Title 10
PART 100 APPENDIX A
| Minimum length 1 | |
|---|---|
| Distance from the site (miles): | |
| 0 to 20 | 1 |
| Greater than 20 to 50 | 5 |
| Greater than 50 to 100 | 10 |
| Greater than 100 to 150 | 20 |
| Greater than 150 to 200 | 40 |
1 Minimum length of fault (miles) which shall be considered in establishing Safe Shutdown Earthquake.
(8) For capable faults, any part of which is within 200 miles 2 of the site and which may be of significance in establishing the Safe Shutdown Earthquake, determination of:
(i) The length of the fault;
(ii) The relationship of the fault to regional tectonic structures; and
(iii) The nature, amount, and geologic history of displacements along the fault, including particularly the estimated amount of the maximum Quaternary displacement related to any one earthquake along the fault.
(b) Required Investigation for Surface Faulting. The purpose of the investigations required by this paragraph is to obtain information to determine whether and to what extent the nuclear power plant need be designed for surface faulting. If the design basis for surface faulting can be clearly established by investigations of a lesser scope, not all of the steps in paragraphs (b)(4) through (b)(7) of this section need be carried out. The investigations shall include the following:
(1) Determination of the lithologic, stratigraphic, hydrologic, and structural geologic conditions of the site and the area surrounding the site, including its geologic history;
(2) Evaluation of tectonic structures underlying the site, whether buried or expressed at the surface, with regard to their potential for causing surface displacement at or near the site. The evaluation shall consider the possible effects caused by man's activities such as withdrawal of fluid from or addition of fluid to the subsurface, extraction of minerals, or the loading effects of dams or reservoirs;
(3) Determination of geologic evidence of fault offset at or near the ground surface at or near the site;
(4) For faults greater than 1000 feet long, any part of which is within 5 miles 5 of the site, determination of whether these faults are to be considered as capable faults; 6 7
5 If the design basis for surface faulting can be determined from a fault closer than 5 miles to the site, the procedures of paragraphs (b)(4) through (b)(7) of this section need not be carried out for successively more remote faults.
6 In the absence of absolute dating, evidence of recency of movement may be obtained by applying relative dating techniques to ruptured, offset, warped or otherwise structurally disturbed surface of near-surface materials or geomorphic features.
7 The applicant shall evaluate whether or not a fault is a capable fault with respect to the characteristics outlined in paragraphs III(g)(1), (2), and (3) by conducting a reasonable investigation using suitable geological and geophysical techniques.
(5) Listing of all historically reported earthquakes which can reasonably be associated with capable faults greater than 1000 feet long, any part of which is within 5 miles 5 of the site, including the date of occurrence and the following measured or estimated data: magnitude or highest intensity, and a plot of the epicenter or region of highest intensity;
(6) Correlation of epicenters or locations of highest intensity of historically reported earthquakes with capable faults greater than 1000 feet long, any part of which is located within 5 miles 5 of the site;
(7) For capable faults greater than 1000 feet long, any part of which is within 5 miles 5 of the site, determination of:
(i) The length of the fault;
(ii) The relationship of the fault to regional tectonic structures;
(iii) The nature, amount, and geologic history of displacements along the fault, including particularly the estimated amount of the maximum Quaternary displacement related to any one earthquake along the fault; and
(iv) The outer limits of the fault established by mapping Quaternary fault traces for 10 miles along its trend in both directions from the point of its nearest approach to the site.
(c) Required Investigation for Seismically Induced Floods and Water Waves. (1) For coastal sites, the investigations shall include the determination of:
(i) Information regarding distantly and locally generated waves or tsunami which have affected or could have affected the site. Available evidence regarding the runup and drawdown associated with historic tsunami in the same coastal region as the site shall also be included;
(ii) Local features of coastal topography which might tend to modify tsunami runup or drawdown. Appropriate available evidence regarding historic local modifications in tsunami runup or drawndown at coastal locations having topography similar to that of the site shall also be obtained; and
(iii) Appropriate geologic and seismic evidence to provide information for establishing the design basis for seismically induced floods or water waves from a local offshore earthquake, from local offshore effects of an onshore earthquake, or from coastal subsidence. This evidence shall be determined, to the extent practical, by a procedure similar to that required in paragraphs (a) and (b) of this section. The probable slip characteristics of offshore faults shall also be considered as well as the potential for offshore slides in submarine material.
