Title 17
SECTION 240.3a67-3
240.3a67-3 Definition of “substantial position.”
§ 240.3a67-3 Definition of “substantial position.”(a) General. For purposes of section 3(a)(67) of the Act, 15 U.S.C. 78c(a)(67), and § 240.3a67-1, the term substantial position means security-based swap positions that equal or exceed either of the following thresholds in any major category of security-based swaps:
(1) $1 billion in daily average aggregate uncollateralized outward exposure; or
(2) $2 billion in:
(i) Daily average aggregate uncollateralized outward exposure; plus
(ii) Daily average aggregate potential outward exposure.
(b) Aggregate uncollateralized outward exposure - (1) General. Aggregate uncollateralized outward exposure in general means the sum of the current exposure, obtained by marking-to-market using industry standard practices, of each of the person's security-based swap positions with negative value in a major security-based swap category, less the value of the collateral the person has posted in connection with those positions.
(2) Calculation of aggregate uncollateralized outward exposure. In calculating this amount the person shall, with respect to each of its security-based swap counterparties in a given major security-based swap category:
(i) Determine the dollar value of the aggregate current exposure arising from each of its security-based swap positions with negative value (subject to the netting provisions described below) in that major category by marking-to-market using industry standard practices; and
(ii) Deduct from that dollar amount the aggregate value of the collateral the person has posted with respect to the security-based swap positions.
(iii) The aggregate uncollateralized outward exposure shall be the sum of those uncollateralized amounts across all of the person's security-based swap counterparties in the applicable major category.
(3) Relevance of netting agreements. (i) If a person has one or more master netting agreements with a counterparty, the person may measure the current exposure arising from its security-based swaps in any major category on a net basis, applying the terms of those agreements. Calculation of current exposure may take into account offsetting positions entered into with that particular counterparty involving security-based swaps (in any security-based swap category) as well as swaps and securities financing transactions (consisting of securities lending and borrowing, securities margin lending and repurchase and reverse repurchase agreements), and other financial instruments that are subject to netting offsets for purposes of applicable bankruptcy law, to the extent these are consistent with the offsets permitted by the master netting agreements.
(ii) Such adjustments may not take into account any offset associated with positions that the person has with separate counterparties.
(4) Allocation of uncollateralized outward exposure. If a person calculates current exposure with a particular counterparty on a net basis, as provided by paragraph (b)(3) of this section, the amount of current uncollateralized exposure attributable to each “major” category of security-based swaps should be calculated according to the following formula:
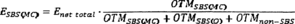 Note to
paragraph (b)(4).
Note to
paragraph (b)(4).
Where: ESBS(MC) equals the amount of aggregate current exposure attributable to the entity's security-based swap positions in the “major” category at issue (either security-based credit derivatives or other security-based swaps); Enet total equals the entity's aggregate current exposure to the counterparty at issue, after accounting for the netting of positions and the posting of collateral; OTMSBS(MC) equals the current exposure associated with the entity's out-of-the-money positions in security-based swaps in the “major” category at issue, subject to those netting arrangements; and OTMSBS(O) equals the current exposure associated with the entity's out-of-the-money positions in the other “major” category of security-based swaps, subject to those netting arrangements; and OTMnon-SBS equals the current exposure associated with the entity's out-of-the-money positions associated with instruments, other than security-based swaps, that are subject to those netting arrangements.
(c) Aggregate potential outward exposure - (1) General. Aggregate potential outward exposure means the sum of:
(i) The aggregate potential outward exposure for each of the person's security-based swap positions in a major security-based swap category that are neither cleared by a registered or exempt clearing agency nor subject to daily mark-to-market margining, as calculated in accordance with paragraph (c)(2) of this section; and
(ii) The aggregate potential outward exposure for each of the person's security-based swap positions in a major security-based swap category that are either cleared by a registered or exempt clearing agency or subject to daily mark-to-market margining, as calculated in accordance with paragraph (c)(3) of this section.
(2) Calculation of potential outward exposure for security-based swaps that are not cleared by a registered or exempt clearing agency or subject to daily mark-to-market margining - (i) General - (A)(1) For positions in security-based swaps that are not cleared by a registered or exempt clearing agency or subject to daily mark-to-market margining, potential outward exposure equals the total notional principal amount of those positions, multiplied by the following factors on a position-by-position basis reflecting the type of security-based swap. For any security-based swap that is not of the “debt” type, the “equity and other” conversion factors are to be used:
| Residual maturity | Debt | Equity and other |
|---|---|---|
| One year or less | 0.10 | 0.06 |
| Over one to five years | 0.10 | 0.08 |
| Over five years | 0.10 | 0.10 |
(2) If a security-based swap is structured such that on specified dates any outstanding exposure is settled and the terms are reset so that the market value of the security-based swap is zero, the remaining maturity equals the time until the next reset date.
