Appendix BB to Subpart B of Part 430 - Uniform Test Method for Measuring the Input Power, Lumen Output, Lamp Efficacy, Correlated Color Temperature (CCT), Color Rendering Index (CRI), Power Factor, Time to Failure, and Standby Mode Power of Integrated Light-Emitting Diode (LED) Lamps
10:3.0.1.4.18.3.13.6.40 : Appendix BB
Appendix BB to Subpart B of Part 430 - Uniform Test Method for
Measuring the Input Power, Lumen Output, Lamp Efficacy, Correlated
Color Temperature (CCT), Color Rendering Index (CRI), Power Factor,
Time to Failure, and Standby Mode Power of Integrated
Light-Emitting Diode (LED) Lamps Note:
On or after March 20, 2019, any representations made with
respect to the energy use or efficiency of integrated
light-emitting diode lamps must be made in accordance with the
results of testing pursuant to this appendix.
1. Scope: This appendix specifies the test methods
required to measure input power, lumen output, lamp efficacy, CCT,
CRI, power factor, time to failure, and standby mode power for
integrated LED lamps.
2. Definitions
2.1. The definitions specified in section 1.3 of IES LM-79-08
except section 1.3(f) (incorporated by reference; see § 430.3)
apply.
2.2. Initial lumen output means the measured lumen output
after the lamp is initially energized and stabilized using the
stabilization procedures in section 3 of this appendix.
2.3. Interval lumen output means the measured lumen
output at constant intervals after the initial lumen output
measurement in accordance with section 4 of this appendix.
2.4. Rated input voltage means the voltage(s) marked on
the lamp as the intended operating voltage. If not marked on the
lamp, assume 120 V.
2.5. Test duration means the operating time of the LED
lamp after the initial lumen output measurement and before, during,
and including the final lumen output measurement, in units of
hours.
2.6. Time to failure means the time elapsed between the
initial lumen output measurement and the point at which the lamp
reaches 70 percent lumen maintenance as measured in section 4 of
this appendix.
3. Active Mode Test Method for Determining Lumen Output, Input
Power, CCT, CRI, Power Factor, and Lamp Efficacy
In cases where there is a conflict, the language of the test
procedure in this appendix takes precedence over IES LM-79-08
(incorporated by reference; see § 430.3).
3.1. Test Conditions and Setup
3.1.1. Establish the ambient conditions, power supply,
electrical settings, and instrumentation in accordance with the
specifications in sections 2.0, 3.0, 7.0, and 8.0 of IES LM-79-08
(incorporated by reference; see § 430.3), respectively.
3.1.2. Position an equal number of integrated LED lamps in the
base-up and base-down orientations throughout testing; if the
position is restricted by the manufacturer, test units in the
manufacturer-specified position.
3.1.3. Operate the integrated LED lamp at the rated voltage
throughout testing. For an integrated LED lamp with multiple rated
voltages including 120 volts, operate the lamp at 120 volts. If an
integrated LED lamp with multiple rated voltages is not rated for
120 volts, operate the lamp at the highest rated input voltage.
Additional tests may be conducted at other rated voltages.
3.1.4. Operate the lamp at the maximum input power. If multiple
modes occur at the same maximum input power (such as variable CCT
or CRI), the manufacturer can select any of these modes for
testing; however, all measurements described in sections 3 and 4 of
this appendix must be taken at the same selected mode. The test
report must indicate which mode was selected for testing and
include detail such that another laboratory could operate the lamp
in the same mode.
3.2. Test Method, Measurements, and Calculations
3.2.1. The test conditions and setup described in section 3.1 of
this appendix apply to this section 3.2.
3.2.2. Stabilize the integrated LED lamp prior to measurement as
specified in section 5.0 of IES LM-79-08 (incorporated by
reference; see § 430.3). Calculate the stabilization variation as
[(maximum - minimum)/minimum] of at least three readings of the
input power and lumen output over a period of 30 minutes, taken 15
minutes apart.
3.2.3. Measure the input power in watts as specified in section
8.0 of IES LM-79-08.
3.2.4. Measure the input voltage in volts as specified in
section 8.0 of IES LM-79-08.
3.2.5. Measure the input current in amps as specified in section
8.0 of IES LM-79-08.