(2) For sites located near lakes and rivers, investigations similar to those required in paragraph (c)(1) of this section shall be carried out, as appropriate, to determine the potential for the nuclear power plant to be exposed to seismically induced floods and water waves as, for example, from the failure during an earthquake of an upstream dam or from slides of earth or debris into a nearby lake.
v. seismic and geologic design bases(a) Determination of Design Basis for Vibratory Ground Motion. The design of each nuclear power plant shall take into account the potential effects of vibratory ground motion caused by earthquakes. The design basis for the maximum vibratory ground motion and the expected vibratory ground motion should be determined through evaluation of the seismology, geology, and the seismic and geologic history of the site and the surrounding region. The most severe earthquakes associated with tectonic structures or tectonic provinces in the region surrounding the site should be identified, considering those historically reported earthquakes that can be associated with these structures or provinces and other relevant factors. If faults in the region surrounding the site are capable faults, the most severe earthquakes associated with these faults should be determined by also considering their geologic history. The vibratory ground motion at the site should be then determined by assuming that the epicenters or locations of highest intensity of the earthquakes are situated at the point on the tectonic structures or tectonic provinces nearest to the site. The earthquake which could cause the maximum vibratory ground motion at the site should be designated the Safe Shutdown Earthquake. The specific procedures for determining the design basis for vibratory ground motion are given in the following paragraphs.
(1) Determination of Safe Shutdown Earthquake. The Safe Shutdown Earthquake shall be identified through evaluation of seismic and geologic information developed pursuant to the requirements of paragraph IV(a), as follows:
(i) The historic earthquakes of greatest magnitude or intensity which have been correlated with tectonic structures pursuant to the requirements of paragraph (a)(6) of section IV shall be determined. In addition, for capable faults, the information required by paragraph (a)(8) of section IV shall also be taken into account in determining the earthquakes of greatest magnitude related to the faults. The magnitude or intensity of earthquakes based on geologic evidence may be larger than that of the maximum earthquakes historically recorded. The accelerations at the site shall be determined assuming that the epicenters of the earthquakes of greatest magnitude or the locations of highest intensity related to the tectonic structures are situated at the point on the structures closest to the site;
(ii) Where epicenters or locations of highest intensity of historically reported earthquakes cannot be reasonably related to tectonic structures but are identified pursuant to the requirements of paragraph (a)(6) of section IV with tectonic provinces in which the site is located, the accelerations at the site shall be determined assuming that these earthquakes occur at the site;
(iii) Where epicenters or locations of the highest intensity of historically reported earthquakes cannot be reasonably related to tectonic structures but are identified pursuant to the requirements of paragraph (a)(6) of section IV with tectonic provinces in which the site is not located, the accelerations at the site shall be determined assuming that the epicenters or locations of highest intensity of these earthquakes are at the closest point to the site on the boundary of the tectonic province;
(iv) The earthquake producing the maximum vibratory acceleration at the site, as determined from paragraph (a)(1)(i) through (iii) of this section shall be designated the Safe Shutdown Earthquake for vibratory ground motion, except as noted in paragraph (a)(1)(v) of this section. The characteristics of the Safe Shutdown Earthquake shall be derived from more than one earthquake determined from paragraph (a)(1)(i) through (iii) of this section, where necessary to assure that the maximum vibratory acceleration at the site throughout the frequency range of interest is included. In the case where a causative fault is near the site, the effect of proximity of an earthquake on the spectral characteristics of the Safe Shutdown Earthquake shall be taken into account. The procedures in paragraphs (a)(1)(i) through (a)(1)(iii) of this section shall be applied in a conservative manner. The determinations carried out in accordance with paragraphs (a)(1)(ii) and (a)(1)(iii) shall assure that the safe shutdown earthquake intensity is, as a minimum, equal to the maximum historic earthquake intensity experienced within the tectonic province in which the site is located. In the event that geological and seismological data warrant, the Safe Shutdown Earthquake shall be larger than that derived by use of the procedures set forth in section IV and V of the appendix. The maximum vibratory accelerations of the Safe Shutdown Earthquake at each of the various foundation locations of the nuclear power plant structures at a given site shall be determined taking into account the characteristics of the underlying soil material in transmitting the earthquake-induced motions, obtained pursuant to paragraphs (a)(1), (3), and (4) of section IV. The Safe Shutdown Earthquake shall be defined by response spectra corresponding to the maximum vibratory accelerations as outlined in paragraph (a) of section VI; and
(v) Where the maximum vibratory accelerations of the Safe Shutdown Earthquake at the foundations of the nuclear power plant structures are determined to be less than one-tenth the acceleration of gravity (0.1 g) as a result of the steps required in paragraphs (a)(1)(i) through (iv) of this section, it shall be assumed that the maximum vibratory accelerations of the Safe Shutdown Earthquake at these foundations are at least 0.1 g.
