Appendix D to Part 1194 - Electronic and Information Technology Accessibility Standards as Originally Published on December 21, 2000
36:3.0.9.1.10.0.5.3.19 : Appendix D
Appendix D to Part 1194 - Electronic and Information Technology
Accessibility Standards as Originally Published on December 21,
2000
§ D1194.1 Purpose.
The purpose of this part is to implement section 508 of the
Rehabilitation Act of 1973, as amended (29 U.S.C. 794d). Section
508 requires that when Federal agencies develop, procure, maintain,
or use electronic and information technology, Federal employees
with disabilities have access to and use of information and data
that is comparable to the access and use by Federal employees who
are not individuals with disabilities, unless an undue burden would
be imposed on the agency. Section 508 also requires that
individuals with disabilities, who are members of the public
seeking information or services from a Federal agency, have access
to and use of information and data that is comparable to that
provided to the public who are not individuals with disabilities,
unless an undue burden would be imposed on the agency.
[65 FR 80523, Dec. 21, 2000. Redesignated and amended at 82 FR
5832, Jan. 18, 2017]
§ D1194.2 Application.
(a) Products covered by this part shall comply with all
applicable provisions of this part. When developing, procuring,
maintaining, or using electronic and information technology, each
agency shall ensure that the products comply with the applicable
provisions of this part, unless an undue burden would be imposed on
the agency.
(1) When compliance with the provisions of this part imposes an
undue burden, agencies shall provide individuals with disabilities
with the information and data involved by an alternative means of
access that allows the individual to use the information and
data.
(2) When procuring a product, if an agency determines that
compliance with any provision of this part imposes an undue burden,
the documentation by the agency supporting the procurement shall
explain why, and to what extent, compliance with each such
provision creates an undue burden.
(b) When procuring a product, each agency shall procure products
which comply with the provisions in this part when such products
are available in the commercial marketplace or when such products
are developed in response to a Government solicitation. Agencies
cannot claim a product as a whole is nt commercially available
because no product in the marketplace meets all the standards. If
products are commercially available that meet some but not all of
the standards, the agency must procure the product that best meets
the standards.
(c) Except as provided by § 1194.3(b), this part applies to
electronic and information technology developed, procured,
maintained, or used by agencies directly or used by a contractor
under a contract with an agency which requires the use of such
product, or requires the use, to a significant extent, of such
product in the performance of a service or the furnishing of a
product.
[65 FR 80523, Dec. 21, 2000. Redesignated and amended at 82 FR
5832, Jan. 18, 2017]
§ D1194.3 General exceptions.
(a) This part does not apply to any electronic and information
technology operated by agencies, the function, operation, or use of
which involves intelligence activities, cryptologic activities
related to national security, command and control of military
forces, equipment that is an integral part of a weapon or weapons
system, or systems which are critical to the direct fulfillment of
military or intelligence missions. Systems which are critical to
the direct fulfillment of military or intelligence missions do not
include a system that is to be used for routine administrative and
business applications (including payroll, finance, logistics, and
personnel management applications).
(b) This part does not apply to electronic and information
technology that is acquired by a contractor incidental to a
contract.
(c) Except as required to comply with the provisions in this
part, this part does not require the installation of specific
accessibility-related software or the attachment of an assistive
technology device at a workstation of a Federal employee who is not
an individual with a disability.
(d) When agencies provide access to the public to information or
data through electronic and information technology, agencies are
not required to make products owned by the agency available for
access and use by individuals with disabilities at a location other
than that where the electronic and information technology is
provided to the public, or to purchase products for access and use
by individuals with disabilities at a location other than that
where the electronic and information technology is provided to the
public.
(e) This part shall not be construed to require a fundamental
alteration in the nature of a product or its components.
(f) Products located in spaces frequented only by service
personnel for maintenance, repair, or occasional monitoring of
equipment are not required to comply with this part.
[65 FR 80523, Dec. 21, 2000. Redesignated and amended at 82 FR
5832, Jan. 18, 2017]
§ D1194.4 Definitions.
The following definitions apply to this part:
Agency. Any Federal department or agency, including the
United States Postal Service.
Alternate formats. Alternate formats usable by people
with disabilities may include, but are not limited to, Braille,
ASCII text, large print, recorded audio, and electronic formats
that comply with this part.
Alternate methods. Different means of providing
information, including product documentation, to people with
disabilities. Alternate methods may include, but are not limited
to, voice, fax, relay service, TTY, Internet posting, captioning,
text-to-speech synthesis, and audio description.