(B) Use of effective notional amounts. If the stated notional amount on a position is leveraged or enhanced by the structure of the position, the calculation in paragraph (c)(2)(i)(A) of this section shall be based on the effective notional amount of the position rather than on the stated notional amount.
(C) Exclusion of certain positions. The calculation in paragraph (c)(2)(i)(A) of this section shall exclude:
(1) Positions that constitute the purchase of an option, such that the person has no additional payment obligations under the position;
(2) Other positions for which the person has prepaid or otherwise satisfied all of its payment obligations; and
(3) Positions for which, pursuant to regulatory requirement, the person has assigned an amount of cash or U.S. Treasury securities that is sufficient to pay the person's maximum possible liability under the position, and the person may not use that cash or those Treasury securities for other purposes.
(D) Adjustment for certain positions. Notwithstanding paragraph (c)(2)(i)(A) of this section, the potential outward exposure associated with a position by which a person buys credit protection using a credit default swap, or associated with a position by which a person purchases an option for which the person retains additional payment obligations under the position, is capped at the net present value of the unpaid premiums.
(ii) Adjustment for netting agreements. Notwithstanding paragraph (c)(2)(i) of this section, for positions subject to master netting agreements the potential outward exposure associated with the person's security-based swaps with each counterparty equals a weighted average of the potential outward exposure for the person's security-based swaps with that counterparty as calculated under paragraph (c)(2)(i) of this section, and that amount reduced by the ratio of net current exposure to gross current exposure, consistent with the following equation as calculated on a counterparty-by-counterparty basis:
PNet = 0.4 × PGross + 0.6 × NGR × PGross Note to paragraph (c)(2)(ii):Where: PNet is the potential outward exposure, adjusted for bilateral netting, of the person's security-based swaps with a particular counterparty; PGross is the potential outward exposure without adjustment for bilateral netting, as calculated pursuant to paragraph (c)(2)(i) of this section; and NGR is the ratio of:
1. The current exposure arising from its security-based swaps in the major category as calculated on a net basis according to paragraphs (b)(3) and (4) of this section, divided by
2. The current exposure arising from its security-based swaps in the major category as calculated in the absence of those netting procedures.
(3) Calculation of potential outward exposure for security-based swaps that are either cleared by a registered or exempt clearing agency or subject to daily mark-to-market margining. For positions in security-based swaps that are cleared by a registered or exempt clearing agency or subject to daily mark-to-market margining:
(i) Potential outward exposure equals the potential outward exposure that would be attributed to such positions using the procedures in paragraph (c)(2) of this section, multiplied by:
(A) 0.1, in the case of positions cleared by a registered or exempt clearing agency; or
(B) 0.2, in the case of positions that are subject to daily mark-to-market margining but that are not cleared by a registered or exempt clearing agency.
(ii) Solely for purposes of calculating potential outward exposure:
(A) A security-based swap shall be considered to be subject to daily mark-to-market margining if, and for as long as, the counterparties follow the daily practice of exchanging collateral to reflect changes in the current exposure arising from the security-based swap (after taking into account any other financial positions addressed by a netting agreement between the counterparties).
(B) If the person is permitted by agreement to maintain a threshold for which it is not required to post collateral, the position still will be considered to be subject to daily mark-to-market margining for purposes of calculating potential outward exposure, but the total amount of that threshold (regardless of the actual exposure at any time) less any initial margin posted up to the amount of that threshold, shall be added to the person's aggregate uncollateralized outward exposure for purposes of paragraph (a)(2) of this section.
(C) If the minimum transfer amount under the agreement is in excess of $1 million, the position still will be considered to be subject to daily mark-to-market margining for purposes of calculating potential outward exposure, but the entirety of the minimum transfer amount shall be added to the person's aggregate uncollateralized outward exposure for purposes of paragraph (a)(2) of this section.
(D) A person may, at its discretion, calculate the potential outward exposure of positions in security-based swaps that are subject to daily mark-to-market margining in accordance with paragraph (c)(2) of this section in lieu of calculating the potential outward exposure of such positions in accordance with this paragraph (c)(3).
(d) Calculation of daily average. Measures of daily average aggregate uncollateralized outward exposure and daily average aggregate potential outward exposure shall equal the arithmetic mean of the applicable measure of exposure at the close of each business day, beginning the first business day of each calendar quarter and continuing through the last business day of that quarter.
(e) Inter-affiliate activities. In calculating its aggregate uncollateralized outward exposure and its aggregate potential outward exposure, a person shall not consider its security-based swap positions with counterparties that are majority-owned affiliates. For these purposes the parties are majority-owned affiliates if one party directly or indirectly owns a majority interest in the other, or if a third party directly or indirectly owns a majority interest in both counterparties to the security-based swap, where “majority interest” is the right to vote or direct the vote of a majority of a class of voting securities of an entity, the power to sell or direct the sale of a majority of a class of voting securities of an entity, or the right to receive upon dissolution or the contribution of a majority of the capital of a partnership.