(2) Determination of Operating Basis Earthquake. The Operating Basis Earthquake shall be specified by the applicant after considering the seismology and geology of the region surrounding the site. If vibratory ground motion exceeding that of the Operating Basis Earthquake occurs, shutdown of the nuclear power plant will be required. Prior to resuming operations, the licensee will be required to demonstrate to the Commission that no functional damage has occurred to those features necessary for continued operation without undue risk to the health and safety of the public.
The maximum vibratory ground acceleration of the Operating Basis Earthquake shall be at least one-half the maximum vibratory ground acceleration of the Safe Shutdown Earthquake.
(b) Determination of Need to Design for Surface Faulting. In order to determine whether a nuclear power plant is required to be designed to withstand the effects of surface faulting, the location of the nuclear power plant with respect to capable faults shall be considered. The area over which each of these faults has caused surface faulting in the past is identified by mapping its fault traces in the vicinity of the site. The fault traces are mapped along the trend of the fault for 10 miles in both directions from the point of its nearest approach to the nuclear power plant because, for example, traces may be obscured along portions of the fault. The maximum width of the mapped fault traces, called the control width, is then determined from this map. Because surface faulting has sometimes occurred beyond the limit of mapped fault traces or where fault traces have not been previously recognized, the control width of the fault is increased by a factor which is dependent upon the largest potential earthquake related to the fault. This larger width delineates a zone, called the zone requiring detailed faulting investigation, in which the possibility of surface faulting is to be determined. The following paragraphs outline the specific procedures for determining the zone requiring detailed faulting investigation for a capable fault.
(1) Determination of Zone Requiring Detailed Faulting Investigation. The zone requiring detailed faulting investigation for a capable fault which was investigated pursuant to the requirement of paragraph (b)(7) of section IV shall be determined through use of the following table:
Table 2 - Determination of Zone Requiring Detailed Faulting Investigation
| Magnitude of earthquake | Width of zone requiring detailed faulting investigation (See fig. 1) |
|---|---|
| Less than 5.5 | 1 × control width. |
| 5.5-6.4 | 2 × control width. |
| 6.5-7.5 | 3 × control width. |
| Greater than 7.5 | 4 × control width. |
The largest magnitude earthquake related to the fault shall be used in table 2. This earthquake shall be determined from the information developed pursuant to the requirements of paragraph (b) of Section IV for the fault, taking into account the information required by paragraph (b)(7) of section IV. The control width used in table 2 is determined by mapping the outer limits of the fault traces from information developed pursuant to paragraph (b)(7)(iv) of section IV. The control width shall be used in table 2 unless the characteristics of the fault are obscured for a significant portion of the 10 miles on either side of the point of nearest approach to the nuclear power plant. In this event, the use in table 2 of the width of mapped fault traces more than 10 miles from the point of nearest approach to the nuclear power plant may be appropriate.
The zone requiring detailed faulting investigation, as determined from table 2, shall be used for the fault except where:
(i) The zone requiring detailed faulting investigation from table 2 is less than one-half mile in width. In this case the zone shall be at least one-half mile in width; or
(ii) Definitive evidence concerning the regional and local characteristics of the fault justifies use of a different value. For example, thrust or bedding-plane faults may require an increase in width of the zone to account for the projected dip of the fault plane; or
(iii) More detailed three-dimensional information, such as that obtained from precise investigative techniques, may justify the use of a narrower zone. Possible examples of such techniques are the use of accurate records from closely spaced drill holes or from closely spaced, high-resolution offshore geophysical surveys.
In delineating the zone requiring detailed faulting investigation for a fault, the center of the zone shall coincide with the center of the fault at the point of nearest approach of the fault to the nuclear power plant as illustrated in figure 1.
(c) Determination of Design Bases for Seismically Induced Floods and Water Waves. The size of seismically induced floods and water waves which could affect a site from either locally or distantly generated seismic activity shall be determined, taking into consideration the results of the investigation required by paragraph (c) of section IV. Local topographic characteristics which might tend to modify the possible runup and drawdown at the site shall be considered. Adverse tide conditions shall also be taken into account in determining the effect of the floods and waves on the site. The characteristics of the earthquake to be used in evaluating the offshore effects of local earthquakes shall be determined by a procedure similar to that used to determine the characteristics of the Safe Shutdown Earthquake in paragraph V(a).