Assistive technology. Any item, piece of equipment, or
system, whether acquired commercially, modified, or customized,
that is commonly used to increase, maintain, or improve functional
capabilities of individuals with disabilities.
Electronic and information technology. Includes
information technology and any equipment or interconnected system
or subsystem of equipment, that is used in the creation,
conversion, or duplication of data or information. The term
electronic and information technology includes, but is not limited
to, telecommunications products (such as telephones), information
kiosks and transaction machines, World Wide Web sites, multimedia,
and office equipment such as copiers and fax machines. The term
does not include any equipment that contains embedded information
technology that is used as an integral part of the product, but the
principal function of which is not the acquisition, storage,
manipulation, management, movement, control, display, switching,
interchange, transmission, or reception of data or information. For
example, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning)
equipment such as thermostats or temperature control devices, and
medical equipment where information technology is integral to its
operation, are not information technology.
Information technology. Any equipment or interconnected
system or subsystem of equipment, that is used in the automatic
acquisition, storage, manipulation, management, movement, control,
display, switching, interchange, transmission, or reception of data
or information. The term information technology includes computers,
ancillary equipment, software, firmware and similar procedures,
services (including support services), and related resources.
Operable controls. A component of a product that requires
physical contact for normal operation. Operable controls include,
but are not limited to, mechanically operated controls, input and
output trays, card slots, keyboards, or keypads.
Product. Electronic and information technology.
Self Contained, Closed Products. Products that generally
have embedded software and are commonly designed in such a fashion
that a user cannot easily attach or install assistive technology.
These products include, but are not limited to, information kiosks
and information transaction machines, copiers, printers,
calculators, fax machines, and other similar types of products.
Telecommunications. The transmission, between or among
points specified by the user, of information of the user's
choosing, without change in the form or content of the information
as sent and received.
TTY. An abbreviation for teletypewriter. Machinery or
equipment that employs interactive text based communications
through the transmission of coded signals across the telephone
network. TTYs may include, for example, devices known as TDDs
(telecommunication display devices or telecommunication devices for
deaf persons) or computers with special modems. TTYs are also
called text telephones.
Undue burden. Undue burden means significant difficulty
or expense. In determining whether an action would result in an
undue burden, an agency shall consider all agency resources
available to the program or component for which the product is
being developed, procured, maintained, or used.
[65 FR 80523, Dec. 21, 2000. Redesignated and amended at 82 FR
5832, Jan. 18, 2017]
§ D1194.5 Equivalent facilitation.
Nothing in this part is intended to prevent the use of designs
or technologies as alternatives to those prescribed in this part
provided they result in substantially equivalent or greater access
to and use of a product for people with disabilities.
[65 FR 80523, Dec. 21, 2000. Redesignated and amended at 82 FR
5832, Jan. 18, 2017]
§§ D1194.6-D1194.20 [Reserved] §
D1194.21 Software applications and operating systems.
(a) When software is designed to run on a system that has a
keyboard, product functions shall be executable from a keyboard
where the function itself or the result of performing a function
can be discerned textually.
(b) Applications shall not disrupt or disable activated features
of other products that are identified as accessibility features,
where those features are developed and documented according to
industry standards. Applications also shall not disrupt or disable
activated features of any operating system that are identified as
accessibility features where the application programming interface
for those accessibility features has been documented by the
manufacturer of the operating system and is available to the
product developer.
(c) A well-defined on-screen indication of the current focus
shall be provided that moves among interactive interface elements
as the input focus changes. The focus shall be programmatically
exposed so that assistive technology can track focus and focus
changes.
(d) Sufficient information about a user interface element
including the identity, operation and state of the element shall be
available to assistive technology. When an image represents a
program element, the information conveyed by the image must also be
available in text.
(e) When bitmap images are used to identify controls, status
indicators, or other programmatic elements, the meaning assigned to
those images shall be consistent throughout an application's
performance.
(f) Textual information shall be provided through operating
system functions for displaying text. The minimum information that
shall be made available is text content, text input caret location,
and text attributes.
(g) Applications shall not override user selected contrast and
color selections and other individual display attributes.
(h) When animation is displayed, the information shall be
displayable in at least one non-animated presentation mode at the
option of the user.
(i) Color coding shall not be used as the only means of
conveying information, indicating an action, prompting a response,
or distinguishing a visual element.
(j) When a product permits a user to adjust color and contrast
settings, a variety of color selections capable of producing a
range of contrast levels shall be provided.
(k) Software shall not use flashing or blinking text, objects,
or other elements having a flash or blink frequency greater than 2
Hz and lower than 55 Hz.
