Appendix AA to Subpart B of Part 430 - Uniform Test Method for Measuring the Energy Consumption of Furnace Fans
10:3.0.1.4.18.3.13.6.39 : Appendix AA
Appendix AA to Subpart B of Part 430 - Uniform Test Method for
Measuring the Energy Consumption of Furnace Fans Note:
Any representation made after July 2, 2014 for energy
consumption of furnace fans must be based upon results generated
under this test procedure. Upon the compliance date(s) of any
energy conservation standard(s) for furnace fans, use of the
applicable provisions of this test procedure to demonstrate
compliance with the energy conservation standard will also be
required.
1. Scope. This appendix covers the test requirements used
to measure the energy consumption of fans used in weatherized and
non-weatherized gas furnaces, oil furnaces, electric furnaces, and
modular blowers.
2. Definitions. Definitions include the definitions as
specified in section 3 of ASHRAE 103-2007 (incorporated by
reference, see § 430.3) and the following additional definitions,
some of which supersede definitions found in ASHRAE 103-2007:
2.1. Active mode means the condition in which the product
in which the furnace fan is integrated is connected to a power
source and circulating air through ductwork.
2.2. Airflow-control settings are programmed or wired
control system configurations that control a fan to achieve
discrete, differing ranges of airflow - often designated for
performing a specific function (e.g., cooling, heating, or
constant circulation) - without manual adjustment other than
interaction with a user-operable control such as a thermostat that
meets the manufacturer specifications for installed-use. For the
purposes of this appendix, manufacturer specifications for
installed-use shall be found in the product literature shipped with
the unit.
2.3. ASHRAE 103-2007 means ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 103-2007,
published in 2007 by ASHRAE, approved by the American National
Standards Institute (ANSI) on March 25, 2008, and entitled “Method
of Testing for Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency of Residential
Central Furnaces and Boilers”. Only those sections of ASHRAE
103-2007 (incorporated by reference; see § 430.3) specifically
referenced in this test procedure are part of this test procedure.
In cases where there is a conflict, the language of the test
procedure in this appendix takes precedence over ASHRAE
103-2007.
2.4. ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 41.1-1986 (RA 2006) means the
test standard published in 1986, approved by ANSI on February 18,
1987, reaffirmed in 2006, and entitled “Standard Method for
Temperature Measurement” (incorporated by reference; see §
430.3).
2.5. ASHRAE Standard 37-2009 means the test standard
published in 2009 by ASHRAE entitled “Methods of Testing for Rating
Unitary Air-Conditioning and Heat Pump Equipment” (incorporated by
reference; see § 430.3).
2.6. Default airflow-control settings are the
airflow-control settings specified for installed-use by the
manufacturer. For the purposes of this appendix, manufacturer
specifications for installed-use are those specifications provided
for typical consumer installations in the product literature
shipped with the product in which the furnace fan is installed. In
instances where a manufacturer specifies multiple airflow-control
settings for a given function to account for varying installation
scenarios, the highest airflow-control setting specified for the
given function shall be used for the procedures specified in this
appendix.
2.7. External static pressure (ESP) means the difference
between static pressures measured in the outlet duct and return air
opening (or return air duct when used for testing) of the product
in which the furnace fan is integrated.
2.8. Furnace fan means an electrically-powered device
used in a consumer product for the purpose of circulating air
through ductwork.
2.9. Modular blower means a product which only uses
single-phase electric current, and which:
(a) Is designed to be the principal air circulation source for
the living space of a residence;
(b) Is not contained within the same cabinet as a furnace or
central air conditioner; and
(c) Is designed to be paired with HVAC products that have a heat
input rate of less than 225,000 Btu per hour and cooling capacity
less than 65,000 Btu per hour.
2.10. Off mode means the condition in which the product
in which the furnace fan is integrated either is not connected to
the power source or is connected to the power source but not
energized.
2.11. Seasonal off switch means a switch on the product
in which the furnace fan is integrated that, when activated,
results in a measurable change in energy consumption between the
standby and off modes.
2.12. Standby mode means the condition in which the
product in which the furnace fan is integrated is connected to the
power source, energized, but the furnace fan is not circulating
air.
2.13. Thermal stack damper means a type of stack damper
that opens only during the direct conversion of thermal energy of
the stack gases.
