuel flowmeter system installed on a peaking unit (as defined in § 72.2 of this chapter), then substitute for each hour of missing data using the maximum potential fuel flow rate. The maximum potential fuel flow rate is the lesser of the following:
(a) The maximum fuel flow rate the unit is capable of combusting or
(b) The maximum flow rate that the fuel flowmeter can measure (i.e., the upper range value of the flowmeter).
2.4.2.2 Standard Missing Data Procedures - Single Fuel HoursFor missing data periods that occur when only one type of fuel is being combusted, provide substitute data for each hour in the missing data period as follows.
2.4.2.2.1 If load-based missing data procedures are used, substitute the arithmetic average of the hourly fuel flow rate(s) measured and recorded by a certified fuel flowmeter system at the corresponding operating unit load range during the previous 720 operating hours in which the unit combusted only that same fuel. If no fuel flow rate data are available at the corresponding load range, use data from the next higher load range, if such data are available. If no quality-assured fuel flow rate data are available at either the corresponding load range or a higher load range, substitute the maximum potential fuel flow rate (as defined in section 2.4.2.1 of this appendix) for each hour of the missing data period.
2.4.2.2.2 For units that do not produce electrical or thermal output and therefore cannot use load-based missing data procedures, provide substitute data for each hour of the missing data period as follows. Substitute the arithmetic average of the hourly fuel flow rates measured and recorded by a certified fuel flowmeter system during the previous 720 operating hours in which the unit combusted only that same fuel. If no quality-assured fuel flow rate data are available, substitute the maximum potential fuel flow rate (as defined in section 2.4.2.1 of this appendix) for each hour of the missing data period.
2.4.2.3 Standard Missing Data Procedures - Multiple Fuel HoursFor missing data periods that occur when two or more different types of fuel are being co-fired, provide substitute fuel flow rate data for each hour of the missing data period as follows.
2.4.2.3.1 If load-based missing data procedures are used, substitute the maximum hourly fuel flow rate measured and recorded by a certified fuel flowmeter system at the corresponding load range during the previous 720 operating hours when the fuel for which the flow rate data are missing was co-fired with any other type of fuel. If no such quality-assured fuel flow rate data are available at the corresponding load range, use data from the next higher load range (if available). If no quality-assured fuel flow rate data are available for co-fired hours, either at the corresponding load range or a higher load range, substitute the maximum potential fuel flow rate (as defined in section 2.4.2.1 of this appendix) for each hour of the missing data period.
2.4.2.3.2 For units that do not produce electrical or thermal output and therefore cannot use load-based missing data procedures, provide substitute fuel flow rate data for each hour of the missing data period as follows. Substitute the maximum hourly fuel flow rate measured and recorded by a certified fuel flowmeter system during the previous 720 operating hours in which the fuel for which the flow rate data are missing was co-fired with any other type of fuel. If no quality-assured fuel flow rate data for co-fired hours are available, substitute the maximum potential fuel flow rate (as defined in section 2.4.2.1 of this appendix) for each hour of the missing data period.
2.4.2.3.3 If, during an hour in which different types of fuel are co-fired, quality-assured fuel flow rate data are missing for two or more of the fuels being combusted, apply the procedures in section 2.4.2.3.1 or 2.4.2.3.2 of this appendix (as applicable) separately for each type of fuel.
2.4.2.3.4 If the missing data substitution required in section 2.4.2.3.1 or 2.4.2.3.2 causes the reported hourly heat input rate based on the combined fuel usage to exceed the maximum rated hourly heat input of the unit, adjust the substitute fuel flow rate value(s) so that the reported heat input rate equals the unit's maximum rated hourly heat input. Manual entry of the adjusted substitute data values is permitted.
2.4.3. In any case where the missing data provisions of this section require substitution of data measured and recorded more than three years (26,280 clock hours) prior to the date and time of the missing data period, use three years (26,280 clock hours) in place of the prescribed lookback period. In addition, for a new or newly-affected unit, until 720 hours of quality-assured fuel flowmeter data are available for the lookback periods described in sections 2.4.2.2 and 2.4.2.3 of this appendix, use all of the available fuel flowmeter data to determine the appropriate substitute data values.