(l) When electronic forms are used, the form shall allow people
using assistive technology to access the information, field
elements, and functionality required for completion and submission
of the form, including all directions and cues.
[65 FR 80523, Dec. 21, 2000. Redesignated and amended at 82 FR
5832, Jan. 18, 2017]
§ D1194.22 Web-based intranet and internet
information and applications.
(a) A text equivalent for every non-text element shall be
provided (e.g., via “alt”, “longdesc”, or in element content).
(b) Equivalent alternatives for any multimedia presentation
shall be synchronized with the presentation.
(c) Web pages shall be designed so that all information conveyed
with color is also available without color, for example from
context or markup.
(d) Documents shall be organized so they are readable without
requiring an associated style sheet.
(e) Redundant text links shall be provided for each active
region of a server-side image map.
(f) Client-side image maps shall be provided instead of
server-side image maps except where the regions cannot be defined
with an available geometric shape.
(g) Row and column headers shall be identified for data
tables.
(h) Markup shall be used to associate data cells and header
cells for data tables that have two or more logical levels of row
or column headers.
(i) Frames shall be titled with text that facilitates frame
identification and navigation.
(j) Pages shall be designed to avoid causing the screen to
flicker with a frequency greater than 2 Hz and lower than 55
Hz.
(k) A text-only page, with equivalent information or
functionality, shall be provided to make a web site comply with the
provisions of this part, when compliance cannot be accomplished in
any other way. The content of the text-only page shall be updated
whenever the primary page changes.
(l) When pages utilize scripting languages to display content,
or to create interface elements, the information provided by the
script shall be identified with functional text that can be read by
assistive technology.
(m) When a web page requires that an applet, plug-in or other
application be present on the client system to interpret page
content, the page must provide a link to a plug-in or applet that
complies with § 1194.21(a) through (l).
(n) When electronic forms are designed to be completed on-line,
the form shall allow people using assistive technology to access
the information, field elements, and functionality required for
completion and submission of the form, including all directions and
cues.
(o) A method shall be provided that permits users to skip
repetitive navigation links.
(p) When a timed response is required, the user shall be alerted
and given sufficient time to indicate more time is required.
Note to § D1194.22:
1. The Board interprets paragraphs (a) through (k) of this
section as consistent with the following priority 1 Checkpoints of
the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 1.0 (WCAG 1.0) (May 5,
1999) published by the Web Accessibility Initiative of the World
Wide Web Consortium:
Section 1194.22
paragraph |
WCAG 1.0 checkpoint |
| (a) |
1.1 |
| (b) |
1.4 |
| (c) |
2.1 |
| (d) |
6.1 |
| (e) |
1.2 |
| (f) |
9.1 |
| (g) |
5.1 |
| (h) |
5.2 |
| (i) |
12.1 |
| (j) |
7.1 |
| (k) |
11.4 |
2. Paragraphs (l), (m), (n), (o), and (p) of this section are
different from WCAG 1.0. Web pages that conform to WCAG 1.0, level
A (i.e., all priority 1 checkpoints) must also meet
paragraphs (l), (m), (n), (o), and (p) of this section to comply
with this section. WCAG 1.0 is available at
http://www.w3.org/TR/1999/WAI-WEBCONTENT-19990505.
[65 FR 80523, Dec. 21, 2000. Redesignated and amended at 82 FR
5832, Jan. 18, 2017]
§ D1194.23 Telecommunications products.
(a) Telecommunications products or systems which provide a
function allowing voice communication and which do not themselves
provide a TTY functionality shall provide a standard non-acoustic
connection point for TTYs. Microphones shall be capable of being
turned on and off to allow the user to intermix speech with TTY
use.
(b) Telecommunications products which include voice
communication functionality shall support all commonly used
cross-manufacturer non-proprietary standard TTY signal
protocols.
(c) Voice mail, auto-attendant, and interactive voice response
telecommunications systems shall be usable by TTY users with their
TTYs.
(d) Voice mail, messaging, auto-attendant, and interactive voice
response telecommunications systems that require a response from a
user within a time interval, shall give an alert when the time
interval is about to run out, and shall provide sufficient time for
the user to indicate more time is required.
(e) Where provided, caller identification and similar
telecommunications functions shall also be available for users of
TTYs, and for users who cannot see displays.
(f) For transmitted voice signals, telecommunications products
shall provide a gain adjustable up to a minimum of 20 dB. For
incremental volume control, at least one intermediate step of 12 dB
of gain shall be provided.