(d) Determination of Other Design Conditions - (1) Soil Stability. Vibratory ground motion associated with the Safe Shutdown Earthquake can cause soil instability due to ground disruption such as fissuring, differential consolidation, liquefaction, and cratering which is not directly related to surface faulting. The following geologic features which could affect the foundations of the proposed nuclear power plant structures shall be evaluated, taking into account the information concerning the physical properties of materials underlying the site developed pursuant to paragraphs (a)(1), (3), and (4) of section IV and the effects of the Safe Shutdown Earthquake:
(i) Areas of actual or potential surface or subsurface subsidence, uplift, or collapse resulting from:
(a) Natural features such as tectonic depressions and cavernous or karst terrains, particularly those underlain by calcareous or other soluble deposits;
(b) Man's activities such as withdrawal of fluid from or addition of fluid to the subsurface, extraction of minerals, or the loading effects of dams or reservoirs; and
(c) Regional deformation.
(ii) Deformational zones such as shears, joints, fractures, folds, or combinations of these features.
(iii) Zones of alteration or irregular weathering profiles and zones of structural weakness composed of crushed or disturbed materials.
(iv) Unrelieved residual stresses in bedrock.
(v) Rocks or soils that might be unstable because of their mineralogy, lack of consolidation, water content, or potentially undesirable response to seismic or other events. Seismic response characteristics to be considered shall include liquefaction, thixotropy, differential consolidation, cratering, and fissuring.
(2) Slope stability. Stability of all slopes, both natural and artificial, the failure of which could adversely affect the nuclear power plant, shall be considered. An assessment shall be made of the potential effects of erosion or deposition and of combinations of erosion or deposition with seismic activity, taking into account information concerning the physical property of the materials underlying the site developed pursuant to paragraph (a)(1), (3), and (4) of section IV and the effects of the Safe Shutdown Earthquake.
(3) Cooling water supply. Assurance of adequate cooling water supply for emergency and long-term shutdown decay heat removal shall be considered in the design of the nuclear power plant, taking in to account information concerning the physical properties of the materials underlying the site developed pursuant to paragraphs (a)(1), (3), and (4) of section IV and the effects of the Safe Shutdown Earthquake and the design basis for surface faulting. Consideration of river blockage or diversion or other failures which may block the flow of cooling water, coastal uplift or subsidence, or tsunami runup and drawdown, and failure of dams and intake structures shall be included in the evaluation, where appropriate.
(4) Distant structures. Those structures which are not located in the immediate vicinity of the site but which are safety related shall be designed to withstand the effect of the Safe Shutdown Earthquake and the design basis for surface faulting determined on a comparable basis to that of the nuclear power plant, taking into account the material underlying the structures and the different location with respect to that of the site.
vi. application to engineering design(a) Vibratory ground motion - (1) Safe Shutdown Earthquake. The vibratory ground motion produced by the Safe Shutdown Earthquake shall be defined by response spectra corresponding to the maximum vibratory accelerations at the elevations of the foundations of the nuclear power plant structures determine pursuant to paragraph (a)(1) of section V. The response spectra shall relate the response of the foundations of the nuclear power plant structures to the vibratory ground motion, considering such foundations to be single-degree-of-freedom damped oscillators and neglecting soil-structure interaction effects. In view of the limited data available on vibratory ground motions of strong earthquakes, it usually will be appropriate that the response spectra be smoothed design spectra developed from a series of response spectra related to the vibratory motions caused by more than one earthquake.
The nuclear power plant shall be designed so that, if the Safe Shutdown Earthquake occurs, certain structures, systems, and components will remain functional. These structures, systems, and components are those necessary to assure (i) the integrity of the reactor coolant pressure boundary, (ii) the capability to shut down the reactor and maintain it in a safe condition, or (iii) the capability to prevent or mitigate the consequences of accidents which could result in potential offsite exposures comparable to the guideline exposures of this part. In addition to seismic loads, including aftershocks, applicable concurrent functional and accident-induced loads shall be taken into account in the design of these safety-related structures, systems, and components. The design of the nuclear power plant shall also take into account the possible effects of the Safe Shutdown Earthquake on the facility foundations by ground disruption, such as fissuring, differential consolidation, cratering, liquefaction, and landsliding, as required in paragraph (d) of section V.
The engineering method used to insure that the required safety functions are maintained during and after the vibratory ground motion associated with the Safe Shutdown Earthquake shall involve the use of either a suitable dynamic analysis or a suitable qualification test to demonstrate that structures, systems and components can withstand the seismic and other concurrent loads, except where it can be demonstrated that the use of an equivalent static load method provides adequate conservatism.