3. CalculationsCalculate hourly SO2 mass emission rate from combustion of oil fuel using the procedures in section 3.1 of this appendix. Calculate hourly SO2 mass emission rate from combustion of gaseous fuel using the procedures in section 3.3 of this appendix. (Note: the SO2 mass emission rates in sections 3.1 and 3.3 are calculated such that the rate, when multiplied by unit operating time, yields the hourly SO2 mass emissions for a particular fuel for the unit.) Calculate hourly heat input rate for both oil and gaseous fuels using the procedures in section 3.4 of this appendix. Calculate total SO2 mass emissions and heat input for each hour, each quarter and the year to date using the procedures under section 3.5 of this appendix. Where an oil flowmeter records volumetric flow rate, use the calculation procedures in section 3.2 of this appendix to calculate the mass flow rate of oil.
3.1 SO2 Mass Emission Rate Calculation for Oil3.1.1 Use Equation D-2 to calculate SO2 mass emission rate per hour (lb/hr):
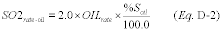 Where:
SO2rate-oil = Hourly mass emission rate of SO2 emitted from
combustion of oil, lb/hr. OILrate = Mass rate of oil consumed per
hr during combustion, lb/hr. %Soil = Percentage of sulfur by weight
in the oil. 2.0 = Ratio of lb SO 2/lb S.
Where:
SO2rate-oil = Hourly mass emission rate of SO2 emitted from
combustion of oil, lb/hr. OILrate = Mass rate of oil consumed per
hr during combustion, lb/hr. %Soil = Percentage of sulfur by weight
in the oil. 2.0 = Ratio of lb SO 2/lb S.
3.1.2 Record the SO2 mass emission rate from oil for each hour that oil is combusted.
3.2 Mass Flow Rate Calculation for Volumetric Oil Flowmeters3.2.1 Where the oil flowmeter records volumetric flow rate rather than mass flow rate, calculate and record the oil mass flow rate for each hourly period using hourly oil flow rate measurements and the density or specific gravity of the oil sample.
3.2.2 Convert density, specific gravity, or API gravity of the oil sample to density of the oil sample at the sampling location's temperature using ASTM D1250-07, Standard Guide for Use of the Petroleum Measurement Tables (incorporated by reference under (§ 75.6 of this part).
3.2.3 Where density of the oil is determined by the applicable ASTM procedures from section 2.2.6 of this appendix, use Equation D-3 to calculate the rate of the mass of oil consumed (in lb/hr):
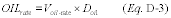 Where:
OILrate = Mass rate of oil consumed per hr, lb/hr. Voil-rate =
Volume rate of oil consumed per hr, measured in scf/hr, gal/hr,
barrels/hr, or m 3/hr. Doil = Density of oil, measured in lb/scf,
lb/gal, lb/barrel, or lb/m 3. 3.3 SO2 Mass Emission Rate
Calculation for Gaseous Fuels
Where:
OILrate = Mass rate of oil consumed per hr, lb/hr. Voil-rate =
Volume rate of oil consumed per hr, measured in scf/hr, gal/hr,
barrels/hr, or m 3/hr. Doil = Density of oil, measured in lb/scf,
lb/gal, lb/barrel, or lb/m 3. 3.3 SO2 Mass Emission Rate
Calculation for Gaseous Fuels
3.3.1 Use Equation D-4 to calculate the SO2 mass emission rate when using the optional gas sampling and analysis procedures in sections 2.3.1 and 2.3.2 of this appendix, or the required gas sampling and analysis procedures in section 2.3.3 of this appendix. Total sulfur content of a fuel must be determined using the procedures of 2.3.3.1.2 of this appendix:
Where: SO2rate-gas = Hourly mass rate of SO2 emitted due to combustion of gaseous fuel, lb/hr. GASrate = Hourly metered flow rate of gaseous fuel combusted, 100 scf/hr. Sgas = Sulfur content of gaseous fuel, in grain/100 scf. 2.0 = Ratio of lb SO2/lb S. 7000 = Conversion of grains/100 scf to lb/100 scf.3.3.2 Use Equation D-5 to calculate the SO2 mass emission rate when using a default emission rate from section 2.3.1.1 or 2.3.2.1.1 of this appendix:
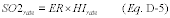 where:
SO2rate = Hourly mass emission rate of SO2 from combustion of a
gaseous fuel, lb/hr. ER = SO2 emission rate from section 2.3.1.1 or
2.3.2.1.1, of this appendix, lb/mmBtu. HIrate = Hourly heat input
rate of a gaseous fuel, calculated using procedures in section
3.4.1 of this appendix, in mmBtu/hr.
where:
SO2rate = Hourly mass emission rate of SO2 from combustion of a
gaseous fuel, lb/hr. ER = SO2 emission rate from section 2.3.1.1 or
2.3.2.1.1, of this appendix, lb/mmBtu. HIrate = Hourly heat input
rate of a gaseous fuel, calculated using procedures in section
3.4.1 of this appendix, in mmBtu/hr.