3.2.6. Measure lumen output as specified in section 9.1 and 9.2
of IES LM-79-08. Do not use goniophotometers.
3.2.7. Determine CCT according to the method specified in
section 12.0 of IES LM-79-08 with the exclusion of section 12.2 and
12.5 of IES LM-79-08. Do not use goniophotometers.
3.2.8. Determine CRI according to the method specified in
section 12.0 of IES LM-79-08 with the exclusion of section 12.2 and
12.5 of IES LM-79-08. Do not use goniophotometers.
3.2.9. Determine lamp efficacy by dividing measured initial
lumen output by the measured input power.
3.2.10. Determine power factor for AC-input lamps by dividing
measured input power by the product of the measured input voltage
and measured input current.
4. Active Mode Test Method to Measure Time to Failure
In cases where there is a conflict, the language of the test
procedure in this appendix takes precedence over IES LM-84
(incorporated by reference; see § 430.3) and IES TM-28
(incorporated by reference; see § 430.3).
4.1. Lamp Handling, Tracking, and Time Recording
4.1.1. Handle, transport, and store the integrated LED lamp as
described in section 7.2 of IES LM-84 (incorporated by reference;
see § 430.3).
4.1.2. Mark and track the integrated LED lamp as specified in
section 7.3 of IES LM-84.
4.1.3. Measure elapsed operating time and calibrate all
equipment as described in section 7.5 of IES LM-84.
4.1.4. Check the integrated LED lamps regularly for failure as
specified in section 7.8 of IES LM-84.
4.2. Measure Initial Lumen Output. Measure the initial
lumen output according to section 3 of this appendix.
4.3. Test Duration. Operate the integrated LED lamp for a
period of time (the test duration) after the initial lumen output
measurement and before, during, and including the final lumen
output measurement.
4.3.1. There is no minimum test duration requirement for the
integrated LED lamp. The test duration is selected by the
manufacturer. See section 4.6 of this appendix for instruction on
the maximum time to failure.
4.3.2. The test duration only includes time when the integrated
LED lamp is energized and operating.
4.4. Operating Conditions and Setup Between Lumen Output
Measurements
4.4.1. Electrical settings must be as described in section 5.1
of IES LM-84 (incorporated by reference; see § 430.3).
4.4.2. LED lamps must be handled and cleaned as described in
section 4.1 of IES LM-84.
4.4.3. Vibration around each lamp must be as described in
section 4.3 of IES LM-84.
4.4.4. Ambient temperature conditions must be as described in
section 4.4 of IES LM-84. Maintain the ambient temperature at 25 °C
± 5 °C or at a manufacturer-selected temperature higher than 25 °C
with the same ±5 °C tolerance.
4.4.5. Humidity in the testing environment must be as described
in section 4.5 of IES LM-84.
4.4.6. Air movement around each lamp must be as described in
section 4.6 of IES LM-84.
4.4.7. Position a lamp in either the base-up and base-down
orientation throughout testing. An equal number of lamps in the
sample must be tested in the base-up and base-down orientations,
except that, if the manufacturer restricts the position, test all
of the units in the sample in the manufacturer-specified
position.
4.4.8. Operate the lamp at the rated input voltage as described
in section 3.1.3 of this appendix for the entire test duration.
4.4.9. Operate the lamp at the maximum input power as described
in section 3.1.4 of this appendix for the entire test duration.
4.4.10. Line voltage waveshape must be as described in section
5.2 of IES LM-84.
4.4.11. Monitor and regulate rated input voltage as described in
section 5.4 of IES LM-84.
4.4.12. Wiring of test racks must be as specified in section 5.5
of IES LM-84.
4.4.13. Operate the integrated LED lamp continuously.
4.5. Measure Interval Lumen Output. Measure interval
lumen output according to section 3 of this appendix.
4.5.1. Record interval lumen output and elapsed operating time
as described in section 4.2 of IES TM-28 (incorporated by
reference; see § 430.3).
4.5.1.1. For test duration values greater than or equal to 3,000
hours and less than 6,000 hours, measure lumen maintenance of the
integrated LED lamp at an interval in accordance with section 4.2.2
of IES TM-28.
4.5.1.2. For test duration values greater than or equal to 6,000
hours, measure lumen maintenance at an interval in accordance with
section 4.2.1 of IES TM-28.