3. Classifications. Classifications are as specified in
section 4 of ASHRAE 103-2007 (incorporated by reference, see §
430.3).
4. Requirements. Requirements are as specified in section
5 of ASHRAE 103-2007 (incorporated by reference, see § 430.3). In
addition, Fan Energy Rating (FER) of furnace fans shall be
determined using test data and estimated national average operating
hours pursuant to section 10.10 of this appendix.
5. Instruments. Instruments must be as specified in
section 6, not including section 6.2, of ASHRAE 103-2007
(incorporated by reference, see § 430.3); and as specified in
section 5.1 and 5.2 of this appendix.
5.1. Temperature. Temperature measuring instruments shall
meet the provisions specified in section 5.1 of ASHRAE 37-2009
(incorporated by reference, see § 430.3) and shall be accurate to
within 0.75 degree Fahrenheit (within 0.4 degrees Celsius).
5.1.1. Outlet Air Temperature Thermocouple Grid. Outlet
air temperature shall be measured as described in section 8.2.1.5.5
of ASHRAE 103-2007 (incorporated by reference, see § 430.3) and
illustrated in Figure 2 of ASHRAE 103-2007. Thermocouples shall be
placed downstream of pressure taps used for external static
pressure measurement.
5.2. Humidity. Air humidity shall be measured with a
relative humidity sensor that is accurate to within 5% relative
humidity. Air humidity shall be measured as close as possible to
the inlet of the product in which the furnace fan is installed.
6. Apparatus. The apparatus used in conjunction with the
furnace during the testing shall be as specified in section 7 of
ASHRAE 103-2007 (incorporated by reference, see § 430.3) except for
section 7.1, the second paragraph of section 7.2.2.2, section
7.2.2.5, and section 7.7, and as specified in sections 6.1, 6.2,
6.3,6.4, 6.5 and 6.6 of this appendix.
6.1. General. The product in which the furnace fan is
integrated shall be installed in the test room in accordance with
the product manufacturer's written instructions that are shipped
with the product unless required otherwise by a specific provision
of this appendix. The apparatus described in this section is used
in conjunction with the product in which the furnace fan is
integrated. Each piece of the apparatus shall conform to material
and construction specifications and the reference standard cited.
Test rooms containing equipment shall have suitable facilities for
providing the utilities necessary for performance of the test and
be able to maintain conditions within the limits specified.
6.2. Downflow furnaces. Install the internal section of
vent pipe the same size as the flue collar for connecting the flue
collar to the top of the unit, if not supplied by the manufacturer.
Do not insulate the internal vent pipe during the jacket loss test
(if conducted) described in section 8.6 of ASHRAE 103-2007
(incorporated by reference, see § 430.3) or the steady-state test
described in section 9.1 of ASHRAE 103-2007. Do not insulate the
internal vent pipe before the cool-down and heat-up tests described
in sections 9.5 and 9.6, respectively, of ASHRAE 103-2007. If the
vent pipe is surrounded by a metal jacket, do not insulate the
metal jacket. Install a 5-ft test stack of the same cross sectional
area or perimeter as the vent pipe above the top of the furnace.
Tape or seal around the junction connecting the vent pipe and the
5-ft test stack. Insulate the 5-ft test stack with insulation
having a minimum R-value of 7 and an outer layer of aluminum foil.
(See Figure 3-E of ASHRAE 103-2007.)
6.3. Modular Blowers. A modular blower shall be equipped
with the electric heat resistance kit that is likely to have the
largest volume of retail sales with that particular basic model of
modular blower.
6.4. Ducts and Plenums. Ducts and plenums shall be built
to the geometrical specifications in section 7 of ASHRAE 103-2007.
An apparatus for measuring external static pressure shall be
integrated in the plenum and test duct as specified in sections
6.4, excluding specifications regarding the minimum length of the
ducting and minimum distance between the external static pressure
taps and product inlet and outlet, and 6.5 of ASHRAE 37-2009
(incorporated by reference, see § 430.3). External static pressure
measuring instruments shall be placed between the furnace openings
and any restrictions or elbows in the test plenums or ducts. For
all test configurations, external static pressure taps shall be
placed 18 inches from the outlet.