(g) If the telecommunications product allows a user to adjust
the receive volume, a function shall be provided to automatically
reset the volume to the default level after every use.
(h) Where a telecommunications product delivers output by an
audio transducer which is normally held up to the ear, a means for
effective magnetic wireless coupling to hearing technologies shall
be provided.
(i) Interference to hearing technologies (including hearing
aids, cochlear implants, and assistive listening devices) shall be
reduced to the lowest possible level that allows a user of hearing
technologies to utilize the telecommunications product.
(j) Products that transmit or conduct information or
communication, shall pass through cross-manufacturer,
non-proprietary, industry-standard codes, translation protocols,
formats or other information necessary to provide the information
or communication in a usable format. Technologies which use
encoding, signal compression, format transformation, or similar
techniques shall not remove information needed for access or shall
restore it upon delivery.
(k) Products which have mechanically operated controls or keys,
shall comply with the following:
(1) Controls and keys shall be tactilely discernible without
activating the controls or keys.
(2) Controls and keys shall be operable with one hand and shall
not require tight grasping, pinching, or twisting of the wrist. The
force required to activate controls and keys shall be 5 lbs. (22.2
N) maximum.
(3) If key repeat is supported, the delay before repeat shall be
adjustable to at least 2 seconds. Key repeat rate shall be
adjustable to 2 seconds per character.
(4) The status of all locking or toggle controls or keys shall
be visually discernible, and discernible either through touch or
sound.
[65 FR 80523, Dec. 21, 2000. Redesignated and amended at 82 FR
5832, Jan. 18, 2017]
§ D1194.24 Video and multimedia
products.
(a) All analog television displays 13 inches and larger, and
computer equipment that includes analog television receiver or
display circuitry, shall be equipped with caption decoder circuitry
which appropriately receives, decodes, and displays closed captions
from broadcast, cable, videotape, and DVD signals. As soon as
practicable, but not later than July 1, 2002, widescreen digital
television (DTV) displays measuring at least 7.8 inches vertically,
DTV sets with conventional displays measuring at least 13 inches
vertically, and stand-alone DTV tuners, whether or not they are
marketed with display screens, and computer equipment that includes
DTV receiver or display circuitry, shall be equipped with caption
decoder circuitry which appropriately receives, decodes, and
displays closed captions from broadcast, cable, videotape, and DVD
signals.
(b) Television tuners, including tuner cards for use in
computers, shall be equipped with secondary audio program playback
circuitry.
(c) All training and informational video and multimedia
productions which support the agency's mission, regardless of
format, that contain speech or other audio information necessary
for the comprehension of the content, shall be open or closed
captioned.
(d) All training and informational video and multimedia
productions which support the agency's mission, regardless of
format, that contain visual information necessary for the
comprehension of the content, shall be audio described.
(e) Display or presentation of alternate text presentation or
audio descriptions shall be user-selectable unless permanent.
[65 FR 80523, Dec. 21, 2000. Redesignated and amended at 82 FR
5832, Jan. 18, 2017]
§ D1194.25 Self contained, closed
products.
(a) Self contained products shall be usable by people with
disabilities without requiring an end-user to attach assistive
technology to the product. Personal headsets for private listening
are not assistive technology.
(b) When a timed response is required, the user shall be alerted
and given sufficient time to indicate more time is required.
(c) Where a product utilizes touchscreens or contact-sensitive
controls, an input method shall be provided that complies with §
1194.23 (k) (1) through (4).
(d) When biometric forms of user identification or control are
used, an alternative form of identification or activation, which
does not require the user to possess particular biological
characteristics, shall also be provided.
(e) When products provide auditory output, the audio signal
shall be provided at a standard signal level through an industry
standard connector that will allow for private listening. The
product must provide the ability to interrupt, pause, and restart
the audio at anytime.
(f) When products deliver voice output in a public area,
incremental volume control shall be provided with output
amplification up to a level of at least 65 dB. Where the ambient
noise level of the environment is above 45 dB, a volume gain of at
least 20 dB above the ambient level shall be user selectable. A
function shall be provided to automatically reset the volume to the
default level after every use.
(g) Color coding shall not be used as the only means of
conveying information, indicating an action, prompting a response,
or distinguishing a visual element.
(h) When a product permits a user to adjust color and contrast
settings, a range of color selections capable of producing a
variety of contrast levels shall be provided.
(i) Products shall be designed to avoid causing the screen to
flicker with a frequency greater than 2 Hz and lower than 55
Hz.