4.6. Calculate Lumen Maintenance and Time to Failure
4.6.1. Calculate the lumen maintenance of the lamp at each
interval by dividing the interval lumen output “xt” by the initial
lumen output “x0”. Measure initial and interval lumen output in
accordance with sections 4.2 and 4.5 of this appendix,
respectively.
4.6.2. For lumen maintenance values less than 0.7, including
lamp failures that result in complete loss of light output, time to
failure is equal to the previously recorded lumen output
measurement (at a shorter test duration) where the lumen
maintenance is greater than or equal to 0.7.
4.6.3. For lumen maintenance values equal to 0.7, time to
failure is equal to the test duration.
4.6.4. For lumen maintenance values greater than 0.7, use the
following method:
4.6.4.1. For test duration values less than 3,000 hours, do not
project time to failure. Time to failure equals the test
duration.
4.6.4.2. For test duration values greater than or equal to 3,000
hours but less than 6,000 hours, time to failure is equal to the
lesser of the projected time to failure calculated according to
section 4.6.4.2.1 of this appendix or the test duration multiplied
by the limiting multiplier calculated in section 4.6.4.2.2 of this
appendix.
4.6.4.2.1. Project time to failure using the projection method
described in section 5.1.4 of IES TM-28 (incorporated by reference;
see § 430.3). Project time to failure for each individual LED lamp.
Do not use data obtained prior to a test duration value of 1,000
hours.
4.6.4.2.2. Calculate the limiting multiplier from the following
equation:
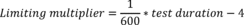
4.6.4.3. For test duration values greater than 6,000 hours, time
to failure is equal to the lesser of the projected time to failure
calculated according to section 4.6.4.3.1 or the test duration
multiplied by six.
4.6.4.3.1. Project time to failure using the projection method
described in section 5.1.4 of IES TM-28 (incorporated by reference;
see § 430.3). Project time to failure for each individual LED lamp.
Data used for the time to failure projection method must be as
specified in section 5.1.3 of IES TM-28.
5. Standby Mode Test Method for Determining Standby Mode Power
Measure standby mode power consumption for integrated LED lamps
capable of operating in standby mode. The standby mode test method
in this section 5 may be completed before or after the active mode
test method for determining lumen output, input power, CCT, CRI,
power factor, and lamp efficacy in section 3 of this appendix. The
standby mode test method in this section 5 must be completed before
the active mode test method for determining time to failure in
section 4 of this appendix. In cases where there is a conflict, the
language of the test procedure in this appendix takes precedence
over IES LM-79 (incorporated by reference; see § 430.3) and IEC
62301 (incorporated by reference; see § 430.3).
5.1. Test Conditions and Setup
5.1.1. Establish the ambient conditions, power supply,
electrical settings, and instrumentation in accordance with the
specifications in sections 2.0, 3.0, 7.0, and 8.0 of IES LM-79
(incorporated by reference; see § 430.3), respectively. Maintain
the ambient temperature at 25 °C ± 1 °C.
5.1.2. Position a lamp in either the base-up and base-down
orientation throughout testing. An equal number of lamps in the
sample must be tested in the base-up and base-down
orientations.
5.1.3. Operate the integrated LED lamp at the rated voltage
throughout testing. For an integrated LED lamp with multiple rated
voltages, operate the integrated LED lamp at 120 volts. If an
integrated LED lamp with multiple rated voltages is not rated for
120 volts, operate the integrated LED lamp at the highest rated
input voltage.
5.2. Test Method, Measurements, and Calculations
5.2.1. The test conditions and setup described in section 3.1 of
this appendix apply to this section.
5.2.2. Connect the integrated LED lamp to the
manufacturer-specified wireless control network (if applicable) and
configure the integrated LED lamp in standby mode by sending a
signal to the integrated LED lamp instructing it to have zero light
output. Lamp must remain connected to the network throughout the
duration of the test.
5.2.3. Stabilize the integrated LED lamp as specified in section
5 of IEC 62301 (incorporated by reference; see § 430.3) prior to
measurement.
5.2.4. Measure the standby mode power in watts as specified in
section 5 of IEC 62301.
[81 FR 43427, July 1, 2016, as amended at 83 FR 47812, Sept. 21,
2018]