6.4.1. For tests conducted using a return air duct.
Additional external static pressure taps shall be placed 12 inches
from the product inlet. Pressure shall be directly measured as a
differential pressure as depicted in Figure 8 of ASHRAE 37-2009
rather than determined by separately measuring inlet and outlet
static pressure and subtracting the results.
6.4.2. For tests conducted without a return air duct.
External static pressure shall be directly measured as the
differential pressure between the outlet duct static pressure and
the ambient static pressure as depicted in Figure 7a of ASHRAE
37-2009.
6.5. Air Filters. Air filters shall be removed.
6.6. Electrical Measurement. Only electrical input power
to the furnace fan (and electric resistance heat kit for electric
furnaces and modular blowers) shall be measured for the purposes of
this appendix. Electrical input power to the furnace fan and
electric resistance hate kit shall be sub-metered separately.
Electrical input power to all other electricity-consuming
components of the product in which the furnace fan is integrated
shall not be included in the electrical input power measurements
used in the FER calculation. If the procedures of this appendix are
being conducted at the same time as another test that requires
metering of components other than the furnace fan and electric
resistance heat kit, the electrical input power to the furnace fan
and electric resistance heat kit shall be sub-metered separately
from one another and separately from other electrical input power
measurements.
7. Test Conditions. The testing conditions shall be as
specified in section 8, not including section 8.6.1.1, of ASHRAE
103-2007 (incorporated by reference, see § 430.3); and as specified
in section 7.1 of this appendix.
7.1. Measurement of Jacket Surface Temperature
(optional). The jacket of the furnace or boiler shall be
subdivided into 6-inch squares when practical, and otherwise into
36-square-inch regions comprising 4 in. x 9 in. or 3 in. x 12 in.
sections, and the surface temperature at the center of each square
or section shall be determined with a surface thermocouple. The
36-square-inch areas shall be recorded in groups where the
temperature differential of the 36-square-inch area is less than 10
°F for temperature up to 100 °F above room temperature and less
than 20 °F for temperature more than 100 °F above room temperature.
For forced air central furnaces, the circulating air blower
compartment is considered as part of the duct system and no surface
temperature measurement of the blower compartment needs to be
recorded for the purpose of this test. For downflow furnaces,
measure all cabinet surface temperatures of the heat exchanger and
combustion section, including the bottom around the outlet duct,
and the burner door, using the 36 square-inch thermocouple grid.
The cabinet surface temperatures around the blower section do not
need to be measured (see figure 3-E of ASHRAE 103-2007.)
8. Test Procedure. Testing and measurements shall be as
specified in section 9 of ASHRAE 103-2007 (incorporated by
reference, see § 430.3) except for sections 9.1.2.1, 9.3, 9.5.1.1,
9.5.1.2.1, 9.5.1.2.2, 9.5.2.1, and section 9.7.1; and as specified
in sections 8.1 through 8.6 of this appendix.
8.1. Direct Measurement of Off-Cycle Losses Testing
Method. [Reserved]
8.2. Measurement of Electrical Standby and Off Mode
Power. [Reserved]
8.3. Steady-State Conditions for Gas and Oil Furnaces.
Steady-state conditions are indicated by an external static
pressure within the range shown in Table 1 and a temperature
variation in three successive readings, taken 15 minutes apart, of
not more than any of the following:
(a) 3 °F in the stack gas temperature for furnaces equipped with
draft diverters;
(b) 5 °F in the stack gas temperature for furnaces equipped with
either draft hoods, direct exhaust, or direct vent systems; and
(c) 1 °F in the flue gas temperature for condensing
furnaces.
8.4. Steady-state Conditions for Electric Furnaces and
Modular Blowers. Steady-state conditions are indicated by an
external static pressure within the range shown in Table 1 and a
temperature variation of not more than 5 °F in the outlet air
temperature in four successive temperature readings taken 15
minutes apart.
8.5. Steady-State Conditions for Cold Flow Tests. For
tests during which the burner or electric heating elements are
turned off (i.e., cold flow tests), steady-state conditions are
indicated by an external static pressure within the range shown in
Table 1 and a variation in the difference between outlet
temperature and ambient temperature of not more than 3 °F in three
successive temperature readings taken 15 minutes apart.