3.3.3 Record the SO2 mass emission rate for each hour when the unit combusts a gaseous fuel.
3.4 Calculation of Heat Input Rate 3.4.1 Heat Input Rate for Gaseous Fuels(a) Determine total hourly gas flow or average hourly gas flow rate with a fuel flowmeter in accordance with the requirements of section 2.1 of this appendix and the fuel GCV in accordance with the requirements of section 2.3.4 of this appendix. If necessary perform the 720-hour test under section 2.3.5 to determine the appropriate fuel GCV sampling frequency.
(b) Then, use Equation D-6 to calculate heat input rate from gaseous fuels for each hour.
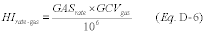 Where:
HIrate-gas = Hourly heat input rate from combustion of the gaseous
fuel, mmBtu/hr. GASrate = Average volumetric flow rate of fuel, for
the portion of the hour in which the unit operated, 100 scf/hr.
GCVgas = Gross calorific value of gaseous fuel, Btu/100 scf. 10 6 =
Conversion of Btu to mmBtu.
Where:
HIrate-gas = Hourly heat input rate from combustion of the gaseous
fuel, mmBtu/hr. GASrate = Average volumetric flow rate of fuel, for
the portion of the hour in which the unit operated, 100 scf/hr.
GCVgas = Gross calorific value of gaseous fuel, Btu/100 scf. 10 6 =
Conversion of Btu to mmBtu.
(c) Note that when fuel flow is measured on an hourly totalized basis (e.g. a fuel flowmeter reports totalized fuel flow for each hour), before Equation D-6 can be used, the total hourly fuel usage must be converted from units of 100 scf to units of 100 scf/hr using Equation D-7:
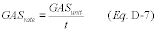 Where:
GASrate = Average volumetric flow rate of fuel for the portion of
the hour in which the unit operated, 100 scf/hr. GASunit = Total
fuel combusted during the hour, 100 scf. t = Unit operating time,
hour or fraction of an hour (in equal increments that can range
from one hundredth to one quarter of an hour, at the option of the
owner or operator). 3.4.2 Heat Input Rate From the Combustion of
Oil
Where:
GASrate = Average volumetric flow rate of fuel for the portion of
the hour in which the unit operated, 100 scf/hr. GASunit = Total
fuel combusted during the hour, 100 scf. t = Unit operating time,
hour or fraction of an hour (in equal increments that can range
from one hundredth to one quarter of an hour, at the option of the
owner or operator). 3.4.2 Heat Input Rate From the Combustion of
Oil
(a) Determine total hourly oil flow or average hourly oil flow rate with a fuel flowmeter, in accordance with the requirements of section 2.1 of this appendix. Determine oil GCV according to the requirements of section 2.2 of this appendix.
Then, use Equation D-8 to calculate hourly heat input rate from oil for each hour:
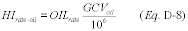 Where:
HIrate-oil = Hourly heat input rate from combustion of oil,
mmBtu/hr. OILrate = Mass rate of oil consumed per hour, as
determined using procedures in section 3.2.3 of this appendix, in
lb/hr, tons/hr, or kg/hr. GCVoil = Gross calorific value of oil,
Btu/lb, Btu/ton, or Btu/kg. 10 6 = Conversion of Btu to mmBtu.
Where:
HIrate-oil = Hourly heat input rate from combustion of oil,
mmBtu/hr. OILrate = Mass rate of oil consumed per hour, as
determined using procedures in section 3.2.3 of this appendix, in
lb/hr, tons/hr, or kg/hr. GCVoil = Gross calorific value of oil,
Btu/lb, Btu/ton, or Btu/kg. 10 6 = Conversion of Btu to mmBtu.