(j) Products which are freestanding, non-portable, and intended
to be used in one location and which have operable controls shall
comply with the following:
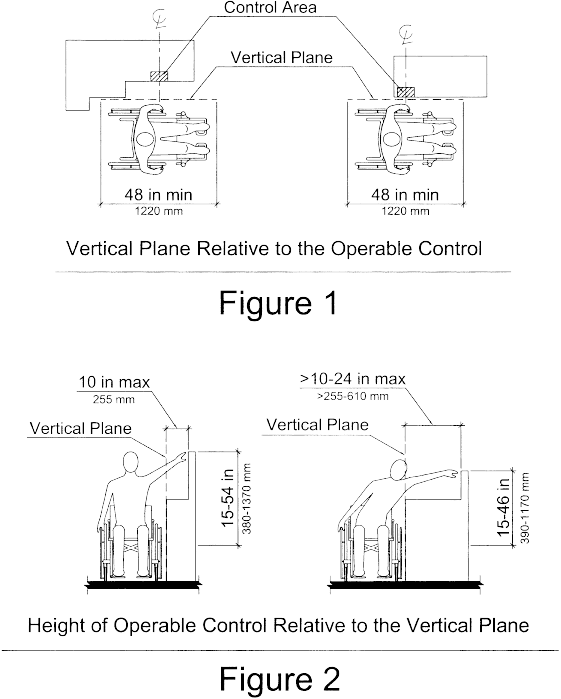
(1) The position of any operable control shall be determined
with respect to a vertical plane, which is 48 inches in length,
centered on the operable control, and at the maximum protrusion of
the product within the 48 inch length (see Figure 1 of this
part).
(2) Where any operable control is 10 inches or less behind the
reference plane, the height shall be 54 inches maximum and 15
inches minimum above the floor.
(3) Where any operable control is more than 10 inches and not
more than 24 inches behind the reference plane, the height shall be
46 inches maximum and 15 inches minimum above the floor.
(4) Operable controls shall not be more than 24 inches behind
the reference plane (see Figure 2 of this part).
[65 FR 80523, Dec. 21, 2000. Redesignated and amended at 82 FR
5832, Jan. 18, 2017]
§ D1194.26 Desktop and portable
computers.
(a) All mechanically operated controls and keys shall comply
with § 1194.23(k)(1) through (4).
(b) If a product utilizes touchscreens or touch-operated
controls, an input method shall be provided that complies with §
1194.23 (k) (1) through (4).
(c) When biometric forms of user identification or control are
used, an alternative form of identification or activation, which
does not require the user to possess particular biological
characteristics, shall also be provided.
(d) Where provided, at least one of each type of expansion
slots, ports and connectors shall comply with publicly available
industry standards.
[65 FR 80523, Dec. 21, 2000. Redesignated and amended at 82 FR
5832, Jan. 18, 2017]
§§ D1194.27-D1194.30 [Reserved] §
D1194.31 Functional performance criteria.
(a) At least one mode of operation and information retrieval
that does not require user vision shall be provided, or support for
assistive technology used by people who are blind or visually
impaired shall be provided.
(b) At least one mode of operation and information retrieval
that does not require visual acuity greater than 20/70 shall be
provided in audio and enlarged print output working together or
independently, or support for assistive technology used by people
who are visually impaired shall be provided.
(c) At least one mode of operation and information retrieval
that does not require user hearing shall be provided, or support
for assistive technology used by people who are deaf or hard of
hearing shall be provided.
(d) Where audio information is important for the use of a
product, at least one mode of operation and information retrieval
shall be provided in an enhanced auditory fashion, or support for
assistive hearing devices shall be provided.
(e) At least one mode of operation and information retrieval
that does not require user speech shall be provided, or support for
assistive technology used by people with disabilities shall be
provided.
(f) At least one mode of operation and information retrieval
that does not require fine motor control or simultaneous actions
and that is operable with limited reach and strength shall be
provided.
[65 FR 80523, Dec. 21, 2000. Redesignated and amended at 82 FR
5832, Jan. 18, 2017]
§§ D1194.32-D1194.40 [Reserved] §
D1194.41 Information, documentation, and support.
(a) Product support documentation provided to end-users shall be
made available in alternate formats upon request, at no additional
charge.
(b) End-users shall have access to a description of the
accessibility and compatibility features of products in alternate
formats or alternate methods upon request, at no additional
charge.
(c) Support services for products shall accommodate the
communication needs of end-users with disabilities.
[65 FR 80523, Dec. 21, 2000. Redesignated and amended at 82 FR
5832, Jan. 18, 2017]
§§ D1194.42-D1194.50 [Reserved] §
D1194.51 Figures