8.6. Fan Energy Rating (FER) Test.
8.6.1. Initial FER test conditions and maximum
airflow-control setting measurements. Measure the relative
humidity (W) and dry bulb temperature (Tdb) of the test room.
8.6.1.1. Furnace fans for which the maximum airflow-control
setting is not a default heating airflow-control setting. The
main burner or electric heating elements shall be turned off.
Adjust the external static pressure to within the range shown in
Table 1 by symmetrically restricting the outlet of the test duct.
Maintain these settings until steady-state conditions are attained
as specified in section 8.3, 8.4, and 8.5 of this appendix. Measure
furnace fan electrical input power (EMax), external static pressure
(ESPMax), and outlet air temperature (TMax,Out).
8.6.1.2. Furnace fans for which the maximum airflow-control
setting is a default heating airflow-control setting. Adjust
the main burner or electric heating element controls to the default
heat setting designated for the maximum airflow-control setting.
Burner adjustments shall be made as specified by section 8.4.1 of
ASHRAE 103-2007 (incorporated by reference, see § 430.3). Adjust
the furnace fan controls to the maximum airflow-control setting.
Adjust the external static to within the range shown in Table 1 by
symmetrically restricting the outlet of the test duct. Maintain
these settings until steady-state conditions are attained as
specified in section 8.3, 8.4, and 8.5 of this appendix and the
temperature rise (ΔTMax) is at least 18 °F. Measure furnace fan
electrical input power (EMax), fuel or electric resistance heat kit
input energy (QIN, Max), external static pressure (ESPMax),
steady-state efficiency for this setting (EffySS, Max) as specified
in sections 11.2 and 11.3 of ASHRAE 103-2007, outlet air
temperature (TMax,Out), and temperature rise (ΔTMax)
Table 1 - Required Minimum External Static
Pressure in the Maximum Airflow-Control Setting by Installation
Type
| Installation type |
ESP (in. wc.) * |
| Units with an
internal, factory-installed evaporator coil |
0.50-0.55 |
| Units designed to
be paired with an evaporator coil, but without one installed |
0.65-0.70 |
| Mobile home |
0.30-0.35 |
Once the specified ESP has been achieved, the same outlet duct
restrictions shall be used for the remainder of the furnace fan
test.
8.6.2. Constant circulation airflow-control setting
measurements. The main burner or electric heating elements
shall be turned off. The furnace fan controls shall be adjusted to
the default constant circulation airflow-control setting. If the
manufacturer does not specify a constant circulation
airflow-control setting, the lowest airflow-control setting shall
be used. Maintain these settings until steady-state conditions are
attained as specified in section 8.3, 8.4, and 8.5 of this
appendix. Measure furnace fan electrical input power (ECirc) and
external static pressure (ESPCirc).
8.6.3. Heating airflow-control setting measurements. For
single-stage gas and oil furnaces, the burner shall be fired at the
maximum heat input rate. For single-stage electric furnaces, the
electric heating elements shall be energized at the maximum heat
input rate. For multi-stage and modulating furnaces the reduced
heat input rate settings shall be used. Burner adjustments shall be
made as specified by section 8.4.1 of ASHRAE 103-2007 (incorporated
by reference, see § 430.3). After the burner is activated and
adjusted or the electric heating elements are energized, the
furnace fan controls shall be adjusted to operate the fan in the
default heat airflow-control setting. In instances where a
manufacturer specifies multiple airflow-control settings for a
given function to account for varying installation scenarios, the
highest airflow-control setting specified for the given function
shall be used. High heat and reduced heat shall be considered
different functions for multi-stage heating units. Maintain these
settings until steady-state conditions are attained as specified in
section 8.3, 8.4, and 8.5 of this appendix and the temperature rise
(ΔTHeat) is at least 18 °F. Measure furnace fan electrical input
power (EHeat), external static pressure (ESPHeat), steady-state
efficiency for this setting (EffySS) as specified in sections 11.2
and 11.3 of ASHRAE 103-2007, outlet air temperature (THeat, Out)
and temperature rise (ΔTHeat).