(b) Note that when fuel flow is measured on an hourly totalized basis (e.g., a fuel flowmeter reports totalized fuel flow for each hour), before equation D-8 can be used, the total hourly fuel usage must be converted from units of lb to units of lb/hr, using equation D-9:
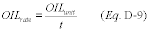 Where:
OILrate = Average fuel flow rate for the portion of the hour which
the unit operated in lb/hr. OILunit = Total fuel combusted during
the hour, lb. t = Unit operating time, hour or fraction of an hour
(in equal increments that can range from one hundredth to one
quarter of an hour, at the option of the owner or operator).
Where:
OILrate = Average fuel flow rate for the portion of the hour which
the unit operated in lb/hr. OILunit = Total fuel combusted during
the hour, lb. t = Unit operating time, hour or fraction of an hour
(in equal increments that can range from one hundredth to one
quarter of an hour, at the option of the owner or operator).
(c) For affected units that are not subject to an Acid Rain emissions limitation, but are regulated under a State or federal NOX mass emissions reduction program that adopts the requirements of subpart H of this part, the following alternative method may be used to determine the heat input rate from oil combustion, when the oil flowmeter measures the flow rate of oil volumetrically. In lieu of measuring the oil density and converting the volumetric oil flow rate to a mass flow rate, Equation D-8 may be applied on a volumetric basis. If this option is selected, express the terms OILrate and GCVoil in Equation D-8 in units of volume rather than mass. For example, the units of OILrate may be gal/hr and the units of GCVoil may be Btu/gal.
3.4.3 Apportioning Heat Input Rate to Multiple Units(a) Use the procedure in this section to apportion hourly heat input rate to two or more units using a single fuel flowmeter which supplies fuel to the units. The designated representative may also petition the Administrator under § 75.66 to use this apportionment procedure to calculate SO2 and CO2 mass emissions.
(b) Determine total hourly fuel flow or flow rate through the fuel flowmeter supplying gas or oil fuel to the units. Convert fuel flow rates to units of 100 scf for gaseous fuels or to lb for oil, using the procedures of this appendix. Apportion the fuel to each unit separately based on hourly output of the unit in MWe or 1000 lb of steam/hr (klb/hr) using Equation F-21a or F-21b in appendix F to this part, as applicable:
Equation D-10 [Reserved]
Equation D-11 [Reserved]
(c) Use the total apportioned fuel flow calculated from Equation F-21a or F-21b to calculate the hourly unit heat input rate, using Equations D-6 and D-7 (for gas) or Equations D-8 and D-9 (for oil).
3.5 Conversion of Hourly Rates to Hourly, Quarterly, and Year-to-Date Totals 3.5.1 Hourly SO2 Mass Emissions from the Combustion of all Fuels. Determine the total mass emissions for each hour from the combustion of all fuels using Equation D-12 (On and after January 1, 2009, determine the total mass emission rate (in lbs/hr) for each hour from the combustion of all fuels by dividing Equation D-12 by the actual unit operating time for the hour): Where: MSO2-hr = Total mass of SO2 emissions from all fuels combusted during the hour, lb. SO2 rate−I = SO2 mass emission rate for each type of gas or oil fuel combusted during the hour, lb/hr. ti = Time each gas or oil fuel was combusted for the hour (fuel usage time), fraction of an hour (in equal increments that can range from one hundredth to one quarter of an hour, at the option of the owner or operator). 3.5.2 Quarterly Total SO2 Mass EmissionsSum the hourly SO2 mass emissions in lb as determined from Equation D-12 for all hours in a quarter using Equation D-13:
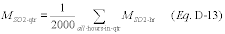 Where:
MSO2-qtr = Total mass of SO2 emissions from all fuels combusted
during the quarter, tons. MSO2-hr = Hourly SO2 mass emissions
determined using Equation D-12, lb. 2000= Conversion factor from lb
to tons. 3.5.3 Year to Date SO2 Mass Emissions
Where:
MSO2-qtr = Total mass of SO2 emissions from all fuels combusted
during the quarter, tons. MSO2-hr = Hourly SO2 mass emissions
determined using Equation D-12, lb. 2000= Conversion factor from lb
to tons. 3.5.3 Year to Date SO2 Mass Emissions
Calculate and record SO2 mass emissions in the year to date using Equation D-14:
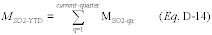 Where:
MSO2-YTD = Total SO2 mass emissions for the year to date, tons.