The analysis or test shall take into account soil-structure interaction effects and the expected duration of vibratory motion. It is permissible to design for strain limits in excess of yield strain in some of these safety-related structures, systems, and components during the Safe Shutdown Earthquake and under the postulated concurrent conditions, provided that the necessary safety functions are maintained.
(2) Operating Basis Earthquake. The Operating Basis Earthquake shall be defined by response spectra. All structures, systems, and components of the nuclear power plant necessary for continued operation without undue risk to the health and safety of the public shall be designed to remain functional and within applicable stress and deformation limits when subjected to the effects of the vibratory motion of the Operating Basis Earthquake in combination with normal operating loads. The engineering method used to insure that these structures, systems, and components are capable of withstanding the effects of the Operating Basis Earthquake shall involve the use of either a suitable dynamic analysis or a suitable qualification test to demonstrate that the structures, systems and components can withstand the seismic and other concurrent loads, except where it can be demonstrated that the use of an equivalent static load method provides adequate conservatism. The analysis or test shall take into account soil-structure interaction effects and the expected duration of vibratory motion.
(3) Required Seismic instrumentation. Suitable instrumentation shall be provided so that the seismic response of nuclear power plant features important to safety can be determined promptly to permit comparison of such response with that used as the design basis. Such a comparison is needed to decide whether the plant can continue to be operated safely and to permit such timely action as may be appropriate.
These criteria do not address the need for instrumentation that would automatically shut down a nuclear power plant when an earthquake occurs which exceeds a predetermined intensity. The need for such instrumentation is under consideration.
(b) Surface Faulting. (1) If the nuclear power plant is to be located within the zone requiring detailed faulting investigation, a detailed investigation of the regional and local geologic and seismic characteristics of the site shall be carried out to determine the need to take into account surface faulting in the design of the nuclear power plant. Where it is determined that surface faulting need not be taken into account, sufficient data to clearly justify the determination shall be presented in the license application.
(2) Where it is determined that surface faulting must be taken into account, the applicant shall, in establishing the design basis for surface faulting on a site take into account evidence concerning the regional and local geologic and seismic characteristics of the site and from any other relevant data.
(3) The design basis for surface faulting shall be taken into account in the design of the nuclear power plant by providing reasonable assurance that in the event of such displacement during faulting certain structures, systems, and components will remain functional. These structures, systems, and components are those necessary to assure (i) the integrity of the reactor coolant pressure boundary, (ii) the capability to shut down the reactor and maintain it in a safe shutdown condition, or (iii) the capability to prevent or mitigate the consequences of accidents which could result in potential offsite exposures comparable to the guideline exposures of this part. In addition to seismic loads, including aftershocks, applicable concurrent functional and accident-induced loads shall be taken into account in the design of such safety features. The design provisions shall be based on an assumption that the design basis for surface faulting can occur in any direction and azimuth and under any part of the nuclear power plant unless evidence indicates this assumption is not appropriate, and shall take into account the estimated rate at which the surface faulting may occur.
(c) Seismically Induced Floods and Water Waves and Other Design Conditions. The design basis for seismically induced floods and water waves from either locally or distantly generated seismic activity and other design conditions determined pursuant to paragraphs (c) and (d) of section V, shall be taken into account in the design of the nuclear power plant so as to prevent undue risk to the health and safety of the public.
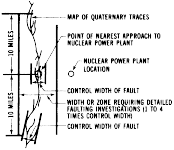 Figure 1
- Diagrammatic Illustration of Delineation of Width of Zone
Requiring Detailed Faulting Investigations For Specific Nuclear
Power Plant Location. (Sec. 201, Pub. L. 93-438, 88 Stat. 1243 (42
U.S.C. 5841)) [38 FR 31281, Nov. 13, 1973, as amended at 38 FR
32575, Nov. 27, 1973; 42 FR 2052, Jan. 10, 1977; 78 FR 34250, June
7, 2013]
Figure 1
- Diagrammatic Illustration of Delineation of Width of Zone
Requiring Detailed Faulting Investigations For Specific Nuclear
Power Plant Location. (Sec. 201, Pub. L. 93-438, 88 Stat. 1243 (42
U.S.C. 5841)) [38 FR 31281, Nov. 13, 1973, as amended at 38 FR
32575, Nov. 27, 1973; 42 FR 2052, Jan. 10, 1977; 78 FR 34250, June
7, 2013]