9. Nomenclature. Nomenclature shall include the
nomenclature specified in section 10 of ASHRAE 103-2007
(incorporated by reference, see § 430.3) and the following
additional variables:
CH = annual furnace fan cooling hours CCH = annual furnace fan
constant-circulation hours ECirc = furnace fan electrical
consumption at the default constant-circulation airflow-control
setting (or minimum airflow-control setting operating point if a
default constant-circulation airflow-control setting is not
specified), in watts EHeat = furnace fan electrical consumption in
the default heat airflow-control setting for single-stage heating
products or the default low-heat setting for multi-stage heating
products, in watts EMax = furnace fan electrical consumption in the
maximum airflow-control setting, in watts ESPi = external static
pressure, in inches water column, at time of the electrical power
measurement in airflow-control setting
i, where
i can
be “Circ” to represent constant-circulation (or minimum airflow)
mode, “Heat” to represent heating mode, or “Max” to represent
cooling (or maximum airflow) mode. FER = fan energy rating, in
watts/1000 cfm HH = annual furnace fan heating operating hours HCR
= heating capacity ratio (nameplate reduced heat input capacity
divided by nameplate maximum input heat capacity) kref = physical
descriptor characterizing the reference system Tdb = dry bulb
temperature of the test room, in °F Ti, In = inlet air temperature
at time of the electrical power measurement, in °F, in
airflow-control setting
i, where
i can be “Circ” to
represent constant-circulation (or minimum airflow) mode, “Heat” to
represent heating mode, or “Max” to represent maximum airflow
(typically designated for cooling) mode Ti, Out = average outlet
air temperature as measured by the outlet thermocouple grid at time
of the electrical power measurement, in °F, in airflow-control
setting
i, where
i can be “Circ” to represent
constant-circulation (or minimum airflow) mode, “Heat” to represent
heating mode, or “Max” to represent maximum airflow (typically
designated for cooling) mode ΔTi = Ti, Out minus Ti, In, which is
the air throughput temperature rise in setting
i, in °F Qi =
airflow in airflow-control setting
i, in cubic feet per
minute (CFM) QIN,i = for electric furnaces and modular blowers, the
measured electrical input power to the electric resistance heat kit
at specified operating conditions
i in kW. For gas and oil
furnaces, measured fuel energy input rate, in Btu/h, at specified
operating conditions
i based on the fuel's high heating
value determined as required in section 8.2.1.3 or 8.2.2.3 of
ASHRAE 103-2007, where
i can be “Max” for the maximum heat
setting or “R” for the reduced heat setting. W = humidity ratio in
pounds water vapor per pounds dry air
vair = specific volume
of dry air at specified operating conditions per the equations in
the psychrometric chapter in 2001 ASHRAE Handbook - Fundamentals in
lb/ft 3
10. Calculation of derived results from test measurements for
a single unit. Calculations shall be as specified in section 11
of ASHRAE 103-2007 (incorporated by reference, see § 430.3), except
for appendices B and C; and as specified in sections 10.1 through
10.10 and Figure 1 of this appendix.
10.1. Fan Energy Rating (FER)
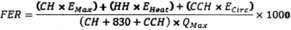
Where:
Qmax =
Qheat for products for which the maximum
airflow-control setting is a default heat setting, or
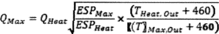
for products for which the maximum airflow control setting is
only designated for cooling; and
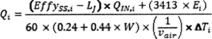
The estimated national average operating hours presented in
Table IV.2 shall be used to calculate FER.
Table IV.2 - Estimated National Average
Operating Hour Values for Calculating FER
| Operating mode |
Variable |
Single-stage
(hours) |
Multi-stage or
modulating (hours) |
| Heating |
HH |
830 |
830/HCR. |
| Cooling |
CH |
640 |
640. |
| Constant
Circulation |
CCH |
400 |
400. |
Where:
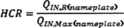
[79 FR 521, Jan. 3, 2014]
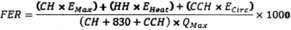 Where:
Qmax = Qheat for products for which the maximum
airflow-control setting is a default heat setting, or
Where:
Qmax = Qheat for products for which the maximum
airflow-control setting is a default heat setting, or 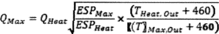
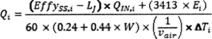
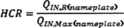 [79 FR 521, Jan. 3, 2014]
[79 FR 521, Jan. 3, 2014]