MSO2-qtr = Total SO2 mass emissions for the quarter, tons. 3.5.4
Hourly Total Heat Input Rate and Heat Input from the Combustion of
all Fuels
Where:
MSO2-YTD = Total SO2 mass emissions for the year to date, tons.
MSO2-qtr = Total SO2 mass emissions for the quarter, tons. 3.5.4
Hourly Total Heat Input Rate and Heat Input from the Combustion of
all Fuels
3.5.4.1 Determine the total heat input in mmBtu for each hour from the combustion of all fuels using Equation D-15:
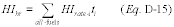 Where:
HIhr = Total heat input from all fuels combusted during the hour,
mmBtu. HIrate-i = Heat input rate for each type of gas or oil
combusted during the hour, mmBtu/hr. ti = Time each gas or oil fuel
was combusted for the hour (fuel usage time), fraction of an hour
(in equal increments that can range from one hundredth to one
quarter of an hour, at the option of the owner or operator).
Where:
HIhr = Total heat input from all fuels combusted during the hour,
mmBtu. HIrate-i = Heat input rate for each type of gas or oil
combusted during the hour, mmBtu/hr. ti = Time each gas or oil fuel
was combusted for the hour (fuel usage time), fraction of an hour
(in equal increments that can range from one hundredth to one
quarter of an hour, at the option of the owner or operator).
3.5.4.2 For reporting purposes, determine the heat input rate to each unit, in mmBtu/hr, for each hour from the combustion of all fuels using Equation D-15a:
Where: HIrate-hr = Total heat input rate from all fuels combusted during the hour, mmBtu/hr. HIrate-i = Heat input rate for each type of gas or oil combusted during the hour, mmBtu/hr. ti = Time each gas or oil fuel was combusted for the hour (fuel usage time), fraction of an hour (in equal increments that can range from one hundredth to one quarter of an hour, at the option of the owner or operator). tu = Unit operating time 3.5.5 Quarterly Heat InputSum the hourly heat input values determined from equation D-15 for all hours in a quarter using Equation D-16:
Where: HIqtr = Total heat input from all fuels combusted during the quarter, mmBtu. HIqtr = Hourly heat input determined using Equation D-15, mmBtu. 3.5.6 Year-to-Date Heat InputCalculate and record the total heat input in the year to date using Equation D-17.
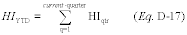 HIYTD =
Total heat input for the year to date, mmBtu. HIqtr = Total heat
input for the quarter, mmBtu. 3.6 Records and Reports
HIYTD =
Total heat input for the year to date, mmBtu. HIqtr = Total heat
input for the quarter, mmBtu. 3.6 Records and Reports
Calculate and record quarterly and cumulative SO2 mass emissions and heat input for each calendar quarter using the procedures and equations of section 3.5 of this appendix. Calculate and record SO2 emissions and heat input data using a data acquisition and handling system. Report these data in a standard electronic format specified by the Administrator.
[58 FR 3701, Jan. 11, 1993, as amended at 60 FR 26548, 26551, May 17, 1995; 61 FR 25585, May 22, 1996; 61 FR 59166, Nov. 20, 1996; 63 FR 57513, Oct. 27, 1998; 64 FR 28652, May 26, 1999; 64 FR 37582, July 12, 1999; 67 FR 40460, 40472, June 12, 2002; 67 FR 53505, Aug. 16, 2002; 73 FR 4369, Jan. 24, 2008; 76 FR 17324, Mar. 28, 2011; 76 FR 20536, Apr. 13, 2011; 77 FR 2460, Jan. 18, 2012] Editorial Note:At 67 FR 53505, Aug. 16, 2002, section 2.4.1 Table D-6 was amended. However, this table is a photographed graphic and the amendments could not be incorporated.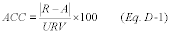 Where:
ACC = Flowmeter accuracy at a particular load level, as a
percentage of the upper range value. R = Average of the three flow
measurements of the reference flowmeter. A = Average of the three
measurements of the flowmeter being tested. URV = Upper range value
of fuel flowmeter being tested (i.e. maximum measurable flow).
Where:
ACC = Flowmeter accuracy at a particular load level, as a
percentage of the upper range value. R = Average of the three flow
measurements of the reference flowmeter. A = Average of the three
measurements of the flowmeter being tested. URV = Upper range value
of fuel flowmeter being tested (i.e. maximum measurable flow).